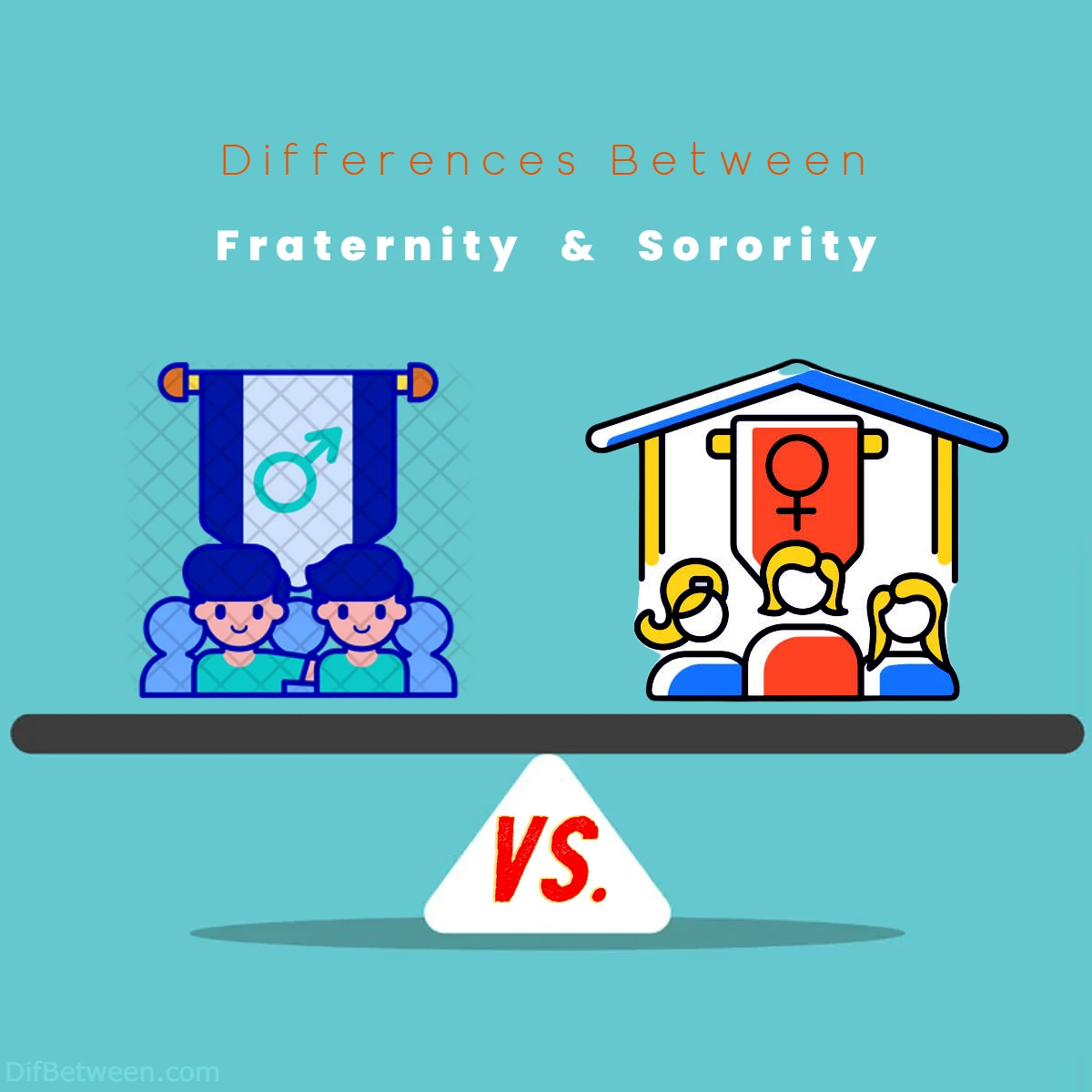
| Aspect | Fraternity | Sorority |
|---|---|---|
| Gender Inclusivity | Male-only, with co-ed options available | Female-only, co-ed sorority fraternities exist |
| History & Tradition | Dating back to late 18th century | Founded later, in the late 19th century |
| Organization Structure | Hierarchical with leadership roles | Hierarchical structure with leadership roles |
| Housing & Accommodations | Fraternity houses for members | Sorority houses for members |
| Rush/Recruitment | Rush for potential new members (PNMs) | Rush for potential new members (PNMs) |
| Pledging/New Member Period | Pledge period to educate new members | New member period to educate new members |
| Greek Letters and Symbols | Use of Greek letters and symbols | Use of Greek letters and symbols |
| Social and Party Culture | Social events and parties | Social events and parties |
| Alumni Engagement and Networking | Strong alumni networks and involvement | Strong alumni networks and involvement |
| Philanthropy and Community Service | Active in philanthropy and service | Active in philanthropy and service |
| Academic Support and Resources | Offer academic support and resources | Offer academic support and resources |
| Financial Commitment | Dues for chapter operations and activities | Dues for chapter operations and activities |
| Community and Social Impact | Active engagement in community and campus | Active engagement in community and campus |
| Support Networks and Friendships | Form strong support networks and friendships | Form strong support networks and friendships |
Fraternities and sororities, often referred to as Greek organizations, have left an indelible mark on college campuses for generations. Both offer students a chance to forge lifelong bonds, engage in community service, and cultivate leadership skills, but their approaches and traditions are diverse.
Differences Between Fraternity and Sorority
The main differences between a fraternity and a sorority lie in their gender inclusivity, with fraternities traditionally being male-only, while sororities are exclusively for females, although co-ed options exist. Additionally, fraternities often have a longer historical presence in the United States, dating back to the late 18th century, whereas sororities emerged in the late 19th century. Their organizational structures, housing arrangements, and rituals differ, and they engage in gender-specific recruitment processes known as “rush.” Fraternities and sororities also exhibit unique social cultures, but both emphasize community service, academic support, and lifelong connections. In essence, these differences encompass the core distinctions between fraternities and sororities.
