| Aspect | Diapsids | Synapsids |
|---|---|---|
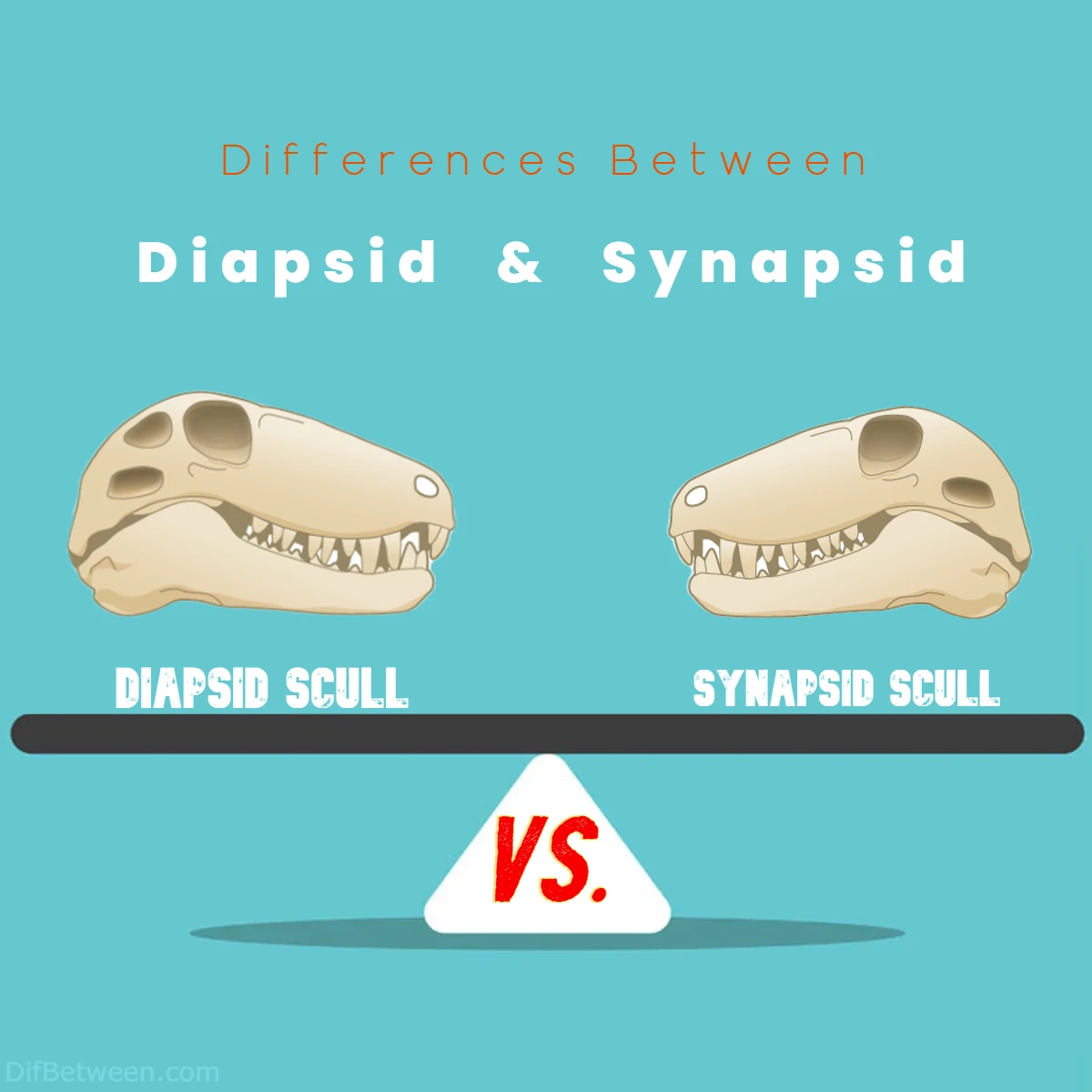
| Skull Fenestrae | Two pairs of temporal fenestrae: Supratemporal and infratemporal fenestrae for muscle attachment. | Single pair of temporal fenestrae: Positioned on each side of the skull, linked to jaw joint. |
| Evolutionary Timeline | Emergence: Late Carboniferous period. Diversified during the Mesozoic era. | Origins: Late Carboniferous period. Flourished through Permian and Triassic periods. |
| Diversity | Vast array of species: Dinosaurs, reptiles, birds. Dominated Mesozoic era. | Path to mammals: Diverse therapsids paved the way for mammals. |
| Modern Representatives | Birds and reptiles: Includes modern birds, reptiles like lizards, snakes, crocodiles, and turtles. | Mammals: Modern mammals represent synapsid lineage, thriving in various ecosystems worldwide. |
| Temporal Fenestrae | Two pairs: Supratemporal and infratemporal fenestrae. | Single pair: One temporal fenestra on each side of the skull. |
| Jaw Muscle Attachment | Powerful biting: Dual fenestrae allow for strong jaw muscle attachment, crucial for predation. | Transition towards mammals: Fenestra linked to jaw joint, indicative of adaptations leading to mammals. |
| Adaptive Radiation | Mesozoic dominance: Diapsids radiated into diverse species including dinosaurs, pterosaurs, reptiles. | Therapsid diversity: Diversification of therapsids marked the pathway to mammalian evolution. |
| Ecological Niche | Variety of habitats: Occupied terrestrial, aquatic, and aerial niches. | Adaptive niches: Synapsids diversified into various ecological roles, laying groundwork for mammals. |
| Reproductive Traits | Egg-laying: Most diapsids lay eggs, often with protective shells. | Parental care: Synapsids exhibited varying levels of parental care, reflecting mammalian tendencies. |
| Modern Examples | Modern birds and reptiles: Eagles, crocodiles, snakes, and lizards. | Modern mammals: Dogs, cats, whales, humans, showcasing a broad spectrum of morphological diversity. |
| Major Evolutionary Era | Mesozoic era: Diapsids were prominent and diversified. | Permian and Triassic periods: Synapsids flourished and set the stage for mammalian emergence. |
Imagine creatures with jaw structures that tell tales of their predatory prowess, and ancient lineages that paved the way for the emergence of mammals as we know them today. As we unravel the pages of history, you’ll be captivated by the anatomical marvels that distinguish diapsids, boasting double the temporal fenestrae for powerful bites, and synapsids, with their singular fenestra leading the way to the rise of mammals.
Differences Between Diapsid and Synapsid
The main differences between Diapsids and Synapsids lie in their skull structures and evolutionary trajectories. Diapsids possess two pairs of temporal fenestrae, allowing for powerful jaw muscle attachment, while Synapsids feature a single pair of these openings associated with the jaw joint. Diapsids, including dinosaurs and modern reptiles, dominated the Mesozoic era, while Synapsids, exemplified by early mammalian ancestors, thrived during the Permian and Triassic periods. These distinctions highlight the diverse evolutionary paths of these vertebrate groups, shaping the rich tapestry of life on Earth.
