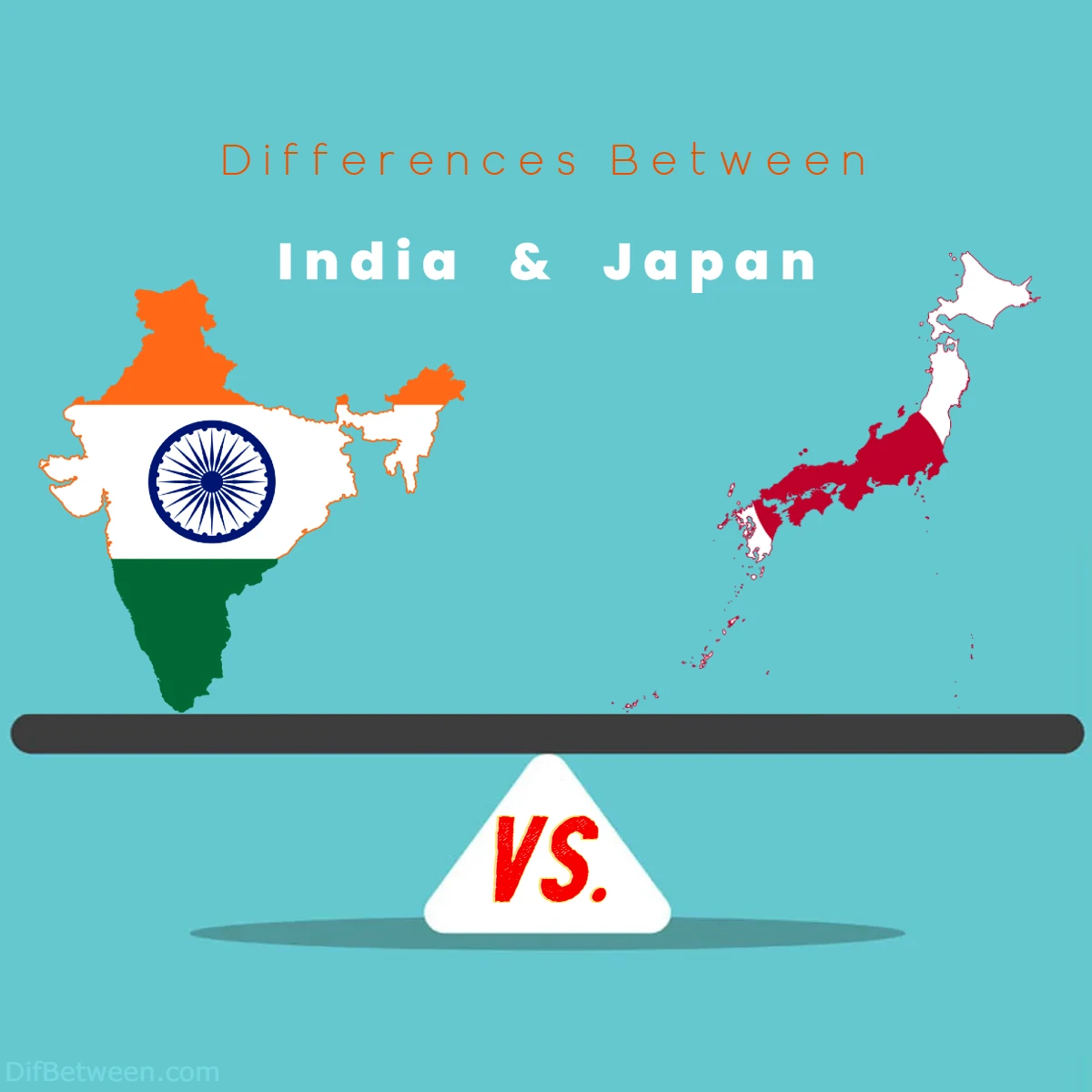
| Aspect | India | Japan |
|---|---|---|
| Historical Perspective | Rich cultural history, ancient civilizations, and diverse empires. | Feudal past, Meiji Restoration, and rapid modernization. |
| Cultural Diversity | Multicultural, diverse languages, and rich religious traditions. | Homogeneous culture with a strong emphasis on tradition. |
| Economic Landscape | Rapidly growing economy with a focus on services and agriculture. | Technologically advanced economy with a strong manufacturing sector. |
| Social Structure | Diverse social fabric with influence of caste and extended families. | Homogeneous society with an emphasis on hierarchy. |
| Governance and Political Systems | Federal democracy with a multi-party system. | Constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary government. |
| Infrastructure and Urbanization | Mix of modern infrastructure and disparities, rapid urbanization. | Efficient and advanced infrastructure with an emphasis on safety. |
| Environmental Concerns | Challenges related to pollution, water, and deforestation. | Commitment to sustainability, high earthquake preparedness. |
| Education Systems | Diverse education landscape with a mix of boards and institutions. | Structured and rigorous education system with competitive entrance exams. |
| Healthcare Systems | Diverse healthcare landscape, public and private providers. | Comprehensive and universal healthcare system. |
| Transportation Systems | Expansive and diverse network with challenges. | Highly efficient and well-maintained transportation system. |
| Culinary Traditions | Spices, diverse cuisine with regional specialties. | Artful, simple, and fresh cuisine with an emphasis on presentation. |
| Arts and Entertainment | Diverse arts scene rooted in tradition and contemporary cinema. | Creative pop culture with a strong focus on anime and manga. |
| Sports and Recreation | Passion for cricket, diverse sports, and recreational activities. | Love for baseball, martial arts, and appreciation of nature. |
India and Japan, each a treasure trove of unique history, culture, and traditions, offer a delightful contrast that promises to spark your curiosity. In this friendly, globe-trotting narrative, we’ll traverse the divergent landscapes of these two incredible countries.
Differences Between India and Japan
