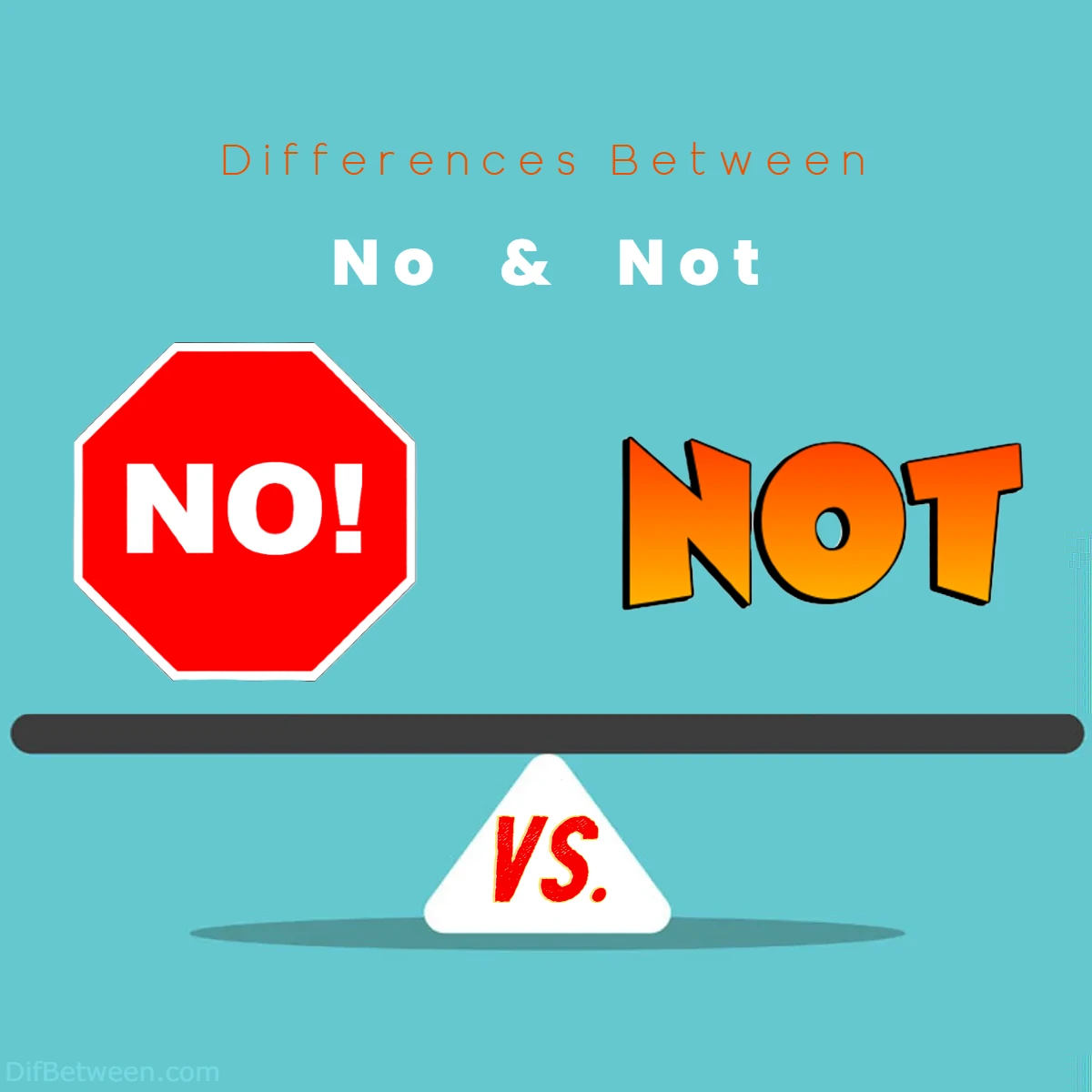
| Aspect | “No” | “Not” |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Indicates the absence or lack of something. | Negates verbs, adjectives, or adverbs. |
| Usage in Negative Sentences | Used to deny the existence or occurrence of something. | Negates verbs, adjectives, or adverbs within a sentence. |
| Usage in Negative Questions | Used to seek confirmation of a negative statement expecting a positive response. | Used to form negative questions expecting a negative response. |
| Emphasis and Context | Can be used for strong emphasis and certainty. | Can be used for emphasis but tends to be less forceful than “no.” |
| Formality | Considered more formal and used in formal writing and speech. | Versatile and can be used in both formal and informal contexts. |
| Idiomatic Expressions | Found in idiomatic expressions like “No can do” and “No way.” | Found in idiomatic expressions like “Not a chance” and “Not in a million years.” |
| Regional and Cultural Variations | Usage may vary by region and culture. | Usage may vary by region and culture. |
| Advanced Usage | Can be used in noun phrases to emphasize the absence of something. | Typically not used in noun phrases. |
| Double Negatives | When used together, they cancel each other out, creating an affirmative statement. | When used together, they cancel each other out, creating an affirmative statement. |
In the vast tapestry of the English language, even the tiniest words can wield incredible power. Today, we set our linguistic magnifying glass on two such words: “no” and “not.” These unassuming members of our vocabulary often work behind the scenes, quietly shaping the meaning of our sentences.