Definition and Purpose
Fraternity:
A fraternity is a social organization typically exclusive to male members, although some co-ed fraternities exist. The primary purpose of a fraternity is to create a brotherhood that supports its members throughout their college years and beyond. Fraternities often emphasize values like friendship, leadership, and community service. Members, known as “brothers,” come together to form lasting bonds, engage in philanthropic activities, and participate in social events.
Fraternities often have a strong focus on personal development, leadership skills, and the development of a sense of belonging. These organizations provide a platform for members to network, socialize, and engage in shared experiences that can shape their college years and future lives.
Sorority:
A sorority is a similar social organization, but it is exclusive to female members. Like fraternities, sororities aim to create sisterhoods that offer support and friendship during college and beyond. Sororities place a significant emphasis on values like sisterhood, community service, and personal growth. Members, referred to as “sisters,” form tight-knit relationships, participate in philanthropic endeavors, and organize social events.
Sororities also focus on personal development and leadership skills, helping members grow as individuals and empowering them to be leaders both within their organizations and in their broader communities. The sense of belonging and the bonds formed within sororities can be profound, shaping members’ college experiences and influencing their futures.
History and Tradition
Fraternity:
Fraternities have a long history in the United States, dating back to the late 18th century. The first fraternity, Phi Beta Kappa, was established at the College of William and Mary in 1776. Since then, countless fraternities have been founded, each with its own unique history and traditions. Many fraternities have deep historical roots and are often associated with specific universities or regions.
Fraternities often have a strong tradition of secrecy and symbolism, with rituals and ceremonies that are passed down from generation to generation. These traditions create a sense of continuity and connection among fraternity members.
Sorority:
Sororities also have a rich history in the United States, with the first Greek-letter sorority, Kappa Alpha Theta, founded in 1870. Like fraternities, sororities have their own unique histories and traditions. While sororities are a relatively newer phenomenon compared to fraternities, they have grown to become a significant part of the college experience for many young women.
