Biology Science Nature
Welcome to our comprehensive category page dedicated to the intriguing subject of differences in biology, science, and nature! Here, we delve into the captivating realm of variations and distinctions that exist within these fields, shedding light on diverse terms, concepts, and other fascinating elements. Whether you’re a biology enthusiast, a science lover, or simply curious about the wonders of nature, this collection of content will leave you amazed and enlightened.
-

Difference Between Peas and Beans
In the culinary arena, the distinction between beans and peas extends beyond their appearances to encompass a rich tapestry of flavors, nutritional content, and culinary applications. While beans, nestled under the Phaseolus genus, showcase an array of types like kidney, black, and chickpeas, peas, a proud member of the Pisum genus, come in variations like green, split, and sugar snap peas. The nutritional divergence is notable; beans, celebrated for their protein and fiber abundance, stand as dietary powerhouses, whereas peas, with their sweet undertones, offer a lighter yet equally nutritious alternative. The versatility of beans is evident in their role across diverse global cuisines, from hearty Latin American stews to Mediterranean hummus. Conversely, peas, with their delicate sweetness, grace salads, soups, and sides, providing a burst of flavor. As you navigate the intricate world of legumes, understanding these distinctions will not only elevate your culinary expertise but also empower you to make mindful choices in crafting nutritious and delightful meals. Join us on this gastronomic journey as we unravel the nuanced differences between beans and peas, unlocking the secrets behind these culinary companions.
-

Difference Between Beans and Legumes
Dive into the intricate world of legumes vs beans as we decipher the fascinating tapestry of botanical distinctions, culinary nuances, and nutritional benefits. Legumes, a diverse family within Fabaceae, boast an array of members like peas, lentils, and chickpeas. In contrast, beans carve their culinary niche as a subset of legumes, featuring varieties such as kidney beans and black beans within the Phaseolus genus. Discover the protein-rich prowess they share, with beans standing out for their lysine content, contributing to a well-rounded amino acid profile. Delve into the digestive dynamics, where soaking strategies and culinary techniques play a role in enhancing digestibility. Uncover the eco-friendly side, exploring how both legumes and beans contribute to sustainable agriculture. From the global culinary stage to individual dietary considerations, this guide navigates the complexities, inviting you to savor the flavors and make informed choices. Elevate your culinary wisdom as we unravel the distinctions between legumes and beans – a journey that goes beyond the kitchen, touching upon botanical wonders and sustainable living.
-

Difference Between Animal Hair and Human
The comparison between human and animal hair delves into a realm where science meets aesthetics, and functionality blends with cultural significance. Human hair, with its multi-layered structure, undergoes a meticulously orchestrated growth cycle that produces a rainbow of colors. Beyond its cosmetic allure, human hair serves as a sensory organ, a protector against UV radiation, and a canvas for personal expression. On the other side of this follicular coin lies animal hair, a world teeming with diversity. From the lustrous coats of domesticated pets to the insulating fur of wild creatures, animal hair adapts to a myriad of functions. Camouflage, communication, and insulation are just a few roles it plays in the survival and behavior of different species. As we explore these distinctions, we unravel the mysteries of hair's composition, the evolution of its role in our lives, and its ever-evolving place in culture. Whether you're curious about the science behind hair, interested in caring for your own tresses, or pondering the ethics of fur in fashion, the differences between human and animal hair provide a captivating journey through the interconnected realms of biology, culture, and individuality. Join us as we unveil the enchanting tapestry of these hair disparities, unlocking the secrets of what makes each strand unique.
-

Difference Between Myosin and Actin
Actin and Myosin, two pivotal proteins within our cells, are the dynamic duo behind muscle contraction, cellular motility, and a host of other vital functions. Actin, often described as the "thin filament," serves as the structural backbone, participating in cell shape maintenance, immune cell migration, and even the elegant process of cytokinesis. On the other hand, Myosin, the "thick filament," emerges as the energy powerhouse, orchestrating the mechanical force required for muscle contraction and driving the movement of cells and their internal cargo. Intriguingly, Actin and Myosin are not confined to muscle cells; they play integral roles in non-muscle cells, influence our cardiac health, and even contribute to the aging process. Furthermore, these proteins have sparked interest in the realm of drug development, particularly in the context of cardiac medications. Join us on a captivating journey as we unveil the multifaceted world of Actin and Myosin, providing insights into their structural disparities, functions, and their wide-ranging impact on biology, medicine, and beyond.
-

