-
Polymer Chemistry

Plastic vs Polymer
In the vast landscape of materials that shape our world, polymers and plastics stand as two prominent players. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they are not synonymous. Understanding the differences between polymers and plastics is not only fascinating but also essential in today's environmentally conscious era. Composition and Structure: Polymers are a diverse class of materials comprising both natural and synthetic substances. They consist of large molecules formed by repeating structural units, known as monomers. These monomers are chemically bonded together, creating long chains or networks. On the other hand, plastics are a subset of synthetic polymers, specifically chosen for their ability to be molded when exposed to heat or pressure. They are typically derived from petrochemicals through a process called polymerization. Properties: Polymers exhibit a wide range of properties, from flexibility and strength to varying thermal characteristics. Their properties depend on factors like the type of monomers and their arrangement. Plastics, as synthetic polymers, inherit these properties but often have added moldability due to their specific composition. Applications: Polymers find applications in numerous industries, including medical, construction, automotive, and electronics. In contrast, plastics, with their moldable nature, are ubiquitous in packaging, consumer goods, and agriculture, among others. Environmental Impact: One of the most critical distinctions lies in their environmental impact. While some polymers, especially natural ones, can be biodegradable, many synthetic polymers, including traditional plastics, are non-biodegradable and contribute to environmental challenges like plastic pollution.
-
Field

Chemical Engineering vs Chemistry
When it comes to the world of molecules, compounds, and chemical reactions, Chemistry and Chemical Engineering stand out as two captivating yet distinct fields. While they share common roots in the realm of chemicals and elements, they diverge significantly in terms of focus, education, and career paths. Chemistry, often known as the "central science," delves into the study of matter, its properties, and the intricate dance of atoms and molecules. Chemists are the scientific explorers of this microscopic realm, seeking to understand the fundamental principles of chemistry. Their work often takes place in laboratories, where they conduct experiments, analyze substances, and uncover the secrets of chemical reactions. On the other hand, Chemical Engineering applies the principles of chemistry and engineering to design, optimize, and oversee large-scale processes for the production of chemicals, materials, and energy. Chemical engineers are the architects of industrial processes, ensuring that scientific discoveries are translated into practical applications that power various industries. Their work is often found on the plant floor, where they oversee the operation of chemical processes, troubleshoot issues, and maximize efficiency. In this comprehensive comparison, we will explore the educational pathways, career prospects, work environments, and problem-solving approaches that set these two fields apart. Whether you're a student contemplating your academic journey or a professional considering a career change, understanding the differences between Chemistry and Chemical Engineering is the first step toward choosing the path that aligns with your passion and goals.
-
Agriculture

Modern Farming vs Traditional
In the ever-evolving realm of agriculture, the dichotomy between tradition and modernity stands as a testament to human innovation and adaptation. Traditional farming, deeply rooted in time-honored practices, finds itself on a contrasting path with modern farming, fueled by cutting-edge technology and scientific advancements. To understand the essence of this divergence, we delve into the profound disparities that distinguish these two agricultural approaches. Labor Intensity: Traditional farming bears the hallmark of hard work, relying on manual labor and rudimentary tools. Generations of farmers toiled the land, often as a collective effort within close-knit communities. In stark contrast, modern farming has harnessed the power of machinery and automation, significantly reducing labor demands and ushering in a new era of efficiency. Productivity and Yield: Traditional farming, while deeply ingrained in heritage, often yielded modest results. Modern farming, armed with high-yielding crop varieties and precision techniques, boasts consistently higher productivity and crop yields. Sustainability and Environmental Impact: Traditional farming, with its focus on local resources and organic practices, often scores well in terms of sustainability. On the other hand, modern farming's resource-intensive practices demand careful management to mitigate environmental concerns. Cost and Investment: The upfront investment in modern farming, including technology and inputs, is substantial, while traditional farming relies on simpler, less costly tools and family labor. As we journey through these disparities, we unravel the intricate tapestry of agriculture's past and present, each strand weaving a unique story of resilience and adaptation. The choice between tradition and innovation ultimately depends on the goals, values, and resources of those who till the soil, shaping the future of farming.
-
Raw Material foods