Sororities, too, have a tradition of rituals and ceremonies that promote sisterhood and a sense of belonging. These traditions help create a strong bond among sorority sisters and contribute to the enduring legacy of these organizations.
Membership and Gender Inclusivity
Fraternity:
Fraternities are traditionally male-only organizations. However, there are co-ed fraternities that welcome both male and female members. These co-ed fraternities have a distinct approach to membership, focusing on inclusivity and diversity.
In traditional all-male fraternities, membership is limited to men who share common values and interests. The exclusivity of these organizations is often seen as a way to build strong brotherhoods and create a sense of unity among members.
Sorority:
Sororities are exclusively for women, with no male members. They are committed to fostering sisterhood and providing a safe and supportive environment for female college students. This exclusivity is a core aspect of sorority culture and is seen as essential in creating close-knit sisterhoods.
While sororities are typically gender-exclusive, co-ed fraternities sometimes have a sorority counterpart known as a “sorority fraternity,” which allows for both male and female members. These organizations combine elements of both fraternities and sororities to create a unique experience.
Organization Structure
Fraternity:
Fraternities often have a hierarchical organizational structure. Members may hold positions such as president, vice president, treasurer, and more. These leadership roles are typically rotated among members, allowing them to gain valuable leadership experience.
Fraternities are known for their strong alumni networks, which can provide mentorship and career opportunities for current members. Alumni often remain closely connected to their fraternity and may even return to campus for reunions and events.
Sorority:
Sororities also have a structured organizational hierarchy. Members can hold leadership positions such as president, vice president, secretary, and treasurer, among others. Like fraternities, these positions are usually held on a rotational basis.
Sororities, too, have robust alumni networks that offer support and mentorship to current members. Alumni involvement is encouraged, and many sorority members maintain lifelong connections with their organizations.
Activities and Philanthropy
Fraternity:
Fraternities engage in a wide range of activities, from social events and parties to academic support and community service. They often host philanthropic events to raise money for charitable causes and community initiatives. These events can include charity runs, fundraisers, and volunteer work.
Fraternities may also have their own unique traditions, such as “Greek Week” or “Fraternity Formal,” which provide opportunities for bonding and fun.
Sorority:
Sororities, like fraternities, participate in a variety of activities, including social events, academic support, and community service. Philanthropy is a significant focus for sororities, and they often organize events like charity auctions, food drives, and volunteer work in the community.
Sororities may have their own traditions and events that strengthen the bonds among sisters. These can include “Big-Little Reveal” ceremonies, sisterhood retreats, and themed social gatherings.
Housing and Accommodations
Fraternity:
Fraternities often have dedicated fraternity houses where members live together. These houses serve as a hub for social activities and gatherings. Living in a fraternity house can be an enriching experience, as it provides a close-knit community and fosters camaraderie among members.
Fraternity houses vary in size and amenities, with some being quite grand and others more modest. Living in a fraternity house is typically optional, and not all fraternity members choose to do so.
Sorority:
Sororities also have dedicated sorority houses where members can choose to live. These houses serve as a central location for sisterhood events and gatherings. Living in a sorority house can be a bonding experience and offers a strong sense of community.
Sorority houses vary in size and style, but they are generally well-maintained and provide a comfortable living environment. Just like fraternities, living in a sorority house is optional, and not all sorority members opt to reside there.
Rush and Recruitment
Fraternity:
Fraternity rush, also known as recruitment, is the process through which potential new members (PNMs) become acquainted with different fraternities and ultimately decide which one to join. Rush typically involves a series of events, parties, and interviews where PNMs and fraternity members get to know each other.
At the end of the rush process, PNMs may receive invitations to join a specific fraternity, and they can choose whether to accept these bids. Rush is an important part of fraternity life, as it determines the composition of the new pledge class.