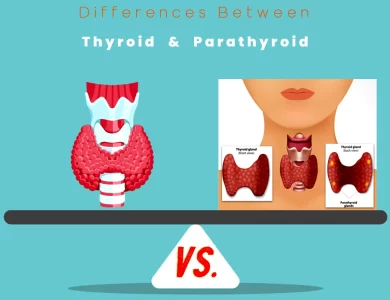
Difference Between Parathyroid and Thyroid
In the world of human anatomy, certain pairs of organs or glands can be confusingly similar in name yet distinctly different in function. Two such glands that often lead to head-scratching moments are the thyroid and parathyroid. Positioned in the neck, these vital endocrine glands play pivotal roles in maintaining overall health, but they do so in unique and divergent ways. Let's embark on a journey to uncover the key disparities between the thyroid and parathyroid, shedding light on their functions, locations, and the profound implications they have on our well-being. The thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped structure positioned in the front of the neck, is the body's metabolic control center. It regulates our metabolic rate, energy expenditure, and even our body temperature. Producing hormones like thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), the thyroid orchestrates the symphony of bodily processes that keep us going. On the contrary, the parathyroid glands, four small but mighty companions, reside on the posterior surface of the thyroid and focus their efforts on maintaining the delicate balance of calcium in our bloodstream. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) is their tool of choice, ensuring that calcium levels remain within the narrow window required for optimal health. The distinctions between these glands don't end with function and location; they extend to their regulation, development, and even surgical considerations. Understanding the differences between the thyroid and parathyroid is more than a mere exercise in anatomy; it's a journey toward comprehending the intricacies of our body's endocrine system. So, read on to grasp why these differences matter and how they influence your health and well-being.
-

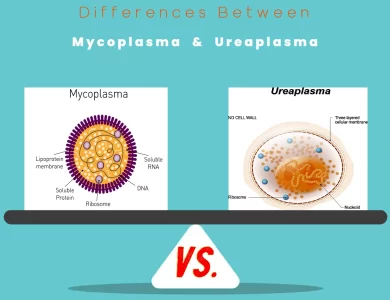
Ureaplasma vs Mycoplasma
In the microscopic realm of bacteria, two intriguing genera, Mycoplasma and Ureaplasma, hold a world of differences that often go unnoticed. Mycoplasma, often referred to as "nature's minimalists," and Ureaplasma, the urea metabolizers, share a common thread – both lack a peptidoglycan cell wall, setting them apart from most other bacteria. Their small size, ranging from 0.2 to 0.8 µm in Mycoplasma and 0.15 to 0.3 µm in Ureaplasma, makes them barely visible to the naked eye. However, it's their unique metabolic capabilities that truly differentiate them. Mycoplasma, despite its small size, cannot metabolize urea, while Ureaplasma is known for its ability to break down urea, producing ammonia as a byproduct. These bacteria also diverge in terms of their ecological niches. Mycoplasma showcases versatility, thriving in environments as diverse as soil, plants, and various animal hosts. In contrast, Ureaplasma primarily colonizes the urogenital tract of humans. Their pathogenic potential further separates them, with some Mycoplasma species causing a range of diseases in humans and animals, while certain Ureaplasma strains are associated with urinary and reproductive infections. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for discerning the roles Mycoplasma and Ureaplasma play in the intricate world of microorganisms. Explore the intricate details of these microbial marvels to grasp their significance in the grand tapestry of microbiology.
-

Chlamydia vs Mycoplasma
In the microscopic realm of infectious agents, Mycoplasma and Chlamydia stand as distinct genera, each with its unique characteristics and impacts on health. "Mycoplasma vs Chlamydia" is a captivating exploration of these microorganisms, delving into the nuances that set them apart. One of the most striking differences lies in their cell walls: Mycoplasma flaunts their minimalistic approach, being devoid of a cell wall, while Chlamydia sports an atypical one. This divergence influences not only their structural integrity but also their response to antibiotics. Beyond the cellular disparities, their genomes paint a vivid contrast. Mycoplasma boasts one of the smallest genomes among cellular life forms, whereas Chlamydia wields a larger and more complex genetic blueprint. These distinctions have significant implications for their nutritional requirements, host tissue preferences, and roles in diseases. Furthermore, the unique reproductive strategies of Mycoplasma through binary fission and Chlamydia's alternation between elementary and reticulate bodies add layers to their differences. Understanding these dissimilarities is paramount, as it affects diagnosis, treatment, and public health. While Mycoplasma infections can lead to outbreaks and respiratory issues, Chlamydia poses a substantial public health challenge as a leading cause of sexually transmitted infections. This exploration takes you on a journey to grasp the captivating "Differences Between Mycoplasma vs Chlamydia," revealing the microbial intricacies that shape the health landscape.
-