The main differences between India and Japan are rooted in their historical, cultural, and socio-economic contrasts. India, a culturally diverse nation with a rich history, boasts a multicultural society and a rapidly growing economy with a strong focus on services and agriculture. In contrast, Japan, with its homogeneous culture, is known for its technological prowess and efficient manufacturing sector. These distinctions extend to their social structures, governance systems, and healthcare and education landscapes. While India’s society is characterized by its diversity and more extensive healthcare and education options, Japan offers a highly structured and efficient educational system, comprehensive healthcare, and advanced infrastructure. These are just a few of the key differences that make India and Japan unique in their own right.
Historical Perspectives
India’s Ancient Tapestry
India’s history is a captivating tapestry, woven with threads of ancient civilizations, empires, and dynasties. Dating back over 5,000 years, India has seen the rise and fall of various powers, including the Indus Valley Civilization, the Maurya Empire, the Gupta Empire, and the Mughal Empire, before British colonial rule. India’s struggle for independence led to its partition in 1947, creating two independent nations, India and Pakistan.
The history of India is characterized by its rich cultural diversity, religious pluralism, and numerous invasions and migrations, contributing to the vibrant mosaic of Indian society. The influence of Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, Islam, Christianity, Sikhism, and other faiths has left an indelible mark on the nation’s identity.
Japan’s Feudal Past and Modernization
Japan’s history is equally compelling, albeit with a different narrative. The Land of the Rising Sun was marked by feudalism for many centuries, with samurai, shoguns, and daimyos governing the land. The Tokugawa Shogunate, which lasted from 1603 to 1868, was a pivotal period of isolationism, known as the Edo period.
However, Japan underwent a remarkable transformation during the Meiji Restoration in the late 19th century. It rapidly modernized, adopting Western technology and practices, and became an imperial power. Japan’s involvement in World War II ended with the devastating atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, leading to its post-war reconstruction and pacifist constitution.
In terms of history, India and Japan have contrasting trajectories. India’s history is marked by millennia of cultural and religious diversity, while Japan experienced a more isolated feudal past before modernization and globalization.