White Quinoa vs Red Quinoa
When it comes to nutritious grains, quinoa reigns supreme, and it comes in a dazzling array of colors, with red and white being two of the most popular varieties. Each type of quinoa has its unique qualities, making it essential to understand the differences between red quinoa vs. white quinoa to make informed choices in the kitchen. Flavor and Texture: Red quinoa boasts a hearty and robust flavor with earthy undertones. Its chewy texture makes it ideal for recipes where you want a pronounced grain presence, such as grain bowls or hearty salads. In contrast, white quinoa offers a milder, more neutral taste, with a lighter and fluffier texture. This versatility allows it to seamlessly blend into various dishes, from savory stir-fries to sweet breakfast bowls. Visual Distinctions: The differences between these quinoa varieties are not just about taste and texture. Red quinoa flaunts a deep maroon or reddish hue that adds a visually stunning element to your culinary creations. In contrast, white quinoa presents as an ivory or pale yellow grain, offering a subtle, classic appearance that complements a wide range of recipes. Nutritional Nuances: Both red and white quinoa are nutritional powerhouses, providing complete protein and a host of essential nutrients. Red quinoa, however, contains anthocyanins, antioxidants associated with potential health benefits. White quinoa, on the other hand, edges ahead in protein content, making it a preferred choice for those focused on maximizing their protein intake. Cooking Considerations: Red quinoa has a slightly longer cooking time due to its thicker seed coat, while white quinoa cooks faster, making it a convenient choice for those on tight schedules. In the world of quinoa, your choice between red and white is a flavorful journey. Whether you're drawn to the bold presence of red quinoa or the versatile subtlety of white…
-
Foods & Drinks

Whole Grain vs Whole Wheat
In the quest for a healthier diet, the choices we make in our daily meals play a pivotal role. Among the dietary decisions we encounter, one of the most common dilemmas is choosing between whole wheat and whole grain. While these terms might seem interchangeable, they represent distinct categories in the world of nutrition, each with its unique characteristics and benefits. Whole Wheat: The Wheat-Centric Option Whole wheat, as the name suggests, is all about wheat—the hearty grain that's been a dietary staple for centuries. When you opt for whole wheat products, you're diving into a world where wheat reigns supreme. It encompasses the entire wheat kernel, including the bran, germ, and endosperm, making it a nutritional powerhouse. Nutritionally, whole wheat is known for its fiber content, which supports healthy digestion and provides a sense of fullness. It's also rich in essential B vitamins like folate, niacin, and riboflavin, crucial for energy production and overall health. Minerals such as iron, magnesium, and selenium are also present in whole wheat, contributing to various bodily functions. But who should embrace whole wheat? Whole wheat is an excellent choice for those who relish the nutty, slightly bitter flavor it imparts. If you appreciate the dense, rustic texture of whole wheat bread or the wholesomeness of whole wheat pasta, you're in the right camp. Moreover, if you're not gluten-sensitive and want to maintain a diet brimming with B vitamins and minerals, whole wheat can be a valuable addition to your plate.
-
Agriculture

Farming vs Agriculture
When it comes to the world of food production, the terms "agriculture" and "farming" are often used interchangeably, but beneath the surface, they represent distinct facets of a complex system. Understanding the differences between agriculture vs. farming is crucial for gaining insights into the various aspects of our global food supply chain. Agriculture, in a broad sense, serves as the overarching umbrella that encompasses a multitude of activities related to the cultivation and management of plants and animals for various purposes. This expansive field encompasses not only farming but also research, technology development, agribusiness, and more. It involves scientists and policymakers working collaboratively to address global challenges like food security and sustainability. Agriculture's goals extend beyond the farm, aiming to strike a balance between economic viability and environmental stewardship. Farming, on the other hand, represents the hands-on, practical component of agriculture. It is the core practice within the agricultural domain, focusing primarily on the cultivation of crops and the rearing of animals. Farming is where the rubber meets the road, where the sweat and toil of planting, tending, and harvesting crops or caring for livestock occur. Farmers are responsible for ensuring that the raw agricultural products required to feed the world are efficiently and profitably produced. Intrigued to delve deeper into these distinctions and uncover which path aligns best with your interests and goals? Let's explore the key differences between agriculture and farming, shedding light on the unique roles each plays in sustaining our global food supply.
-
Zoology

