| Aspect | LCD | TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Technology | Liquid Crystal Display | Subset of LCD with Thin-Film Transistors |
| Image Quality | Variable; depends on quality and model | Enhanced color accuracy and clarity |
| Viewing Angles | Limited; color shift at extreme angles | Wider and more consistent viewing angles |
| Response Time | Typically slower (5ms-8ms or more) | Faster (1ms-5ms); reduced motion blur |
| Power Consumption | Higher; constant backlight usage | Lower; dynamic backlight control |
| Durability | Varies based on build quality | Varies; enhanced build quality available |
| Connectivity Options | HDMI, DisplayPort, VGA, DVI, etc. | HDMI, DisplayPort, VGA, DVI, etc. |
| Compatibility | Compatible with various devices and OS | Compatible with various devices and OS |
If you’re in the market for a new display, you’ve probably come across the terms LCD and TFT. But what do these acronyms really mean, and more importantly, what sets them apart? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll take you on a journey through the world of display technology, shedding light on the key differences between LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) and TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) screens. By the time you’re done reading, you’ll be well-equipped to make an informed decision when it comes to choosing the right display for your needs.
Differences Between LCD and TFT Technology
The primary differences between LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) and TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) technology lie in image quality, viewing angles, response time, power consumption, and durability. While LCDs offer varying image quality depending on the model and may have limited viewing angles with potential color shifts, TFT-LCDs excel in color accuracy and provide wider and more consistent viewing angles. TFT technology boasts faster response times, reducing motion blur, making it ideal for gaming and multimedia. Moreover, TFT-LCDs are more energy-efficient due to dynamic backlight control, potentially lowering power consumption and costs. Durability can vary, but TFT-LCDs often come with enhanced build quality.
The Basics: Understanding LCD and TFT
Before we dive into the differences, let’s establish a solid understanding of what LCD and TFT actually are.
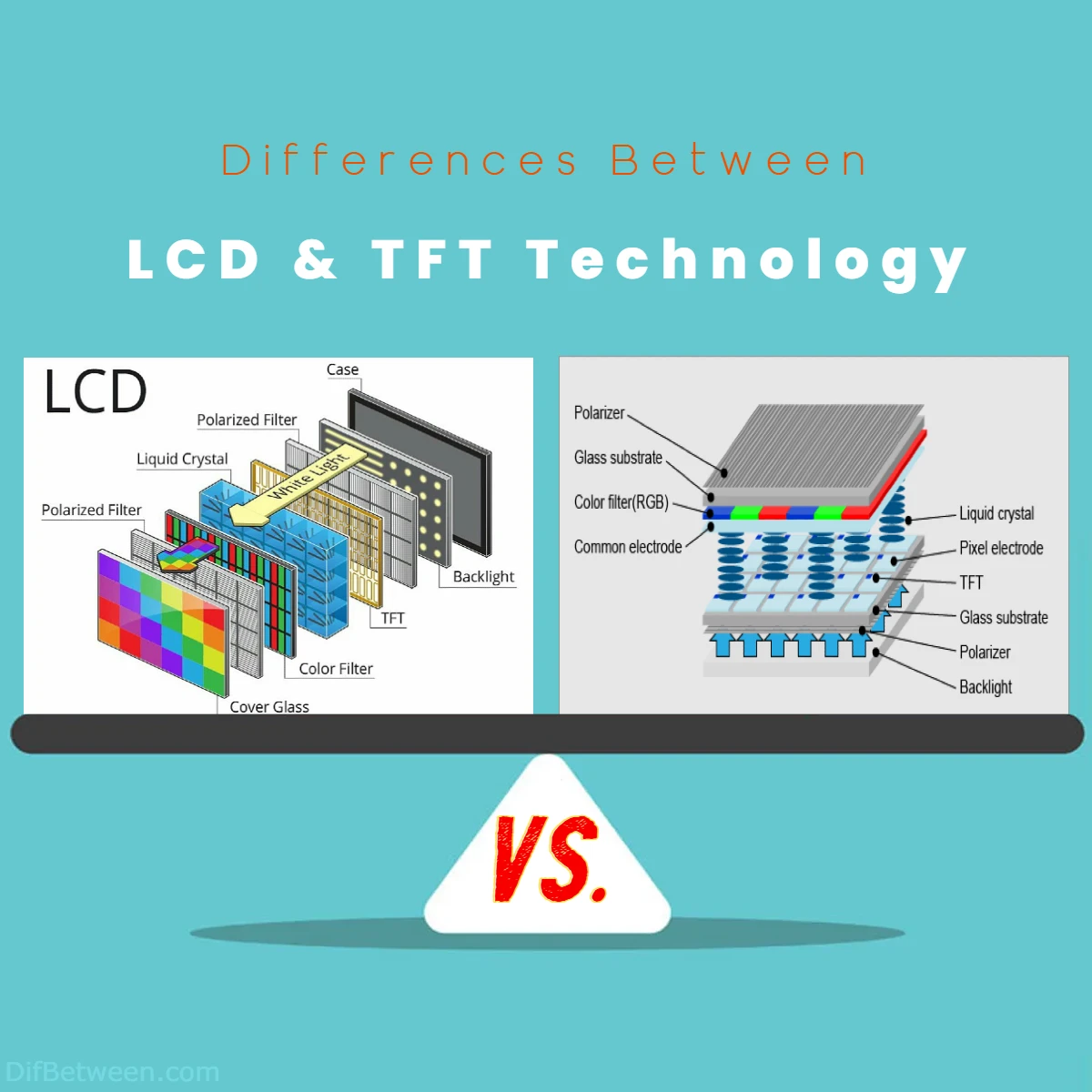
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)
LCD at a Glance:
- LCD stands for “Liquid Crystal Display.”
- It’s a type of flat-panel display technology that has been around for several decades.
- LCDs are commonly used in computer monitors, TVs, smartphones, and various other devices.
- They operate by manipulating liquid crystals to control the passage of light through them.