Cultural Contrasts
India’s Melting Pot of Cultures
India’s cultural landscape is a vivid tapestry of diversity. With a population of over 1.3 billion people, the country is home to a multitude of ethnicities, languages, and religions. Hinduism, Buddhism, Islam, and Sikhism have deep roots in India, each contributing to the nation’s unique cultural fabric.
One of India’s most iconic features is its cuisine. From the spicy curries of the south to the aromatic biryanis of the north, Indian food is as diverse as its people. Moreover, Indian festivals like Diwali, Holi, Eid, and Christmas are celebrated with great enthusiasm, reflecting the cultural plurality of the nation.
India is also renowned for its classical arts, including dance (such as Bharatanatyam and Kathak), music (Hindustani and Carnatic), and traditional crafts like hand-woven textiles, pottery, and jewelry. Bollywood, India’s film industry, produces a vast number of movies each year, showcasing the country’s passion for storytelling through cinema.
Japan’s Tradition and Precision
In contrast, Japan’s culture is marked by its precision, discipline, and a deep respect for tradition. Shintoism and Buddhism are the primary religious influences in Japan, and they permeate many aspects of Japanese life. The Japanese tea ceremony, Ikebana (flower arranging), and calligraphy are examples of traditional practices that continue to be revered in modern Japan.
Japanese cuisine is celebrated worldwide for its delicacy and presentation. Sushi, sashimi, tempura, and ramen are beloved dishes that emphasize fresh, high-quality ingredients and meticulous preparation. The concept of “omotenashi,” or selfless hospitality, is deeply ingrained in Japanese culture, making dining experiences a blend of culinary art and gracious service.
Japan’s pop culture, notably anime and manga, has a global following, showcasing a more contemporary side of the country’s creative expression. However, Japan’s traditional arts and customs remain a fundamental part of its identity, coexisting with its modern innovations.
Economic Contrasts
India’s Thriving but Diverse Economy
India boasts a rapidly growing and diverse economy. It is one of the world’s fastest-growing major economies, driven by a burgeoning population and a dynamic service sector. The information technology (IT) and software services industry have played a significant role in India’s economic development, earning it the moniker “Silicon Valley of India.”
Agriculture remains a crucial sector, employing a significant portion of the population. India’s agricultural practices range from traditional farming methods to modern, technology-driven approaches. The country is also one of the world’s largest producers of textiles, gems and jewelry, pharmaceuticals, and automobiles.
However, India faces economic challenges related to income inequality, poverty, and infrastructure development. The gap between urban and rural areas remains substantial, and economic disparities persist.
Japan’s Technological Powerhouse
Japan stands as a technological powerhouse with a highly advanced and export-oriented economy. It is renowned for its contributions to electronics, robotics, and the automotive industry. Companies like Toyota, Sony, and Panasonic have achieved global recognition for their innovation and quality.
The Japanese work ethic is characterized by precision, punctuality, and dedication, which has contributed to the nation’s economic success. Despite a shrinking population, Japan has a highly skilled and educated workforce.
While Japan’s economy is prosperous, it faces challenges associated with an aging population and low birth rates. This demographic shift poses long-term concerns for the country’s economic sustainability.
In summary, India’s economy is diverse and expanding, while Japan’s is technologically advanced and export-focused. Both countries grapple with unique economic challenges stemming from their demographics and development.
| Indicator | India | Japan |
|---|---|---|
| GDP (Nominal) | $3.05 trillion (2020) | $5.08 trillion (2020) |
| GDP per Capita | $2,172 (2020) | $40,247 (2020) |
| Main Industries | IT, Agriculture, Pharmaceuticals | Electronics, Automotive, Tech |
| Labor Force | 520 million (2020) | 67 million (2020) |
| Unemployment Rate | 6.2% (2021) | 2.8% (2021) |
(Data source: World Bank and Statista)
Social Structure and Society
India’s Diverse Social Fabric
India’s society is a tapestry woven from the threads of caste, religion, and language. The caste system, while officially abolished, continues to influence social interactions, marriage, and occupation. India is home to a myriad of languages, with Hindi and English serving as the official languages, and diverse regional languages and dialects.