Sorority:
Sorority recruitment, often referred to as rush, follows a similar process to fraternity rush but with some differences. During sorority rush, potential new members (PNMs) have the opportunity to meet members of different sororities and explore their options.
Throughout the rush period, PNMs attend events and interviews with sorority members. At the end of the recruitment process, PNMs receive bids from specific sororities, and they can choose to accept these bids if they wish. Sorority rush is a significant event in the lives of many college women, as it leads to the formation of close bonds with fellow sisters.
Pledging and New Member Period
Fraternity:
After receiving an invitation to join a fraternity, new members typically go through a “pledge” period. This period can vary in length but usually involves a series of activities and rituals designed to educate and bond new members with their fraternity brothers.
During the pledging period, new members learn about the history, values, and traditions of the fraternity. They also develop close relationships with current members. Once the pledging period is complete, new members are initiated as full-fledged brothers of the fraternity.
Sorority:
Similarly, sororities have a “new member” or “pledge” period for those who accept bids to join. This period introduces new members to the values, history, and traditions of the sorority, fostering connections with current sisters.
The length and specific activities of the new member period can vary among sororities, but it serves to educate and integrate new members into the sorority. After successfully completing this period, new members are initiated as full-fledged sisters.
Greek Letters and Symbols
Fraternity:
Fraternities are known for their use of Greek letters and symbols. Each fraternity has its own unique set of Greek letters and emblem, which often have specific meanings and associations. These letters and symbols are displayed on fraternity paraphernalia, clothing, and fraternity houses.
Members of fraternities wear their Greek letters proudly and often take part in the tradition of “crossing” into the fraternity, a symbolic initiation rite where they receive their official letters and other fraternity symbols.
Sorority:
Sororities, like fraternities, use Greek letters and symbols to represent their organizations. Each sorority has its own set of Greek letters and emblem, each carrying its own significance and symbolism.
Sorority members wear their Greek letters on clothing, jewelry, and other items as a symbol of their affiliation. They may also participate in a crossing ceremony, which is a special ritual to officially receive their Greek letters and other sorority symbols.
Social and Party Culture
Fraternity:
Fraternities are often associated with a lively social scene, including parties and gatherings. While social events are a part of fraternity life, many fraternities also place a strong emphasis on responsible and safe partying.
Social events and parties can be a way for fraternities to build connections with other Greek organizations and the broader student body. It’s essential to note that responsible drinking and safety are important aspects of fraternity social events.
Sorority:
Sororities also host social events, including mixers and parties, as part of their college experience. These events are an opportunity for sorority sisters to socialize with members of other Greek organizations and create memorable moments with their sisters.
Like fraternities, sororities prioritize responsible drinking and safety during their social events. The goal is to provide an enjoyable and safe environment for all attendees.
Alumni Involvement and Networking
Fraternity:
Fraternities often maintain strong alumni networks, with former members staying connected to their fraternity long after their college years. Alumni can offer mentorship, career guidance, and even job opportunities to current members. Fraternity reunions and events are common ways for alumni to stay involved and maintain their bonds with their brothers.
Alumni support can be a valuable resource for fraternity members as they transition from college to the professional world. These connections can open doors and help members establish themselves in their chosen careers.
Sorority:
Sororities, too, have robust alumni networks that offer support to current members. Alumni can provide mentorship, career advice, and networking opportunities. Many sorority members continue to stay involved with their sorority even after graduation, attending reunions and events.
The alumni connections within sororities can be a significant asset to members as they navigate the post-college years. The bonds formed during their time in the sorority can lead to lasting friendships and professional opportunities.
Philanthropy and Community Service
Fraternity:
Philanthropy and community service are integral to many fraternities. These organizations often support charitable causes and community initiatives through fundraisers, volunteer work, and other activities.
Each fraternity may have a specific philanthropic focus, and members dedicate time and effort to making a positive impact on their communities. Philanthropy events can be a way for fraternities to give back and contribute to society.