How LCD Works: In a typical LCD, liquid crystals are sandwiched between two layers of glass or plastic. These liquid crystals can change their alignment when subjected to an electric current. By applying varying voltages to different regions of the screen, specific pixels can be made to allow light to pass through or block it entirely, creating the images you see on the display.
Thin-Film Transistor (TFT)
TFT at a Glance:
- TFT stands for “Thin-Film Transistor.”
- It’s a specific type of technology used in LCD screens to improve their performance.
- TFT technology is responsible for individual pixel control and faster refresh rates.
- Most modern LCD displays are actually TFT-LCDs.
How TFT Works: In TFT-LCD screens, each pixel is associated with its own thin-film transistor. This transistor acts like a tiny switch, controlling the passage of light through the pixel. This level of individual control is what allows for high-resolution displays and quick refresh rates, making TFT-LCDs suitable for applications requiring fast-moving visuals, such as gaming and video playback.
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s delve into the key differences between LCD and TFT technology.
Display Quality: Resolution and Color Reproduction
When it comes to choosing a display, one of the first factors to consider is the quality of the visuals it delivers.
LCD Display Quality
LCDs offer a wide range of quality options, from basic to high-end. The quality of an LCD screen is primarily determined by its resolution and color reproduction capabilities.
- Resolution: LCDs come in various resolutions, including HD (High Definition), Full HD, 4K, and even 8K in some cases. Higher resolution screens offer sharper and more detailed images, making them ideal for tasks like photo and video editing.
- Color Reproduction: The color accuracy of LCDs can vary. Some models have excellent color reproduction, while others may not be as precise. If you’re a graphic designer or photographer, you’ll want an LCD with a wide color gamut and good color calibration options.
TFT Display Quality
TFT-LCDs, being a subset of LCDs, inherit the qualities of standard LCDs. However, they often excel in certain aspects.
- Resolution: TFT-LCDs can also have varying resolutions, with high-resolution options available. The presence of individual transistors for each pixel enables better control over pixel switching, contributing to improved image clarity.
- Color Reproduction: TFT-LCDs typically offer better color accuracy and faster response times compared to non-TFT LCDs. This makes them well-suited for applications where color precision and rapid screen updates are crucial, such as gaming and multimedia content consumption.
Viewing Angles: Flexibility in Perspective
The way a display handles viewing angles can significantly impact the user experience, particularly in shared or dynamic settings.