Family plays a central role in Indian society. Multi-generational households are common, and familial bonds are deeply cherished. Arranged marriages are prevalent, with families playing a key role in the match-making process. The joint family system, where multiple generations live together, is still a predominant living arrangement in many parts of the country.
Gender roles in India have evolved, but traditional expectations often persist. While women have made significant strides in various fields, gender disparities, especially in rural areas, are still a concern.
Japan’s Homogeneous and Hierarchical Society
Japan’s society is relatively homogeneous, with the vast majority of the population being of Japanese descent. The Japanese value social harmony and consensus, which is reflected in their hierarchical social structure. Respect for authority, especially in the workplace, is a fundamental cultural tenet.
Japanese society places great importance on education, and the rigorous school system is designed to produce disciplined and hardworking individuals. Entrance exams for prestigious universities are highly competitive, and the pursuit of academic excellence is a common goal.
Family in Japan is also significant, and the extended family structure was more common in the past. However, modernization has led to smaller nuclear families, particularly in urban areas. While traditional gender roles are evolving, Japan continues to grapple with gender inequality and work-life balance issues.
In summary, India’s society is characterized by its diversity in language, religion, and caste, while Japan’s society is relatively homogeneous and places a strong emphasis on hierarchy and education.
Governance and Political Systems
India’s Complex Federal Democracy
India is the world’s largest democracy, governed by a complex federal structure. The President is the head of state, while the Prime Minister is the head of government. The country’s political landscape is marked by a multi-party system, with the Indian National Congress and the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) being two of the prominent political parties.
The Indian Parliament consists of two houses: the Lok Sabha (House of the People) and the Rajya Sabha (Council of States). The federal structure divides power between the central government and individual states, each with its own elected government.
India’s democracy, while vibrant, faces challenges such as corruption, bureaucracy, and the need to address the diverse needs of its massive population.
Japan’s Constitutional Monarchy
Japan’s political system is a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary government. The Emperor of Japan is a symbolic figurehead, and the Prime Minister is the head of government. Japan’s political landscape is dominated by the Liberal Democratic Party (LDP), which has maintained a stronghold on power for much of Japan’s post-war history.
The National Diet, Japan’s legislative body, consists of two houses: the House of Representatives and the House of Councillors. Japan’s political system is characterized by stability and consensus-oriented decision-making.
Both India and Japan face unique political challenges. India must navigate the complexities of a federal democracy, while Japan seeks to address issues such as an aging population and constitutional reforms.
Infrastructure and Urbanization
India’s Dynamic but Varied Infrastructure
India’s infrastructure is a blend of modern marvels and stark disparities. The country has made significant investments in its road network, with projects like the Golden Quadrilateral and the development of modern airports. The Delhi Metro and the Mumbai local train system are examples of urban public transportation that have transformed commuting in major cities.
However, rural areas often lack access to basic amenities like clean water, electricity, and quality healthcare. Slums and informal settlements are common in many urban centers, highlighting the urban-rural divide.
India’s Smart Cities Mission aims to address these disparities by modernizing infrastructure and improving the quality of life in urban areas.
Japan’s Efficient and Advanced Infrastructure
Japan boasts some of the world’s most advanced and efficient infrastructure. The Shinkansen, or bullet train, is a symbol of Japan’s technological prowess and is renowned for its speed, safety, and punctuality. Japan also has an extensive network of well-maintained roads and bridges.
Urbanization in Japan has led to the development of efficient public transportation systems, such as Tokyo’s intricate subway network. The country’s earthquake-resistant building designs are a testament to its commitment to safety.
Despite Japan’s advanced infrastructure, it faces challenges related to natural disasters, particularly earthquakes and tsunamis.