The Basics: Diapsids and Synapsids
Diapsids: Imagine a world where reptiles, birds, and dinosaurs reign supreme. This is the realm of diapsids. These remarkable creatures are united by a distinct feature: they possess two openings on each side of their skulls, known as temporal fenestrae. These fenestrae, or openings, serve as attachment points for jaw muscles, granting diapsids enhanced biting power. As diapsids evolved, they branched into a variety of lineages, giving rise to some of the most iconic and diverse species in Earth’s history.
Synapsids: Now, let’s shift our gaze to a different group of fascinating beings. Synapsids are often heralded as the pioneers of the mammalian lineage. These creatures boast a single pair of temporal fenestrae on their skulls. This feature distinguishes them from diapsids and showcases their unique evolutionary journey. Synapsids evolved into an extraordinary array of forms, eventually leading to the emergence of mammals as we know them today. Their story is one of adaptation, survival, and transformation.
Head to Head: Comparative Differences
In this section, we’ll delve into a side-by-side comparison of the key differences between diapsids and synapsids. Let’s explore their anatomical disparities, evolutionary timelines, and the remarkable diversity they’ve contributed to the natural world.
| Aspect | Diapsids | Synapsids |
|---|---|---|
| Skull Fenestrae | Two pairs of temporal fenestrae: The upper fenestra is the supratemporal fenestra, and the lower is the infratemporal fenestra. These openings offer space for powerful jaw muscles. | Single pair of temporal fenestrae: This lone fenestra accommodates jaw muscles and is a defining trait. |
| Evolutionary Timeline | Emergence in the Late Carboniferous period: Diapsids gained prominence and diversified during the Mesozoic era. | Origins in the Late Carboniferous period: Synapsids paved the way for mammals, flourishing through the Permian and Triassic periods. |
| Diversity | Vast array of species: Diapsids include dinosaurs, reptiles, birds, and more. The Mesozoic era was dominated by iconic diapsid species. | Path to mammalian diversity: Synapsids underwent an incredible adaptive radiation, leading to the rise of early mammals and, eventually, modern mammals. |
| Modern Representatives | Birds and reptiles: Diapsids are represented by modern birds, reptiles, and some of the most awe-inspiring creatures to walk the Earth. | Mammals: Synapsids paved the way for mammals, and today, they continue to thrive in diverse ecosystems worldwide. |
The Evolutionary Odyssey of Diapsids
The story of diapsids begins around 300 million years ago, during the Late Carboniferous period. These creatures embarked on an evolutionary journey that would lead to the creation of awe-inspiring species that once dominated the Mesozoic era. Diapsids quickly adapted to various ecological niches, giving rise to an extraordinary range of forms.