Differences Between No and Not
The main differences between “no” and “not” lie in their grammatical functions and semantic roles in sentences. “No” primarily serves as a determiner and noun, indicating the absence or lack of something, and it is often used in negative sentences and questions to deny the existence or occurrence of a particular thing or action. On the other hand, “not” functions as an adverb, negating verbs, adjectives, and adverbs within a sentence. It is more versatile and can be used in various contexts to create negative statements, questions, or to emphasize a point. Understanding when to use “no” to indicate absence and “not” for negation is essential for precise and effective communication in the English language.
Definition and Usage
No
No is a determiner and noun that is used to indicate the absence or lack of something. It is often employed to give a negative response to a question or to make a statement of denial.
Example 1: “There is no coffee left in the pot.” Example 2: “She said no to the invitation.”
Not
Not, on the other hand, is an adverb that is used to negate verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs in a sentence. It is a versatile word that can be used to create negative sentences, questions, and more.
Example 1: “I do not like broccoli.” Example 2: “He will not be attending the meeting.”
Negative Sentences
Using “No” in Negative Sentences
When you use “no” in negative sentences, you are typically indicating the absence or lack of something. It is used to deny the existence or occurrence of a particular thing or action.
Example 1: “There is no milk in the refrigerator.”
In this sentence, “no” is used to state that there is an absence of milk in the refrigerator.
Example 2: “I have no interest in sports.”
Here, “no” is used to express the complete lack of interest in sports.
Using “Not” in Negative Sentences
When you use “not” in negative sentences, you are negating a specific verb or action within the sentence. It indicates that the action is not happening or the state is not as described.
Example 1: “She does not like horror movies.”
In this sentence, “not” negates the verb “like,” indicating that she does not have a preference for horror movies.
Example 2: “The weather is not sunny today.”
Here, “not” negates the adjective “sunny,” conveying that the weather is not characterized by sunshine.
In summary, “no” is used to indicate the absence or lack of something, while “not” is used to negate verbs, adjectives, or adverbs in negative sentences.
Negative Questions
Using “No” in Negative Questions
Negative questions are formed by placing “no” at the beginning of a question to seek confirmation of a negative statement. These questions often expect a positive response.
Example 1: “No, you didn’t finish your homework, did you?”
Here, the speaker is using “no” at the beginning of the question to confirm the negative statement that the homework was not completed.
Example 2: “No, they haven’t arrived yet, have they?”
In this question, “no” precedes the negative statement that they have not arrived, expecting a positive response.
Using “Not” in Negative Questions
“Not” can also be used in negative questions to form interrogative sentences that expect a negative response.
Example 1: “You’re not coming to the party, are you?”
In this question, “not” is used to create a negative question, expecting the response that the person is not coming to the party.
Example 2: “She’s not going to the concert, is she?”
Here, “not” precedes the negative statement about her attendance at the concert, anticipating a negative response.
In negative questions, both “no” and “not” can be used to seek confirmation, but the choice depends on whether a positive or negative response is expected.
Emphasis and Context
Using “No” for Emphasis
“No” can be used for emphasis to make a strong, definitive statement. It often conveys a sense of certainty and finality.
Example 1: “There is absolutely no way I can do that.”
In this sentence, “no” emphasizes the impossibility of the situation.
Example 2: “I have no doubt about his honesty.”
Here, “no” emphasizes the speaker’s complete confidence in the person’s honesty.
Using “Not” for Emphasis
“Not” can also be used for emphasis, but it tends to be less forceful than “no.” It can convey a sense of uncertainty or softening of the negative statement.
Example 1: “I’m not entirely sure if I can make it.”
In this sentence, “not” softens the uncertainty about the speaker’s availability.
Example 2: “It’s not that bad, actually.”
Here, “not” reduces the negativity of the situation, suggesting that it may not be as bad as initially thought.
In cases of emphasis, both “no” and “not” can be used, but “no” typically adds more intensity and finality to the statement.
Double Negatives
Using “No” and “Not” in Double Negatives
Double negatives occur when both “no” and “not” are used in a sentence. In standard English grammar, double negatives cancel each other out, resulting in an affirmative statement.
Example 1: “There’s no way I can not help you.”
In this sentence, the double negative “no” and “not” cancels each other out, making it affirmative. The speaker is expressing their willingness to help.
Example 2: “I have no doubt that he did not steal the money.”
Here, the double negative emphasizes the speaker’s confidence that he is innocent.
While double negatives can be used for emphasis or in informal speech, it’s essential to be aware that they can create confusion and are not always accepted in formal writing or standard English.
Common Mistakes
Understanding the differences between “no” and “not” can help you avoid common mistakes in your writing and speech. Here are some common errors to watch out for:
- Using “no” when “not” is needed:
- Incorrect: “I have no idea your name.”
- Correct: “I have not heard your name.”
- Using “not” when “no” is needed:
- Incorrect: “I have not money.”