In summary, India’s infrastructure reflects a mix of modern development and disparities, while Japan is celebrated for its advanced and efficient infrastructure. Both nations have initiatives aimed at addressing their unique infrastructure challenges.
| Infrastructure Indicator | India | Japan |
|---|---|---|
| Road Quality | Varied, from excellent to poor | High-quality and well-maintained |
| High-Speed Rail Network | Developing | Extensive, including Shinkansen |
| Access to Clean Water | Disparities between urban and rural | Universal access |
| Internet Penetration | Expanding rapidly | High and widespread |
(Data source: World Bank and Statista)
Environmental Concerns
India’s Environmental Challenges
India faces several environmental challenges, including air pollution, water pollution, and deforestation. Rapid industrialization and urbanization have contributed to air quality issues in major cities like Delhi. Water pollution in rivers and lakes is a concern due to industrial discharges and inadequate waste management.
The country also grapples with deforestation, impacting biodiversity and contributing to soil erosion. Efforts to combat these issues include afforestation programs and the promotion of renewable energy sources.
Japan’s Commitment to Sustainability
Japan has a strong commitment to environmental sustainability. Despite being an industrialized nation, it has made significant strides in reducing air pollution and increasing energy efficiency. Japan also invests in renewable energy sources like solar and wind power.
The country’s disaster preparedness is a response to its vulnerability to earthquakes and tsunamis. Japan has strict building codes and early warning systems to mitigate the impact of natural disasters.
Japan’s reverence for nature is reflected in its cultural practices, such as cherry blossom viewing (hanami) and the celebration of the changing seasons.
In summary, India faces pressing environmental challenges, while Japan is committed to sustainability and disaster preparedness. Both nations recognize the importance of environmental conservation.
Education Systems
India’s Vast and Diverse Education Landscape
India boasts a vast and diverse education system, with numerous educational boards and institutions. The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) and the Indian Certificate of Secondary Education (ICSE) are two major educational boards, each offering a slightly different curriculum.
Higher education in India is highly competitive, with numerous universities, colleges, and institutes. The Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) and the Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs) are world-renowned for their engineering and management programs. The National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (NEET) and Joint Entrance Examination (JEE) are highly competitive entrance exams for medical and engineering programs, respectively.
Despite its academic strengths, India’s education system faces challenges related to access, quality, and disparities between urban and rural areas. The country continues to work on improving access to education for all its citizens.
Japan’s Rigorous Educational System
Japan’s education system is rigorous and highly structured. It emphasizes discipline and hard work. Japanese students are known for their long school days and a culture of extracurricular activities and “cram schools” (juku) to prepare for entrance exams.
The Japanese school year begins in April and consists of three trimesters. The 6-3-3-4 system includes six years of elementary school, three years of junior high, three years of high school, and four years of university or college. Entrance exams are highly competitive, and success on these exams often determines a student’s educational and career trajectory.
Japan’s commitment to education has resulted in high literacy rates and a well-educated population. However, there is a growing concern about the intense pressure on students and the need for more creativity in the education system.
In summary, India’s education system is diverse, with a wide range of boards and institutions, while Japan’s system is highly structured and known for its rigor and competitive entrance exams.
Healthcare Systems
India’s Growing Healthcare Sector
India’s healthcare system is diverse, encompassing both public and private healthcare providers. The country is a global hub for medical tourism, offering world-class treatments at a fraction of the cost in Western countries. Indian doctors and medical professionals are highly regarded and often work in various parts of the world.
The government operates public healthcare facilities, including primary health centers and district hospitals. However, these facilities face challenges related to overcrowding, resource shortages, and quality of care. The private healthcare sector in India is robust, with modern hospitals and specialized clinics that cater to a range of medical needs.
One of India’s strengths is its pharmaceutical industry, which is a major producer of generic drugs and vaccines. Despite these strengths, India faces health challenges, such as disparities in access to healthcare and the burden of communicable diseases.