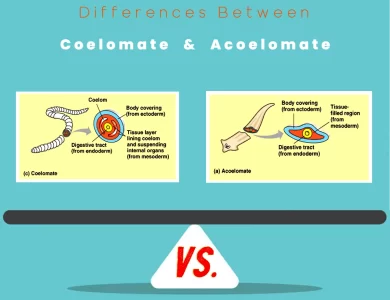
Acoelomate vs Coelomate
In the intricate tapestry of the animal kingdom, two distinct groups, coelomate and acoelomate organisms, stand out with their contrasting features. The primary divergence lies in their body structure. Coelomates, as the name suggests, possess a true coelom—a fluid-filled body cavity that separates their internal organs from the body wall. This coelomic cavity offers vital advantages such as organ protection, support, and enabling efficient organ movement. In contrast, acoelomates lack this coelomic cushion; their bodies are solid, with organs directly in contact with the body wall. This fundamental difference shapes their evolutionary history, embryonic development, and various physiological aspects. Coelomate animals are often considered more advanced and diverse, showcasing complexity in their anatomy and adaptability. Vertebrates like humans, arthropods (comprising insects and spiders), and annelids (including segmented worms) fall into this category. On the other hand, acoelomate organisms, such as flatworms (planarians) and certain primitive invertebrates, exhibit simplicity in their body structure, adapted to specific environments or niches. These remarkable differences extend to locomotion, digestive systems, reproductive strategies, and immune mechanisms, making the study of coelomate vs. acoelomate animals a captivating journey into the wonders of biological diversity.
-
Raw Material foods

Arrowroot vs Corn Flour
When it comes to thickening agents in the culinary world, two contenders often take the stage: corn flour and arrowroot. While they may appear similar at first glance, these kitchen staples possess distinct properties that can significantly influence your recipes. Corn flour, derived from maize (corn), boasts a glossy finish and robust thickening abilities, making it a go-to choice for gravies, pies, and creamy sauces. On the other hand, arrowroot, extracted from the rhizomes of tropical plants, offers clarity and is ideal for creating clear, translucent sauces and glazes. The differences extend beyond appearance. Corn flour has a stronger thickening power and can withstand prolonged cooking, while arrowroot thickens rapidly but is sensitive to high temperatures. Moreover, arrowroot is the preferred option for those with gluten sensitivities, as it is naturally gluten-free, while corn flour contains gluten. To delve deeper into these distinctions and make informed choices in your culinary adventures, read on to explore the fascinating world of Corn Flour vs Arrowroot.
-
Martial Arts

Difference Between Brazilian Jiu Jitsu and Jiu Jitsu
In the world of martial arts, the distinctions between Jiu Jitsu and Brazilian Jiu Jitsu (BJJ) often spark curiosity and intrigue. While their names share a common thread, these two disciplines have evolved into distinct martial arts with unique histories, techniques, and philosophies. Jiu Jitsu, with roots tracing back over 2,000 years to ancient Japan, embodies a diverse array of techniques. It encompasses joint locks, throws, strikes, and an unwavering focus on self-defense. Jiu Jitsu's historical background as a battlefield combat system is evident in its practicality and emphasis on neutralizing threats. On the other hand, Brazilian Jiu Jitsu (BJJ), born in the early 20th century in Brazil, has become synonymous with ground-fighting expertise. BJJ prioritizes positional control, submissions, and sportive techniques, making it a formidable force in competitive martial arts and mixed martial arts (MMA). The differences between these two martial arts extend to their belt systems, training methodologies, and philosophical foundations. While Jiu Jitsu embraces traditional martial arts philosophy and a holistic approach, BJJ's focus is primarily on practicality and competition.
-
Martial Arts

Difference Between Affliction and UFC
In the dynamic world of Mixed Martial Arts (MMA), two names stand out: the Ultimate Fighting Championship (UFC) and Affliction. While both have made indelible marks, they represent contrasting tales in the realm of cage fighting. The UFC, founded in 1993, pioneered modern MMA, overcoming challenges to evolve into a global phenomenon. It boasts an extensive and diverse fighter roster, with fighters hailing from various corners of the globe. With comprehensive fighter development programs, stringent safety measures, and a consistent event format, the UFC has set industry standards. Its legacy is synonymous with the transformation of MMA from a fringe spectacle to a mainstream sport. Affliction, on the other hand, had a brief but memorable stint in the MMA world. Established in 2008, Affliction made waves by signing high-profile fighters like Fedor Emelianenko and creating extravagant events. However, its financial instability and focus on marquee matchups led to its closure after just two events. Affliction's legacy serves as a cautionary tale, emphasizing the challenges of sustainability in the MMA business.