Sorority:
Sororities also have a strong commitment to philanthropy and community service. They organize fundraisers, volunteer opportunities, and other initiatives to support various charitable causes and organizations.
Sororities often have their own specific philanthropic causes and projects, which they passionately support. These efforts provide sorority members with a sense of purpose and the opportunity to make a difference in their communities.
Alumni Engagement and Contributions
Fraternity:
Fraternity alumni play a significant role in supporting their respective organizations. Many fraternities maintain strong alumni chapters that continue to uphold the values and traditions of the fraternity. These alumni chapters often organize events, provide mentorship to current members, and contribute financially to the fraternity’s activities.
Financial contributions from alumni can be crucial in sustaining the fraternity and its programs. These contributions may go towards maintaining fraternity houses, funding scholarships, and supporting philanthropic endeavors. In addition, alumni connections can provide career opportunities and guidance to current fraternity members.
Sorority:
Sorority alumni also maintain active involvement with their organizations. Alumni chapters and alumnae associations offer opportunities for former sorority members to stay engaged and connected. They may organize reunions, mentorship programs, and networking events for current sorority members.
Financial contributions from sorority alumnae often support the sorority’s scholarships, housing, and philanthropic efforts. These donations help ensure the sustainability of the sorority and its meaningful projects. The mentorship and career advice provided by alumni can be invaluable to sorority sisters as they transition into their professional lives.
Values and Rituals
Fraternity:
Fraternities are built on a foundation of shared values, often expressed through rituals, ceremonies, and symbolism. These values can vary from one fraternity to another but typically encompass principles like brotherhood, leadership, scholarship, and service.
Rituals and ceremonies are an essential aspect of fraternity life, and they are meant to instill a sense of tradition and belonging among members. These ceremonies can be both formal and informal, serving to strengthen the bonds between fraternity brothers.
Sorority:
Sororities, too, are rooted in their unique values and rituals. While the specific values may differ among sororities, common themes include sisterhood, personal growth, scholarship, and community service.
Rituals and ceremonies play a significant role in sorority culture, fostering a sense of unity and shared purpose among sorority sisters. These rituals often involve symbols, songs, and traditions that hold deep meaning for the members and contribute to the sorority’s legacy.
National and Local Organizations
Fraternity:
Fraternities often have a dual organizational structure, consisting of both national and local entities. The national organization, which encompasses all chapters of the fraternity across different universities, sets overarching policies and guidelines. This national body also often determines the fraternity’s values and philanthropic causes.
Local chapters, on the other hand, are individual groups associated with specific universities. These chapters have some degree of autonomy and may adapt national policies to fit their local campus culture.
Sorority:
Sororities follow a similar organizational structure to fraternities. A national organization governs all chapters across different campuses. The national organization sets standards, values, and philanthropic initiatives that all chapters are expected to uphold.
Local sorority chapters, affiliated with specific universities, operate within the framework provided by the national organization. They have some flexibility in how they implement the sorority’s principles while maintaining consistency with the national guidelines.
Recruitment and New Member Education
Fraternity:
Fraternity recruitment is a process through which potential new members (PNMs) explore different fraternities and decide which one aligns with their values and interests. Recruitment events, like rush parties, are typically held at the beginning of each academic term, allowing PNMs to meet fraternity members and learn about the organization.
Once a PNM accepts an invitation to join a fraternity, they enter a “pledge” or “new member” period. This period often involves educational activities and bonding experiences to help new members integrate into the fraternity.
Sorority:
Sorority recruitment, commonly known as “rush,” follows a similar structure to fraternity recruitment. Potential new members (PNMs) participate in recruitment events to get to know sorority members and make informed decisions about joining.
After receiving a bid to join a sorority, new members enter a “pledge” or “new member” period. During this time, they engage in activities designed to educate them about the sorority’s history, values, and traditions. The pledge period fosters connections among new members and current sorority sisters.