Japan’s Comprehensive Healthcare
Japan’s healthcare system is renowned for its quality and efficiency. The country offers universal healthcare coverage, which means that all Japanese citizens have access to necessary medical services. The healthcare system is primarily funded through a combination of government funding and health insurance contributions.
Japan has a high life expectancy and a low infant mortality rate, indicating the effectiveness of its healthcare system. Japanese hospitals and clinics are equipped with advanced medical technology and well-trained medical professionals.
One unique aspect of Japan’s healthcare system is the emphasis on preventive care and annual health check-ups. This focus on early detection and prevention contributes to the country’s overall health and well-being.
While Japan’s healthcare system is exemplary, it faces challenges related to the aging population and rising healthcare costs. These issues require innovative solutions to ensure the system’s sustainability.
In summary, India’s healthcare system is characterized by its diversity, with a booming medical tourism sector, while Japan’s healthcare system is comprehensive, efficient, and focused on preventive care.
| Healthcare Indicator | India | Japan |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare Expenditure | 3.5% of GDP (2018) | 10.9% of GDP (2019) |
| Physicians per 1,000 People | 0.8 (2019) | 2.4 (2019) |
| Life Expectancy at Birth | 69.7 years (2020) | 84.6 years (2020) |
| Healthcare Coverage | Mix of public and private providers | Universal healthcare coverage |
(Data source: World Bank and World Health Organization)
Transportation Systems
India’s Expansive and Diverse Transport Network
India’s transportation system is diverse and extensive, catering to a massive and varied population. The country has a vast road network, including national highways that connect major cities. The Indian Railways, one of the world’s largest railway networks, plays a crucial role in transporting passengers and goods.
Metropolitan areas like Delhi, Mumbai, and Bangalore have developed modern public transportation systems, including metro rail networks and bus rapid transit systems. Auto-rickshaws and cycle rickshaws are common modes of transport in many cities.
Air travel is well-established, with several major airports serving as international gateways. India’s aviation sector has seen significant growth, and several airlines operate domestic and international flights.
India’s transportation system faces challenges such as traffic congestion, inadequate road safety measures, and the need for infrastructure development in remote areas.
Japan’s Efficient and Punctual Transport
Japan’s transportation system is renowned for its efficiency and punctuality. The country’s Shinkansen, or bullet train, is famous for its speed and reliability. These high-speed trains connect major cities and are a preferred mode of travel for many Japanese.
The extensive train network is complemented by efficient subway systems in major cities like Tokyo, Osaka, and Kyoto. Buses and trams serve as essential modes of transport in smaller cities and rural areas.
Japan’s road network is well-maintained and characterized by orderly traffic. The country’s airports are modern and well-connected, with Narita International Airport in Tokyo and Kansai International Airport in Osaka serving as major international gateways.
While Japan’s transportation system is efficient, it faces challenges related to natural disasters, particularly earthquakes and typhoons, which can disrupt travel.
In summary, India’s transportation system is expansive and diverse, while Japan’s system is highly efficient and known for its punctuality.
| Transportation Indicator | India | Japan |
|---|---|---|
| Length of Highways | 1.94 million km (2019) | 1.22 million km (2017) |
| Railway Network Length | 68,442 km (2020) | 27,311 km (2020) |
| Airports | Over 400 (2021) | Over 100 (2021) |
| High-Speed Rail Network | Developing | Extensive, including Shinkansen |
(Data source: World Bank and Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism – Japan)
Culinary Traditions
India’s Spices and Diverse Cuisine
Indian cuisine is celebrated for its use of spices, herbs, and a wide variety of ingredients. Each region in India has its culinary specialties, and the diversity of dishes is staggering. North India is known for its tandoori kebabs, biryanis, and rich gravies, while South India offers spicy curries, dosas, and coconut-based dishes.
Vegetarianism is prevalent in India, and the country is known for its array of vegetarian dishes, including the popular paneer dishes and lentil-based curries. Indian bread, such as naan and roti, is a staple in many meals.