Mesozoic Marvels: Dinosaurs and More
The Mesozoic era, often referred to as the “Age of Reptiles,” witnessed the spectacular rise of diapsids to ecological supremacy. Dinosaurs, perhaps the most iconic diapsids, ruled the land with unmatched might. From the towering Tyrannosaurus rex to the long-necked Brachiosaurus, these creatures showcased the incredible adaptability and diversity within the diapsid lineage.
But diapsids weren’t confined to land. The skies welcomed the majestic Pterosaurs, a group of flying diapsids that ruled the aerial domain. With their wingspans rivaling small airplanes, these creatures demonstrated the boundless possibilities of evolutionary innovation.
A Glimpse Into Modern Diapsids
The legacy of diapsids lives on in the modern world. Two prominent groups stand as testaments to their enduring success: reptiles and birds.
Reptiles: A Varied and Tenacious Group
Modern reptiles, including lizards, snakes, crocodiles, and turtles, represent the continuation of the diapsid lineage. These animals have adapted to diverse environments, from scorching deserts to lush rainforests. Their scales, efficient lungs, and ectothermic metabolisms are all hallmarks of the reptilian legacy.
Birds: The Avian Innovators
Among the most remarkable living diapsids are birds. Evolving from theropod dinosaurs, birds conquered the skies through the refinement of feathers and the development of hollow bones. From the acrobatic hummingbird to the regal eagle, avian diversity showcases the enduring success of diapsids in adapting to changing environments.
Unveiling the Synapsid Saga: A Deeper Understanding
Synapsids, with their single pair of temporal fenestrae, have a tale of resilience and adaptation that led to the emergence of mammals. Let’s journey into the synapsid saga and uncover their pivotal role in shaping the course of life on Earth.
Pioneering the Path to Mammals
The synapsid story begins around the same time as the emergence of diapsids, roughly 300 million years ago during the Late Carboniferous period. These early synapsids, often resembling modern-day reptiles, paved the way for a transformation that would ultimately lead to the rise of mammals.
Permian Triumph: Diversification and Dominance
The Permian period marked a significant turning point for synapsids. A diverse range of forms emerged, from small, insectivorous species to large, apex predators. One of the most notable groups was the therapsids, which exhibited advanced traits such as erect limbs positioned beneath the body—a feature associated with the efficient locomotion of mammals.
The Triumph of Mammals
The story of synapsids reaches its climax with the triumphant rise of mammals, a group that would come to dominate diverse ecosystems across the globe. Mammals possess a unique set of traits that set them apart from other vertebrates:
- Hair: Mammals are characterized by the presence of hair or fur on their bodies, which serves various functions, including insulation and camouflage.
- Mammary Glands: These glands, present in females, produce milk to nourish their young—a defining feature of mammals.
- Endothermy: Unlike reptiles, mammals are endothermic, meaning they can regulate their body temperature internally, allowing them to thrive in a range of environments.
From Solitary Nocturnals to Diurnal Wonders
Mammals diversified rapidly, occupying a wide range of ecological niches. Some early mammals were likely solitary and nocturnal, utilizing their keen senses and adaptations for low-light conditions. As time went on, mammals evolved into diurnal creatures, exploiting the opportunities presented by daylight.
Anatomical Distinctions: A Closer Examination
Diapsids: Double the Fenestrae, Double the Power
Diapsids are renowned for their unique skull structure, boasting not one, but two pairs of temporal fenestrae. These fenestrae, openings in the skull, serve as anchor points for robust jaw muscles, giving diapsids exceptional biting strength. Let’s explore the significance of each pair:
- Supratemporal Fenestrae: Positioned on the upper portion of the skull, the supratemporal fenestrae accommodate powerful jaw muscles. This feature allowed diapsids to develop formidable bites, crucial for hunting and survival.
- Infratemporal Fenestrae: Located beneath the supratemporal fenestrae, these openings provide additional space for jaw muscle attachment. The combination of both fenestrae sets diapsids apart, enabling them to excel in diverse ecological roles.
Synapsids: A Singular Fenestra Leading to Mammalian Marvels
In stark contrast, synapsids possess a single pair of temporal fenestrae. This lone opening, situated on either side of the skull, has played a pivotal role in their evolutionary journey. The synapsid fenestra is associated with the jaw joint, illustrating the transition toward adaptations that would eventually lead to the emergence of mammals.
Traversing the Eras: Diapsid and Synapsid Evolution
Diapsid Evolution: The Mesozoic Marvels
The emergence of diapsids occurred around 300 million years ago, during the Late Carboniferous period. This marked the beginning of their remarkable journey, which would culminate in the domination of the Mesozoic era—the “Age of Reptiles.” Diapsids radiated into a plethora of species, each uniquely adapted to their environments. Some notable epochs in diapsid evolution include:
- Triassic Period: Diapsids continued to diversify, with archosaurs (a subgroup of diapsids) giving rise to early crocodilians and the ancestors of dinosaurs and birds.