Academic Support and Resources
Fraternity:
Fraternities often provide academic support to their members, recognizing the importance of education alongside social activities. This support may include study groups, tutoring services, and access to academic resources.
Additionally, fraternities may offer scholarships or awards to members who excel academically. These incentives can encourage fraternity members to prioritize their studies and achieve their academic goals.
Sorority:
Sororities also emphasize academic success and provide resources to help members excel in their studies. Many sororities offer study sessions, academic advisors, and access to libraries or study facilities.
Scholarships and academic awards are common within sororities, recognizing and rewarding members who demonstrate exceptional academic achievement. These programs promote a balance between academic and social life for sorority sisters.
Campus and Community Involvement
Fraternity:
Fraternities are often actively engaged in campus and community activities. They may participate in campus events, sports, and student organizations. Additionally, fraternities frequently organize and participate in philanthropic projects, volunteering, and community service initiatives.
This involvement not only benefits the broader community but also helps build a positive reputation for the fraternity on campus. It’s a way for fraternity members to give back and make a difference in the lives of others.
Sorority:
Sororities are also deeply involved in campus and community activities. They often support various causes through philanthropic events and volunteer work. Sorority sisters may participate in leadership roles within student organizations and contribute to the campus community.
Engaging in campus and community activities is an excellent way for sorority members to develop leadership skills, create meaningful connections, and make a positive impact during their college years.
Financial Commitment
Fraternity:
Joining a fraternity typically involves a financial commitment. Members are required to pay dues, which cover various expenses, including chapter operations, housing (if applicable), social events, and national organization fees. The cost of membership can vary depending on the specific fraternity and the university’s location.
It’s essential for prospective fraternity members to understand the financial obligations associated with joining and to budget accordingly.
Sorority:
Sorority membership also comes with financial responsibilities. Members pay dues to cover costs such as chapter operations, housing (if applicable), social events, and national organization fees. The cost of membership varies between sororities and may be influenced by the location of the university.
Prospective sorority members should consider the financial commitment and plan accordingly to ensure a smooth and fulfilling sorority experience.
Community and Social Impact
Fraternity:
Fraternities often have a significant influence on their communities and campuses. They contribute to a sense of unity and belonging among members and organize events that engage the broader student body. Additionally, fraternities actively participate in community service and philanthropic projects, making a positive impact on society.
These organizations have the potential to create a lasting legacy of positive change in the areas they operate.
Sorority:
Sororities, like fraternities, leave a meaningful mark on their communities and campuses. They foster sisterhood among members and host events that bring students together. Sororities also play a crucial role in community service and philanthropic activities, contributing to causes that align with their values.
By actively engaging in community and social impact, sororities make a lasting difference in the lives of their members and those they serve.
Support Networks and Lifelong Friendships
Fraternity:
One of the most significant benefits of joining a fraternity is the creation of a strong support network and the formation of lifelong friendships. Fraternity brothers often form deep bonds that extend beyond their college years. These connections can be a source of emotional support, personal growth, and networking opportunities.
The sense of brotherhood instilled in fraternities often leads to enduring friendships that can last a lifetime.
Sorority:
Sororities provide a similar experience for women, fostering tight-knit relationships that often evolve into lifelong friendships. The connections formed among sorority sisters offer emotional support, mentorship, and a sense of belonging both during and after college.
Sorority bonds can be particularly strong, creating a network of sisters who remain close and engaged throughout their lives.
Fraternity or Sorority: Which One is Right Choose for You?
If you’re considering Greek life in college, you’re in for an exciting journey filled with camaraderie, personal growth, and community impact. Fraternities and sororities offer unique experiences, but the question often arises: which one is the right choice for you? Let’s explore some key factors to help you make an informed decision.
Gender Inclusivity:
- Fraternity: Traditionally male-only, with co-ed options available.
- Sorority: Exclusively for females, with some co-ed sorority fraternities.
History and Tradition:
- Fraternity: Dating back to the late 18th century.