Indian desserts are equally diverse, with sweet treats like gulab jamun, jalebi, and a range of milk-based sweets. The use of spices like cardamom, cumin, and turmeric is a hallmark of Indian cooking.
Japan’s Artful and Fresh Culinary Traditions
Japanese cuisine is characterized by its emphasis on fresh and seasonal ingredients. The country’s traditional dishes, such as sushi, sashimi, tempura, and ramen, are known for their simplicity and clean flavors. Japanese chefs take great pride in their knife skills and presentation, turning meals into works of art.
Rice is a staple in Japanese cuisine, often accompanied by pickled vegetables, miso soup, and fresh seafood. Sushi, in particular, is a global favorite, with its combination of vinegared rice and various toppings.
Japanese sweets, or wagashi, are typically made from ingredients like red bean paste, mochi, and matcha (green tea). These sweets are not overly sweet and often reflect the changing seasons through their design and flavors.
In summary, India’s cuisine is known for its use of spices and diverse regional specialties, while Japan’s cuisine is celebrated for its artful simplicity and focus on fresh ingredients.
Arts and Entertainment
India’s Dynamic Arts and Entertainment Scene
India’s arts and entertainment scene is incredibly diverse, reflecting the country’s rich cultural heritage. Indian classical dance forms like Bharatanatyam, Kathak, and Odissi are celebrated for their intricate movements and storytelling.
Indian music includes both classical traditions, such as Hindustani and Carnatic, and popular music genres like Bollywood music. The country has a strong tradition of live music and is known for its melodic and rhythmic compositions.
Indian cinema, particularly Bollywood, is famous worldwide. Bollywood movies are known for their vibrant song-and-dance sequences, making them a unique blend of entertainment and storytelling. India also has a thriving independent cinema scene with critically acclaimed films.
Traditional arts and crafts, including intricate textiles, pottery, and jewelry, are deeply rooted in Indian culture and continue to be celebrated and practiced.
Japan’s Creative Pop Culture
Japan’s arts and entertainment scene is marked by its creative and contemporary pop culture. Anime and manga are internationally renowned, capturing the imaginations of people of all ages. These visual storytelling mediums cover a wide range of genres and themes.
Japanese music spans various genres, from J-pop to traditional enka. The country has a vibrant contemporary art scene, with contemporary artists pushing the boundaries of artistic expression.
Traditional Japanese theater forms like Noh, Kabuki, and Bunraku continue to be performed and are highly regarded for their artistry and historical significance.
Japan’s pop culture has a global fan base, and events like Comiket (Comic Market) and conventions dedicated to anime and manga draw enthusiasts from around the world.
In summary, India’s arts and entertainment scene is diverse and rooted in tradition, while Japan’s creative pop culture, particularly anime and manga, has gained global popularity.
Sports and Recreation
India’s Passion for Cricket and Diverse Sports
Cricket is India’s most popular sport, and the country has a fervent following for the game. Indian Premier League (IPL) cricket matches are major events that captivate millions of fans. Field hockey, a sport in which India has a storied history, is also widely played.
India’s diverse landscape offers opportunities for various recreational activities, including trekking in the Himalayas, exploring the Thar Desert, and enjoying water sports on its extensive coastline. Kabaddi, a traditional Indian sport, is played in many rural areas and has its leagues.
Other sports like badminton, football, and athletics also have dedicated followers, and India participates in the Olympics with a growing number of athletes.
Japan’s Love for Baseball and Martial Arts
Baseball is one of Japan’s most popular sports, with the Nippon Professional Baseball league being a major attraction. Sumo wrestling is a traditional Japanese sport with a strong following. The country is also known for its martial arts, including judo, karate, and kendo.
Japan’s natural beauty and geography provide opportunities for recreational activities such as hiking in the Japanese Alps, skiing in winter, and cherry blossom viewing (hanami) in spring.
The concept of “karoshi” or death by overwork has been a concern in Japan, highlighting the intensity with which many Japanese approach their work and careers.