LCD Viewing Angles
One drawback of traditional LCDs is their limited viewing angles. When you view an LCD screen from an angle, you may notice a shift in colors and a decrease in brightness and contrast. This phenomenon is known as “color shift” or “viewing angle dependency.”
Color Shift: In an LCD, the liquid crystals work optimally when you view the screen head-on. Deviating from this angle can result in color distortion, which can be problematic in situations where multiple people are viewing the same screen.
TFT Viewing Angles
TFT-LCDs offer improved viewing angles compared to non-TFT LCDs. The inclusion of thin-film transistors for individual pixel control helps mitigate color shift issues.
- Wider Viewing Angles: TFT-LCDs provide more consistent color and brightness across a wider range of viewing angles. This is especially advantageous for larger displays or when multiple individuals are watching content on the same screen.
- Enhanced Outdoor Visibility: TFT-LCDs are often preferred for outdoor applications, such as digital signage or ruggedized devices, because they maintain good visibility even in direct sunlight.
Response Time: The Need for Speed
In today’s fast-paced world, the speed at which a display can change its content is a crucial factor, especially in applications like gaming and video playback.
LCD Response Time
The response time of a display refers to how quickly a pixel can change from one color to another. Traditional LCDs may have response times ranging from 5 to 8 milliseconds (ms) or even higher. While this is sufficient for many tasks, it can lead to motion blur in fast-moving scenes, such as action-packed video games.
Motion Blur: In situations where rapid image changes are required, LCDs may struggle to keep up, resulting in noticeable motion blur. This can be distracting and affect the overall gaming or viewing experience.
TFT Response Time
TFT-LCDs shine when it comes to response times. Thanks to the individual transistors for each pixel, these displays can achieve much faster response times, often as low as 1 ms.
Reduced Motion Blur: For gamers and those who demand smooth video playback, TFT-LCDs are an excellent choice. The rapid response times virtually eliminate motion blur, creating a crisp and fluid visual experience.
Energy Efficiency: Keeping Costs Down
Energy efficiency is a growing concern in today’s world. Choosing a display that consumes less power can lead to lower energy bills and a reduced environmental footprint.
LCD Energy Efficiency
Traditional LCDs are known to consume more power than some other display technologies, especially when displaying bright images. The reason for this is that the backlight used in LCDs remains on continuously, regardless of the content being displayed.
Backlight Always On: In LCDs, the backlight is active at all times, even when displaying mostly dark content. This constant energy consumption can add up over time.
TFT Energy Efficiency
TFT-LCDs address the energy efficiency issue by offering better control over the backlight. Thanks to the individual pixel transistors, the backlight can be adjusted dynamically based on the content being displayed.
Dynamic Backlight Control: TFT-LCDs can reduce power consumption by dimming or turning off the backlight in areas of the screen that are displaying dark content. This “local dimming” technique leads to energy savings, making TFT-LCDs a greener choice.
Cost Considerations: Budget-Friendly Options
Of course, budget plays a significant role in any purchasing decision. Let’s explore how LCDs and TFT-LCDs compare in terms of cost.
LCD Costs
LCDs are available in a wide range of price points, making them suitable for various budgets. Basic models with lower resolutions are often quite affordable, making them accessible for general use.
- Budget-Friendly Options: If you’re looking for a simple display for everyday tasks like web browsing and document editing, you can find LCD monitors that won’t break the bank.
- Premium Choices: On the other end of the spectrum, high-end LCDs with 4K or 8K resolutions and advanced features can be quite expensive, catering to professionals and enthusiasts who demand top-tier performance.
TFT Costs
TFT-LCDs are generally priced competitively, falling within the same price range as their non-TFT counterparts. In fact, many modern LCD monitors and screens are, by default, TFT-LCDs.
- Similar Pricing: When comparing displays with similar specifications, you’ll likely find that TFT-LCDs are priced similarly to non-TFT LCDs.
- Value for Performance: TFT-LCDs offer excellent value for performance, making them a popular choice for gaming and multimedia enthusiasts looking for a responsive and budget-friendly display.
Power Consumption: Saving Energy and Lowering Costs
In an era of growing environmental consciousness and rising energy costs, minimizing power consumption is a smart move. Let’s explore how LCDs and TFT displays stack up in terms of energy efficiency.
LCD Power Consumption
LCDs are known for consuming relatively more power compared to some other display technologies. This is because the backlight in LCD screens remains constantly active, regardless of the content being displayed. The backlight evenly illuminates the entire screen, which can lead to inefficiencies when you’re viewing mostly dark or static content.
Continuous Backlight: In LCDs, the backlight remains on continuously, even when a significant portion of the screen is displaying dark images or text. This can result in higher energy bills over time.
TFT Power Consumption
TFT-LCDs tackle the power consumption issue more effectively by offering better control over the backlight. Thanks to the individual transistors associated with each pixel, the backlight can be dynamically adjusted based on the content being displayed.
- Dynamic Backlight Control: TFT-LCDs can dim or turn off the backlight in areas of the screen that are displaying predominantly dark content. This technique, known as “local dimming,” leads to energy savings and makes TFT-LCDs a greener choice.
- Energy-Efficient Options: Some TFT-LCD monitors come with energy-saving modes and features that further reduce power consumption when the screen is not in active use, contributing to energy and cost savings.
Durability: Withstanding the Test of Time
Durability is a crucial consideration, especially if you plan to use your display in demanding environments or require a long-lasting investment. Let’s examine how LCDs and TFT displays compare in terms of durability.
LCD Durability
The durability of traditional LCDs can vary depending on the quality of materials and manufacturing. Basic LCD screens may not be as robust as their higher-end counterparts. Here are some factors to consider regarding LCD durability:
- Build Quality: The build quality of LCD monitors can range from budget plastic frames to high-quality metal construction. Sturdier frames and reinforced glass or plastic can enhance durability.
- Lifespan: On average, LCDs have a lifespan of around 60,000 hours of use. However, this can vary depending on usage patterns and the quality of components.
- Susceptibility to Pressure: Traditional LCDs can be susceptible to pressure, impacting the screen and potentially leading to pixel damage or screen cracking.
TFT Durability
TFT-LCDs inherit the durability characteristics of standard LCDs. However, some of their features can enhance overall robustness:
- Build Quality: TFT-LCD monitors often feature sturdy construction, with reinforced frames and protective coatings on the display. These enhancements improve their resistance to wear and tear.
- Longevity: Similar to standard LCDs, TFT-LCDs have an average lifespan of approximately 60,000 hours. Proper care and maintenance can extend their longevity.
- Pressure Resistance: While TFT-LCDs are not entirely immune to pressure, their individual pixel control can help minimize damage. A localized impact may affect only specific pixels rather than causing widespread screen damage.
Choosing Based on Power Consumption and Durability
When it comes to making a choice between LCD and TFT displays based on power consumption and durability, consider the following:
- Energy Efficiency: If you prioritize lower energy consumption and want to reduce your environmental impact and energy bills, TFT-LCDs are the better choice. They offer dynamic backlight control and energy-saving features that can make a significant difference in power usage.
- Durability: For durability, both LCD and TFT-LCD displays can be suitable, depending on the build quality and intended usage. If you require a display for rugged environments or anticipate exposure to physical stress, look for models with reinforced frames and protective coatings.
Remember that proper care and maintenance also play a role in the longevity and durability of your display. Regardless of your choice, handling your screen with care, avoiding excessive pressure, and keeping it clean will help ensure it serves you well for years to come.
LCD or TFT Technology: Which One is Right to Choose?
When it comes to choosing between LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) and TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) technology, your decision should be based on your specific needs and preferences. Both technologies have their advantages and are suitable for various use cases. Let’s break down when to choose LCD and when to choose TFT technology:
Choose LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) Technology When:
- Everyday Use: If you need a display for general tasks like web browsing, document editing, and casual media consumption, a standard LCD monitor is a cost-effective choice. LCDs come in various price ranges and offer decent image quality for everyday computing.
- Budget Constraints: LCD monitors are often more budget-friendly than their TFT counterparts. If you’re looking for a display that won’t break the bank, an LCD is a sensible option for basic computing needs.
- Variable Use: LCDs are versatile and can work well in various environments. They are suitable for home offices, classrooms, and workplaces where high-end features are not a primary requirement.
- Compatibility: LCD monitors are generally compatible with a wide range of devices and operating systems, making them a safe choice for most users.
Choose TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) Technology When:
- Gaming and Multimedia: If you’re a gamer or a multimedia enthusiast who demands high-quality visuals and fast response times, TFT-LCD displays are the better choice. Their faster response times and reduced motion blur make them ideal for these applications.
- Color Precision: If your work involves tasks like graphic design, photo editing, or video production that require precise color reproduction, TFT-LCDs typically offer better color accuracy and a wider color gamut.
- Wider Viewing Angles: In scenarios where multiple people need to view the same screen or where you want to maintain color and image consistency even at wide angles, TFT-LCDs with improved viewing angles are preferable.
- Energy Efficiency: If you’re environmentally conscious and want to reduce energy consumption and costs, TFT-LCDs with dynamic backlight control are more energy-efficient.
- Rugged Environments: For applications in challenging environments or situations where the display may be subjected to physical stress, TFT-LCDs with enhanced durability can be a better choice.
- High-End Features: If you’re willing to invest in a display with advanced features like high resolutions (4K or 8K), faster refresh rates, and adaptive sync technologies, TFT-LCD monitors often offer these options.
In summary, LCD technology is a practical choice for everyday computing tasks and when budget constraints are a concern. On the other hand, TFT technology, particularly TFT-LCDs, excels in scenarios where color precision, fast response times, wider viewing angles, energy efficiency, or durability are crucial.
Before making a final decision, it’s essential to consider your specific requirements, the type of content you’ll be working with, and your budget. Additionally, always check the specifications and user reviews of specific models to ensure they meet your needs.
FAQs
The primary difference lies in the way each technology controls the passage of light through the screen. TFT-LCDs use thin-film transistors for individual pixel control, leading to better image quality and faster response times compared to standard LCDs.
TFT-LCDs generally provide better image quality with enhanced color accuracy and higher resolution options. They are ideal for applications requiring precise color reproduction.
Yes, there are significant differences. LCDs often have limited viewing angles, which can result in color shifts and reduced visibility when viewed from the side. TFT-LCDs offer wider and more consistent viewing angles, maintaining image quality even from different perspectives.
Response time is notably faster in TFT-LCDs, typically ranging from 1ms to 5ms. LCDs have slower response times, around 5ms to 8ms or more, which can lead to motion blur in fast-moving scenes.
TFT-LCDs tend to be more energy-efficient due to dynamic backlight control. They can adjust the backlight based on the content being displayed, reducing power consumption, and potentially lowering energy bills.
Durability can vary among specific models, but TFT-LCDs often come with enhanced build quality, making them more robust, especially in rugged environments or situations where the display may be subjected to physical stress.
Yes, both LCD and TFT-LCD displays offer budget-friendly options. Standard LCDs are often more affordable, making them suitable for general use, while TFT-LCDs cater to various price points, including cost-effective models.
TFT-LCDs are the preferred choice for gaming and multimedia enthusiasts due to their faster response times, reduced motion blur, and better overall image quality.
Yes, both LCD and TFT-LCD displays are generally compatible with a wide range of devices and operating systems, including computers, gaming consoles, and streaming devices. However, always check specific models for compatibility with your devices.
Your choice should be based on your usage requirements. If you prioritize factors like fast response times, color accuracy, and energy efficiency, TFT-LCDs are a better fit. For general use and budget-friendly options, standard LCDs are still viable choices.
Read More:
Contents
- Differences Between LCD and TFT Technology
- The Basics: Understanding LCD and TFT
- Display Quality: Resolution and Color Reproduction
- Viewing Angles: Flexibility in Perspective
- Response Time: The Need for Speed
- Energy Efficiency: Keeping Costs Down
- Cost Considerations: Budget-Friendly Options
- Power Consumption: Saving Energy and Lowering Costs
- Durability: Withstanding the Test of Time
- Choosing Based on Power Consumption and Durability
- LCD or TFT Technology: Which One is Right to Choose?
- FAQs