- Sorority: Founded later, in the late 19th century.
Organizational Structure:
- Fraternity: Hierarchical with leadership roles.
- Sorority: Similar hierarchical structure with leadership roles.
Housing and Accommodations:
- Fraternity: Fraternity houses for members.
- Sorority: Sorority houses for members.
Recruitment Process:
- Fraternity: Fraternity rush or recruitment.
- Sorority: Sorority rush or recruitment.
Gender-Specificity:
- Fraternity: May have rituals and traditions specific to male members.
- Sorority: Has rituals and traditions tailored to female members.
Social and Party Culture:
- Fraternity: Known for social events and parties.
- Sorority: Hosts social events and mixers.
Alumni Networks:
- Fraternity: Strong alumni networks and involvement.
- Sorority: Also maintains robust alumni connections.
Philanthropy and Community Service:
- Fraternity: Actively participates in philanthropy and community service.
- Sorority: Shares a strong commitment to charitable initiatives.
Academic Support:
- Fraternity: Offers academic resources and support.
- Sorority: Also provides academic assistance and resources.
Community and Social Impact:
- Fraternity: Actively engages in campus and community activities.
- Sorority: Also contributes positively to campus and the broader community.
Support Networks and Friendships:
- Fraternity: Forms strong brotherhoods and lasting friendships.
- Sorority: Creates close-knit sisterhoods and enduring friendships.
Ultimately, your choice between a fraternity and a sorority should align with your personal values and aspirations during your college years and beyond. Both offer invaluable opportunities for personal growth, community engagement, and lifelong connections. Take the time to explore the specific organizations on your campus to find the one that resonates most with you.
FAQs
The primary difference lies in gender inclusivity. Fraternities are traditionally male-only organizations, while sororities are exclusively for females. Co-ed fraternities and sorority fraternities that accept both males and females do exist, offering a different dynamic.
Fraternities have a longer historical presence in the United States, dating back to the late 18th century, while sororities emerged later in the late 19th century. Each has its own unique history, traditions, and symbolism.
Both fraternities and sororities have hierarchical structures with leadership roles, but the specifics may vary between organizations. Chapters at different universities fall under a national umbrella organization.
Yes, both have dedicated housing options, with fraternity houses for fraternity members and sorority houses for sorority members. Living in these houses can create a close-knit community.
Recruitment, often known as “rush,” follows a similar process for both. Potential new members (PNMs) attend events to get to know the members and receive bids to join. The experience may vary in detail.
Both types of organizations use Greek letters and symbols to represent their identity. These symbols often have specific meanings and play a role in rituals, ceremonies, and clothing items.
Both fraternities and sororities host social events and parties. They emphasize responsible and safe partying, creating enjoyable environments for their members.
Alumni networks are robust in both types of organizations. Fraternity and sorority alumni provide mentorship, career opportunities, and continued involvement with their respective organizations.
Yes, both are active in philanthropy and community service. They often organize events, fundraisers, and volunteer work to support various charitable causes and initiatives.
Both types of organizations provide academic support, such as study groups, tutoring, and access to academic resources. Scholarships and academic awards are also common to encourage members’ academic success.
Read More:
Contents
- Differences Between Fraternity and Sorority
- Definition and Purpose
- History and Tradition
- Membership and Gender Inclusivity
- Organization Structure
- Activities and Philanthropy
- Housing and Accommodations
- Rush and Recruitment
- Pledging and New Member Period
- Sorority:
- Greek Letters and Symbols
- Social and Party Culture
- Alumni Involvement and Networking
- Philanthropy and Community Service
- Alumni Engagement and Contributions
- Values and Rituals
- National and Local Organizations
- Recruitment and New Member Education
- Academic Support and Resources
- Campus and Community Involvement
- Financial Commitment
- Community and Social Impact
- Support Networks and Lifelong Friendships
- Fraternity or Sorority: Which One is Right Choose for You?
- FAQs