In summary, India’s sports scene is marked by its passion for cricket and diverse recreational activities, while Japan has a strong tradition of baseball and martial arts.
India or Japan: Which One is Right Choose for You?
Choosing between India and Japan depends on your personal preferences, interests, and goals. Both countries offer unique experiences and opportunities, so let’s explore some key factors to consider when deciding which one is right for you.
Choosing India
- Cultural Diversity: India is a melting pot of cultures, languages, and traditions. If you’re interested in experiencing a wide range of cultural festivals, art forms, and culinary traditions, India is a vibrant choice.
- History and Heritage: India’s ancient history, with landmarks like the Taj Mahal and historical sites like Varanasi, offers a deep connection to human heritage. If you’re passionate about history and spirituality, India has much to offer.
- Affordable Travel: India is often considered a budget-friendly destination. You can explore its diverse landscapes, from the Himalayas to the deserts of Rajasthan, without breaking the bank.
- Adventure and Nature: India’s diverse geography offers adventure enthusiasts opportunities for trekking, wildlife safaris, and exploring natural wonders, such as Kerala’s backwaters.
- Yoga and Spirituality: India is the birthplace of yoga and is home to numerous spiritual practices and retreats. If you seek spiritual growth and self-discovery, India provides a rich environment.
Choosing Japan
- Efficiency and Technology: Japan is known for its efficient infrastructure, advanced technology, and punctuality. If you value modern amenities and innovation, Japan excels in these areas.
- Safety and Cleanliness: Japan consistently ranks as one of the safest and cleanest countries in the world. If safety and hygiene are top priorities for you, Japan offers a reassuring environment.
- Unique Pop Culture: If you’re a fan of anime, manga, or Japanese pop culture, Japan provides the opportunity to immerse yourself in a world of creativity and artistry.
- Work Opportunities: Japan’s strong economy, particularly in tech and manufacturing, offers job opportunities for expatriates. The country’s work ethic and disciplined approach can be appealing for career growth.
- Natural Beauty and Seasons: Japan’s appreciation for the changing seasons is reflected in its cherry blossom festivals, autumn foliage, and snowy landscapes. If you’re drawn to the beauty of nature, Japan offers diverse scenic experiences.
Ultimately, the choice between India and Japan depends on your interests, career goals, and what kind of experience you seek. Whether you’re captivated by India’s cultural diversity and spirituality or Japan’s technological prowess and orderly society, both countries have much to offer. Consider what resonates most with your aspirations and embark on a unique journey tailored to your preferences.
FAQs
India is known for its cultural diversity, with various languages, religions, and traditions. In contrast, Japan has a more homogeneous culture with a strong emphasis on tradition and hierarchy.
India’s economy is rapidly growing, with a focus on services and agriculture. Japan, on the other hand, is known for its technological prowess and strong manufacturing sector.
India’s society is diverse, with a mix of caste systems and extended families. Japan has a relatively homogeneous society with a strong emphasis on hierarchy and respect for authority.
India is a federal democracy with a multi-party system. Japan has a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary government.
India has a diverse healthcare landscape with public and private providers, while Japan offers a comprehensive and universal healthcare system.
India has an expansive and diverse network with challenges, while Japan’s transportation system is highly efficient and well-maintained.
India is known for its use of spices and diverse regional specialties, while Japan’s cuisine is artful, simple, and emphasizes fresh ingredients and presentation.
India’s arts scene is diverse and rooted in tradition, with contemporary cinema like Bollywood. Japan’s pop culture is creative, with a strong focus on anime and manga.
India has a passion for cricket and diverse sports, while Japan loves baseball, martial arts, and appreciates the changing seasons.
India and Japan differ in historical perspective, cultural diversity, economic landscape, social structure, governance systems, healthcare and education, transportation infrastructure, culinary traditions, arts and entertainment, and sports and recreation, making each of them unique in their own right.
Read More:






