-
Environmental Science

Divergent Evolution vs Convergent
In the grand tapestry of life on Earth, the forces of evolution have woven a complex and mesmerizing narrative. At its core, this narrative is shaped by two distinct yet intertwined processes: convergent and divergent evolution. While these terms might sound like scientific jargon, they hold the keys to understanding how species adapt and diversify over time. Convergent Evolution: Imagine two species, separated by oceans and eons of evolution, developing remarkably similar traits independently. Convergent evolution is the fascinating phenomenon where unrelated organisms evolve analogous features due to shared environmental challenges. Picture the wings of a bat and a bird – although their lineages couldn't be more different, both have evolved wings to achieve the same purpose: flight. Divergent Evolution: On the flip side, we have divergent evolution. It's the story of a common ancestor giving rise to multiple descendants, each marching to the beat of its ecological niche. Over time, these descendants accumulate differences, ultimately becoming unique species. Think of Darwin's finches, whose beak shapes adapted to various diets on the Galápagos Islands.
-
Environmental Science

Food Web vs Food Chain
In the intricate web of life on Earth, there's an underlying system that dictates who eats whom. It's a fundamental concept in ecology, and it helps us understand how energy and nutrients flow through ecosystems. In this journey through the natural world, we'll delve into the key differences between food chains and food webs, shedding light on their unique characteristics and importance. Food Chains: Food chains are like the basic building blocks of ecological relationships. They represent a simplified, linear flow of energy and nutrients from one organism to another, highlighting who eats whom in a straightforward manner. Think of them as the "who eats who" diagrams of the natural world. Food Webs: Food webs, on the other hand, are like the intricate tapestries of the natural world. While food chains are linear and simplistic, food webs depict the complex network of interconnected food chains within an ecosystem. In essence, a food web is a more accurate representation of the real-world relationships among organisms.
-
Behavior

Ethics vs Law
In the intricate web of human society, two guiding principles often play a pivotal role in shaping behavior and decision-making: law and ethics. While they share commonalities in promoting order and moral conduct, they are distinct in their origins, scope, enforcement, and consequences. Law, in its most fundamental sense, is a system of rules and regulations that a governing body establishes and enforces to maintain order within a society. These rules are codified and can be enforced through various mechanisms, including legal authorities, courts, and law enforcement agencies. The primary purpose of law is to provide a structured framework for regulating human behavior and resolving disputes. Ethics, on the other hand, is a set of moral principles and values that guide individual and collective behavior. These principles are not necessarily codified into laws but are deeply rooted in personal beliefs, cultural norms, and societal values. Ethics often revolve around questions of right and wrong, and they serve as a moral compass to help individuals make decisions that align with their values. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the world of law vs. ethics, unraveling the intricate tapestry that sets them apart. We examine their origins, scope, enforcement, flexibility, adaptability, universality, cultural variability, and the crucial role they play in decision-making and behavior. Whether you're a legal enthusiast or someone navigating moral dilemmas, this exploration sheds light on the fascinating distinctions between law and ethics, offering valuable insights into their impact on our society and individual lives.
-
Behavior

Smooch vs Kiss
In the realm of human connection and affection, two simple yet profoundly meaningful gestures often take center stage: the "kiss" and the "smooch." At first glance, these terms may seem interchangeable, but a closer look reveals a world of difference between them. A "kiss" is a versatile expression of affection, encompassing a wide range of lip-to-lip or lip-to-skin contacts. It can convey emotions as diverse as friendly greetings, familial love, or romantic passion. From a gentle peck on the cheek to a passionate French kiss, its interpretations span cultures and contexts. On the other hand, a "smooch" takes kissing to a heightened level. It is the embodiment of deep passion, desire, and intimacy, often associated with romantic relationships. Smooching involves intense and prolonged lip-to-lip contact, occasionally with the use of tongues, symbolizing a profound emotional connection. While both acts share a foundation of affection, the choice between a kiss and a smooch depends on the level of intimacy and the emotions you wish to convey. Join us as we delve deeper into the world of "Kiss vs Smooch," exploring their meanings, cultural connotations, and how they've evolved in our ever-changing world of human connections.
-
Physics Science

Turquoise vs Aqua
In the realm of colors, Aqua and Turquoise stand as enchanting members of the blue-green spectrum. While they share common elements, these shades possess distinctive characteristics that can significantly impact design choices, moods, and cultural symbolism. Aqua, with its lighter and cooler undertones, leans towards a refreshing, aquatic aura. It evokes the tranquility of clear waters, making it a favored choice for creating serene environments. Aqua often finds its place in coastal-themed interiors, spa decor, and the fashion world, particularly in summer collections. Turquoise, in contrast, boasts a deeper and more vivid hue with a pronounced presence of green. This vibrant color exudes energy and positivity, often making a bold statement in fashion, creative spaces, and high-end jewelry. Its cultural significance stretches across time, from being a protective talisman in Native American traditions to a symbol of spiritual growth and healing. When deciding between Aqua and Turquoise, consider the emotions and ambiance you wish to convey. Aqua for calmness and modernity, or Turquoise for vibrancy and spirituality. These colors, each with its unique charm, offer endless possibilities for self-expression and creativity in the colorful tapestry of life.
-
Agriculture