- Jurassic Period: Dinosaurs, the most celebrated diapsids, evolved into a wide array of forms, from swift predators like Velociraptors to colossal herbivores like the Brachiosaurus.
- Cretaceous Period: This era witnessed the peak of dinosaur diversity, with species like Tyrannosaurus rex and Triceratops capturing the imagination of people worldwide.
Synapsid Evolution: Pioneering Mammalian Traits
Around the same time as diapsids, synapsids emerged during the Late Carboniferous period. These early synapsids resembled reptiles, but their unique fenestra set them on a transformative path. Synapsids, particularly the therapsids, thrived during the Permian period, showcasing traits that foreshadowed the rise of mammals:
- Erect Limbs: Many therapsids had limbs positioned beneath their bodies, allowing for more efficient movement. This feature was a crucial step toward the quadrupedal locomotion seen in mammals.
- Diverse Niches: Synapsids occupied a wide range of ecological roles, from small insectivores to apex predators, adapting to a variety of environments.
The Flourishing Present: Modern Diapsids and Synapsids
Diapsids Today: A Legacy in Reptiles and Birds
The legacy of diapsids persists in modern times through two primary branches: reptiles and birds.
- Reptiles: Lizards, snakes, crocodiles, and turtles are living descendants of diapsids. These creatures showcase the evolutionary adaptability of the group, each boasting unique features that enable them to thrive in their respective habitats.
- Birds: Among the most remarkable diapsids are birds, which evolved from theropod dinosaurs. Their feathers, specialized respiratory systems, and hollow bones are testament to the evolutionary innovations that diapsids brought to the world.
Synapsids Today: The Reign of Mammals
The triumph of synapsids culminated in the rise of mammals, a group that dominates terrestrial ecosystems today. Mammals exhibit a remarkable array of adaptations:
- Hair and Fur: Mammals are characterized by their hair or fur, which provides insulation, camouflage, and sensory functions.
- Mammary Glands: A defining trait, mammary glands produce milk to nourish young offspring, fostering strong parent-offspring relationships.
- Endothermy: Mammals are warm-blooded, enabling them to maintain a constant body temperature and thrive in various environments.
FAQs
Diapsids and Synapsids are two distinct groups of vertebrates that showcase different skull structures and evolutionary histories. Diapsids have two pairs of temporal fenestrae on each side of their skulls, while Synapsids possess a single pair of these openings.
Diapsids have two pairs of temporal fenestrae: supratemporal and infratemporal. These fenestrae provide anchoring points for powerful jaw muscles. In contrast, Synapsids have a single pair of temporal fenestrae linked to the jaw joint, reflecting their evolutionary path toward mammals.
The skull structure differences between Diapsids and Synapsids have shaped their evolutionary trajectories. Diapsids gave rise to dinosaurs, reptiles, and birds, dominating the Mesozoic era. Synapsids, on the other hand, paved the way for mammals, thriving during the Permian and Triassic periods.
Diapsids diversified into an array of species, including the iconic dinosaurs and modern reptiles. Synapsids underwent adaptive radiation, with therapsids emerging as diverse species, setting the stage for the rise of mammals.
Diapsids are represented by modern birds and reptiles, such as lizards, snakes, and crocodiles. Synapsids are the ancestors of mammals, with today’s world featuring a diverse range of mammalian species, including dogs, cats, and humans.
The differences between Diapsids and Synapsids have contributed to the incredible diversity of life on Earth. They showcase the adaptability and innovation that evolution brings, resulting in the wide array of species and ecological niches we see today.
Diapsids emerged during the Late Carboniferous period and flourished during the Mesozoic era. Synapsids also appeared in the Late Carboniferous period, and their diversity peaked during the Permian and Triassic periods.
Diapsids and Synapsids provide crucial insights into the evolutionary processes that have shaped life on Earth. Their distinct features and evolutionary pathways offer a glimpse into the transitions and adaptations that have occurred over millions of years.
For a deeper dive into the captivating world of Diapsids vs. Synapsids, explore reputable scientific sources, paleontological research, and educational materials that delve into vertebrate evolution and biodiversity.
Read More:
Contents
- Differences Between Diapsid and Synapsid
- The Basics: Diapsids and Synapsids
- Head to Head: Comparative Differences
- The Evolutionary Odyssey of Diapsids
- A Glimpse Into Modern Diapsids
- Unveiling the Synapsid Saga: A Deeper Understanding
- Permian Triumph: Diversification and Dominance
- Anatomical Distinctions: A Closer Examination
- Traversing the Eras: Diapsid and Synapsid Evolution
- The Flourishing Present: Modern Diapsids and Synapsids
- FAQs