- Correct: “I have no money.”
- Double negatives for emphasis:
- Incorrect (in formal writing): “I can’t find no solution.”
- Correct: “I can’t find any solution” or “I can find no solution.”
Contextual Usage
Using “No” in Context
“No” is often used in contexts where the absence or denial of something is the primary focus. Let’s explore some common situations where “no” is the preferred choice:
1. Expressing Absence:
- “There’s no cake left in the kitchen.”
- “I found no evidence of wrongdoing.”
In these examples, “no” is used to emphasize the complete absence of cake or evidence.
2. Responding to Yes/No Questions:
- “Did you eat all the cookies?” “No, I didn’t.”
- “Is there any gas in the car?” “No, it’s empty.”
When responding to yes/no questions, “no” is used to provide a negative response.
Using “Not” in Context
“Not” is versatile and can be used in a wide range of contexts to negate verbs, adjectives, or adverbs. Let’s explore when “not” is the preferred choice:
1. Verb Negation:
- “I can not attend the meeting.”
- “She did not finish her assignment.”
In these sentences, “not” negates the verbs “attend” and “finish.”
2. Adjective Negation:
- “The movie was not enjoyable.”
- “His performance was not impressive.”
Here, “not” negates the adjectives “enjoyable” and “impressive.”
3. Adverb Negation:
- “She’s not particularly interested in politics.”
- “He doesn’t work not very efficiently.”
In these sentences, “not” negates the adverbs “particularly” and “very.”
Formal vs. Informal Language
The choice between “no” and “not” can also be influenced by the level of formality in your communication. “No” is often considered more formal and can be preferred in written and formal spoken contexts. “Not,” on the other hand, is versatile and can be used in both formal and informal settings.
Formal Example:
- “I have no objections to the proposal.”
Informal Example:
- “I don’t have any issues with the plan.”
In formal writing, using “no” can add a touch of elegance and formality to your language, while “not” is commonly used in everyday conversation.
Idiomatic Expressions
Both “no” and “not” are used in various idiomatic expressions and phrases, which may not follow the standard rules of grammar. Here are a few examples:
1. No can do:
- “I’m sorry, but no can do. I can’t make it to the party.”
2. Not a chance:
- “There’s not a chance that I’ll lend him money again.”
3. No way:
- “There’s no way I’m going to that haunted house.”
These idiomatic expressions often use “no” or “not” for emphasis and are understood as fixed phrases.
Regional and Cultural Variations
Language usage can vary by region and culture, and this includes the choice between “no” and “not.” Some dialects or regional variations of English may have unique preferences for these words. It’s essential to be aware of the linguistic conventions in your specific context.
Advanced Usage: “No” in Noun Phrases
In advanced English grammar, “no” can be used in noun phrases to indicate the absence of a specific thing or condition. For example:
- “She lived a life of no regrets.”
- “He faced a future with no certainty.”
Here, “no” is part of a noun phrase that emphasizes the absence or lack of something within that noun phrase.
Summary
In this comprehensive exploration of “no” vs. “not,” we’ve covered their definitions, usage in negative sentences and questions, emphasis and context, double negatives, common mistakes to avoid, and more. Understanding the subtle differences between these two words can significantly enhance your proficiency in English language and communication.
By recognizing when to use “no” for absence and “not” for negation, considering the level of formality, understanding idiomatic expressions, and being mindful of regional variations, you’ll be well-equipped to use these words effectively in various linguistic contexts. Whether you’re writing a formal report, engaging in casual conversation, or expressing yourself through idiomatic expressions, the nuances of “no” and “not” will serve as valuable tools in your language toolkit.
FAQs
The primary difference lies in their grammatical functions and semantic roles. “No” is typically used to indicate the absence or lack of something, while “not” negates verbs, adjectives, or adverbs in a sentence.
No, they are not interchangeable. “No” and “not” have distinct functions, and using them incorrectly can change the meaning of a sentence.
“No” is used in negative sentences to deny the existence or occurrence of something. For example, “There is no milk in the refrigerator.”
“Not” is used to negate verbs, adjectives, or adverbs in negative sentences. For instance, “She did not finish her assignment.”
Yes, both can be used in negative questions, but the choice depends on whether you expect a positive or negative response. “No” is used for positive responses, and “not” is used for negative responses. For example, “No, you didn’t finish your homework, did you?” expects a positive response.
Yes, there are idiomatic expressions that use both words, such as “No can do” and “Not a chance.” These expressions don’t always follow standard grammatical rules.
Yes, double negatives can be used for emphasis or to intensify a negative statement. However, they are not always accepted in formal writing or standard English.
Yes, language usage can vary by region and culture, and this may include preferences for “no” or “not.” It’s important to be aware of local linguistic conventions.
“No” is generally considered more formal and is often used in formal writing and speech. “Not” is versatile and can be used in both formal and informal contexts.
Reading and practicing sentences that use “no” and “not” in different contexts can help improve your understanding and usage. Additionally, seeking feedback from native speakers or language experts can be valuable in refining your skills.
Read More:
Contents