Khadar vs Bhangar
Bhangar and Khadar soils, two prominent soil types in India's vast plains, differ significantly in origin, characteristics, and agricultural relevance. Bhangar soils, older and coarser, are primarily found in the northern plains of India. They exhibit a darker hue, owing to their mineral-rich content, and generally offer good natural drainage. These soils are versatile, accommodating a range of crops, including wheat, barley, and oilseeds. However, their nutrient content may vary, often necessitating supplementary fertilization. Bhangar soils contribute to stable vegetation, assisting in erosion prevention and groundwater recharge. In contrast, Khadar soils are relatively younger, formed through annual alluvial deposition along riverbanks and low-lying areas. They possess a finer texture, appearing lighter in color, and have superior water retention capabilities. Khadar soils are renowned for their fertility, making them ideal for water-intensive crops like paddy rice, sugarcane, and vegetables. The annual replenishment of nutrient-rich sediments during floods ensures consistently high fertility. Khadar soils also play a crucial role in supporting biodiversity and river ecosystems. The choice between Bhangar and Khadar soils depends on various factors, including crop preferences, access to irrigation, and ecological objectives. Understanding these soil types' nuances is pivotal for sustainable land use and conservation efforts in the diverse agricultural landscapes of India.
-
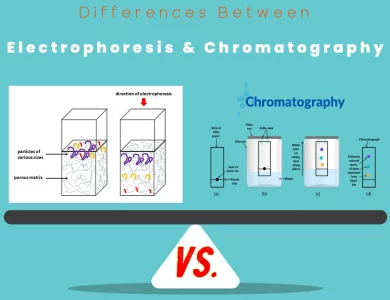
Analytical Chemistry

Chromatography vs Electrophoresis
In the realm of analytical chemistry, the choice between electrophoresis and chromatography can be akin to selecting the right tool from a scientist's treasure chest. These two techniques stand as pillars in the world of molecular analysis, each offering a unique set of capabilities that cater to diverse scientific needs. Electrophoresis, often associated with the graceful migration of DNA bands on a gel, operates on the fundamental principle of charged particle movement in an electric field. This technique is a powerhouse for the separation of charged molecules, including DNA, RNA, proteins, and peptides. It excels at resolving biomolecules based on their size, shape, and charge, making it indispensable in molecular biology, biochemistry, and forensic science. On the other hand, chromatography is like a chameleon in the laboratory, adapting to an extensive range of analytes, both charged and uncharged. Whether you're working with small organic compounds, large biomolecules, or gases, chromatography has you covered. Its magic lies in the differential distribution of compounds between a stationary phase and a mobile phase, guided by properties such as polarity, size, and affinity. This versatility makes chromatography a cornerstone in fields spanning pharmaceuticals, environmental analysis, food science, and beyond.
-
Pathology

Collateral Host vs Alternate Host
In the realm of pathology, where diseases and pathogens weave intricate narratives, two terms, "Alternate Host" and "Collateral Host," stand out as key players in the grand scheme of host-pathogen interactions. These terms might sound similar at first, but they lead us into entirely different corners of the pathology world. Alternate Host, often found in the lush fields of plant pathology, is a secondary host plant that plays a pivotal role in the life cycle of certain pathogens. It's the key player that ensures the pathogen's survival and reproduction, offering a fascinating insight into the dance between organisms. On the other hand, Collateral Host steps onto the stage in various branches of pathology, including human and animal health. It represents organisms, often humans or animals, that temporarily harbor pathogens. These hosts may not be central to the pathogen's life cycle, but they can significantly influence disease transmission and emergence, making them intriguing subjects of study. Diving deeper into the realm of these hosts reveals their unique roles, contexts, and implications in pathology. From plant diseases in agriculture to opportunistic infections in healthcare, the distinctions between Alternate Host and Collateral Host offer valuable insights into the dynamic world of host-pathogen relationships. Join us as we navigate through the intricate web of differences and discover how these terms shape our understanding of diseases and their control.
-
Pathology

Cercospora Leaf Spot vs Anthracnose
In the world of plant diseases, knowledge is your best defense. Understanding the differences between Anthracnose and Cercospora Leaf Spot is essential for gardeners, farmers, and plant enthusiasts seeking to safeguard their green companions from these fungal adversaries. Anthracnose, caused by various Colletotrichum fungi, is notorious for its broad host range, affecting trees, shrubs, vegetables, and fruits. Recognizable by dark, sunken lesions with concentric rings on various plant parts, Anthracnose thrives in warm, humid conditions. It can mar fruits, weaken plants, and pose a significant economic threat. In contrast, Cercospora Leaf Spot predominantly targets leaves, caused by Cercospora fungi. Its symptoms manifest as small, round to irregular spots with gray or tan centers and dark brown or purple margins. This leaf-focused disease prefers warm, moist conditions, making it a common challenge in regions with high humidity.
-
Pathology

Bacterial Leaf Streak vs Bacterial Leaf Blight
When it comes to safeguarding rice crops, knowing the differences between Bacterial Leaf Blight and Bacterial Leaf Streak can make all the difference. These two plant diseases may share a host and a bacterial genus, but they present distinct challenges to farmers and researchers. Bacterial Leaf Blight, caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo), is notorious for its water-soaked lesions, wilting, and significant economic losses. In contrast, Bacterial Leaf Streak, triggered by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola (Xoc), showcases streak-like lesions with less severe wilting. Understanding these differences is vital, as it influences disease management strategies and ultimately impacts crop health and yield. Both diseases primarily affect rice (Oryza sativa) plants, making them critical concerns for rice-growing regions worldwide. While Bacterial Leaf Blight tends to be more economically devastating, Bacterial Leaf Streak also poses challenges that require effective mitigation. Farmers and researchers alike need to grasp these distinctions to ensure healthy and thriving rice crops.