Serratia Marcescens vs E. Coli
In the realm of microbiology, the distinctions between bacterial species can be as intriguing as they are vital. This exploration focuses on two remarkable organisms: E. coli and Serratia marcescens. While they might share a few similarities at first glance, a closer examination reveals a world of differences that influence their roles in our ecosystem and health. E. coli, formally known as Escherichia coli, is a versatile bacterium frequently found in the human gut, forming part of our intestinal microbiota. Its taxonomy places it in the Enterobacteriaceae family, and it serves both beneficial and pathogenic roles in human health. Some E. coli strains are notorious for causing foodborne illnesses and extraintestinal infections. In contrast, Serratia marcescens resides in non-human environments, with a penchant for soil, water, and decaying matter. It's part of the Yersiniaceae family and is often recognized for its distinctive red pigment. This opportunistic pathogen can cause infections, primarily in healthcare settings. Understanding the unique characteristics and roles of these bacteria is essential for microbiologists, healthcare professionals, and anyone intrigued by the world of microorganisms. Join us on this journey as we uncover the fascinating differences between E. coli and Serratia marcescens, shedding light on their taxonomy, ecological niches, pathogenicity, and their contributions to biotechnology and medicine.
-

Pseudomonas Aeruginosa vs E. Coli
In the intricate world of microbiology, where life's tiniest architects wield immense influence, two bacterial species, Escherichia coli (E. coli) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, stand as distinct entities, each with its unique characteristics and roles. Understanding the contrasts between these microscopic powerhouses not only reveals the remarkable diversity of the microbial realm but also sheds light on their significance in human health, genetics, and environmental processes. E. coli, a member of the Enterobacteriaceae family, predominantly finds its niche in the human gastrointestinal tract, playing a dual role as a commensal bacterium and a potential pathogen. On the other hand, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, belonging to the Pseudomonadaceae family, thrives in a much wider array of environments, encompassing soil, water, and even the respiratory tracts of individuals with weakened immune defenses. These contrasting habitats give rise to diverse metabolic strategies, with E. coli being a facultative anaerobe with a knack for utilizing sugars and organic compounds, while Pseudomonas aeruginosa exhibits remarkable adaptability and metabolic diversity, particularly in the breakdown of complex molecules like hydrocarbons. As we embark on this journey of exploration, you'll delve into their genetic intricacies, antibiotic resistance, virulence factors, and roles in various ecosystems. By the end of this journey, you'll have gained a profound appreciation for the differences that make E. coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa such influential players in the captivating world of microbiology.
-

Klebsiella vs E. Coli
In the microscopic world of bacteria, two prominent players often make their appearances – Escherichia coli, fondly known as E. coli, and Klebsiella. These two members of the Enterobacteriaceae family, while belonging to the same bacterial clan, exhibit striking differences that have far-reaching implications in the fields of microbiology and healthcare. Taxonomic Cousins At the core of their dissimilarity lies their taxonomy. E. coli and Klebsiella are both part of the Enterobacteriaceae family and reside in the Proteobacteria phylum. However, their distinct morphological features set them apart. E. coli appears as a rod-shaped, gram-negative bacterium with a single flagellum, while Klebsiella boasts a unique encapsulated structure, making it particularly effective in evading the host's immune system. Pathogenic Profiles The realm of pathogenicity is where these two bacteria truly diverge. E. coli demonstrates a wide spectrum of strains, some of which are benign residents of the human gut, while others can be responsible for various illnesses, ranging from traveler's diarrhea to severe complications like hemolytic uremic syndrome. In contrast, Klebsiella often takes on the role of an opportunistic pathogen, lurking in healthcare settings and causing infections such as pneumonia and urinary tract infections. Its encapsulated form is a formidable asset in this context, as it shields the bacterium from the host's defenses. Antimicrobial Resistance When it comes to antimicrobial resistance, both E. coli and Klebsiella are seasoned contenders. E. coli is known for its adaptability, thanks to plasmids that can carry resistance genes, making it resilient against antibiotics like ampicillin and tetracycline. Klebsiella, however, raises the stakes with its resistance to carbapenem antibiotics, a concerning trait, especially in healthcare-associated infections where treatment options can be limited. Habitats and Clinical Significance Understanding the habitats these bacteria prefer and their clinical significance is essential. E. coli is a versatile inhabitant, residing in the…