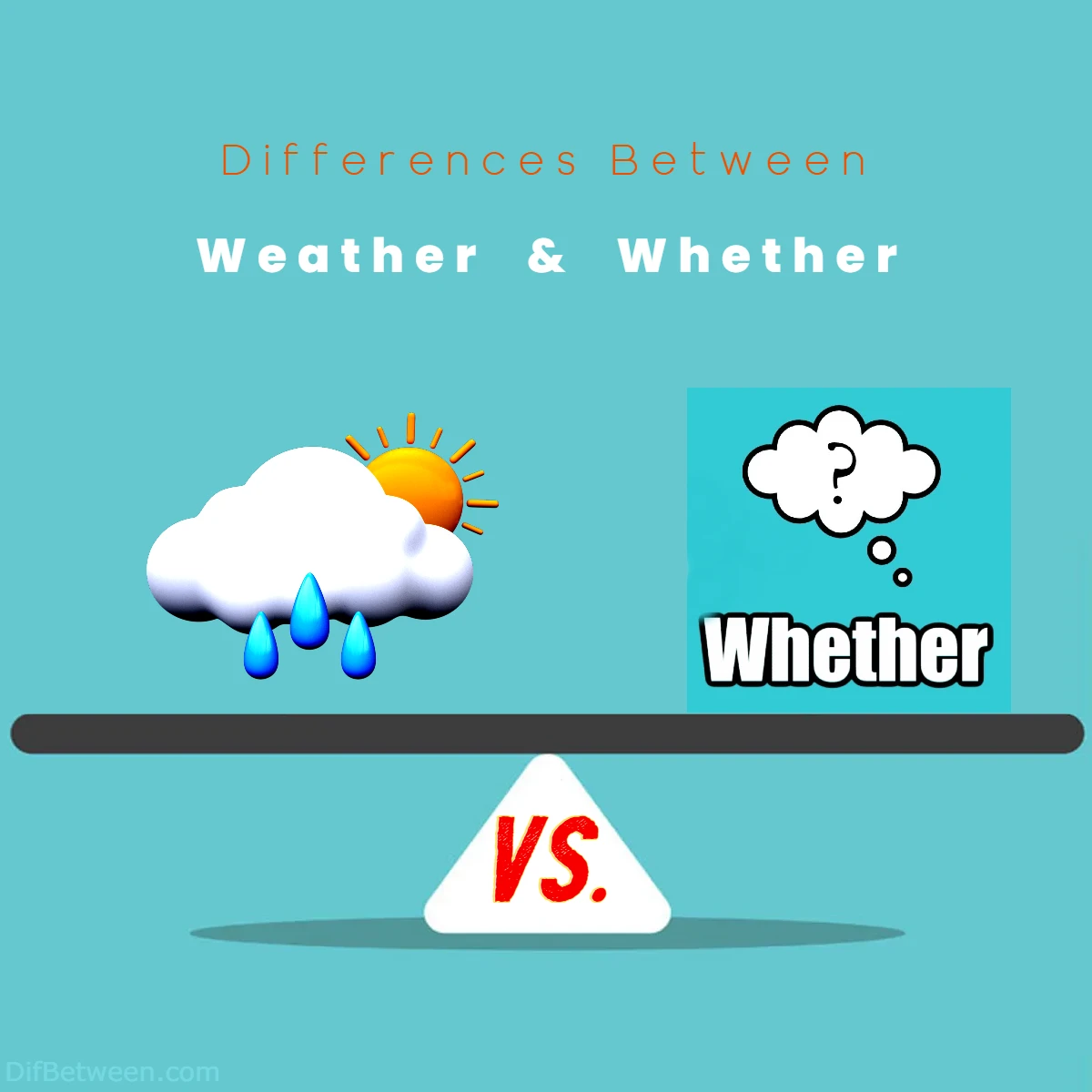
| Aspect | Weather | Whether |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Atmospheric conditions | Introduces choices or conditions |
| Usage | Describe weather-related conditions | Present alternatives, doubt, or uncertainty |
| Context | Weather reports, daily conversations, environment descriptions | Conditional sentences, indirect questions, choices |
| Pronunciation | /ˈwɛðər/ | /ˈwɛðər/ |
| Regional Variations | Pronunciation may vary slightly in different English dialects | Pronunciation may vary slightly in different English dialects |
| Synonyms/Alternatives | Climate, atmosphere | If, dilemma |
| Common Phrases | “Under the weather” (idiom) | “Weather permitting” (phrase) |
| Distinctive Traits | Pertains to atmospheric conditions, often involves small talk or reports | Introduces conditional statements, alternatives, or choices |
Language is a complex tapestry of words, each thread meticulously woven to convey specific meanings and nuances. In this exploration, we’ll dissect the essence of “weather” and “whether,” unraveling their definitions and unveiling their unique roles in the grand tapestry of English.
Differences Between Weather and Whether
The main differences between “Weather” and “Whether” lie in their meanings and usage. “Weather” pertains to atmospheric conditions and is commonly used in weather reports and everyday conversations to describe the state of the environment. In contrast, “Whether” is a conjunction that introduces choices or conditions, often followed by an “or” clause, and is employed to express uncertainty, doubt, or decision-making scenarios. These distinctions make it crucial to use the right word in context, ensuring clear and effective communication.
The Basics
Before we delve into the differences, let’s establish a clear understanding of what “weather” and “whether” actually mean.
Weather
Weather refers to the atmospheric conditions in a specific place at a specific time. It encompasses various elements such as temperature, precipitation, wind, humidity, and visibility. Weather can change from day to day and even hour to hour, making it a common topic of conversation and an essential aspect of our daily lives.
Here’s a simple example of “weather” in a sentence:
The weather forecast predicts rain for tomorrow.
In this context, “weather” is used to describe the atmospheric conditions, specifically the prediction of rain.
Whether
Whether, on the other hand, is a conjunction used to introduce a choice or alternative possibilities. It is often used to express doubt, uncertainty, or a condition where one thing depends on another. “Whether” is typically followed by an “or” clause, indicating a decision between two or more options.
Consider this example:
I can’t decide whether to have pizza or sushi for dinner.
In this sentence, “whether” introduces the choice between pizza and sushi, reflecting a decision-making process.
Now that we’ve clarified the basic definitions, let’s dive deeper into the distinctions between these two words.
Usage Differences
One of the most significant differences between “weather” and “whether” lies in their usage. Understanding how and when to use each word correctly is crucial for effective communication.
Usage of “Weather”
“Weather” is primarily used to discuss atmospheric conditions or describe the state of the atmosphere at a particular time and place. It can be used in various contexts, including daily conversations, weather reports, and descriptions of the environment.
Here are some common ways “weather” is used:
- Weather Descriptions: To talk about the current atmospheric conditions or forecasts.The weather today is sunny and warm.
- Small Talk: As a conversation starter or filler.Nice weather we’re having, isn’t it?
- Weather Reports: In news reports, radio broadcasts, or weather apps to provide information on upcoming conditions.The weather forecast predicts snowfall later this evening.
- Setting the Scene: In literature or storytelling to create atmosphere.The dark and stormy weather outside matched the protagonist’s mood.
Usage of “Whether”
“Whether,” on the other hand, is used to introduce conditional statements or choices. It is typically followed by an “or” clause and is employed when there is uncertainty or a need to make a decision.
Here are common ways “whether” is used:
- Conditional Statements: To introduce a condition with two or more possible outcomes.I’m unsure whether I should accept the job offer or continue searching for other opportunities.
- Choice and Alternatives: When presenting options or alternatives.Let’s discuss whether to go to the beach or explore the mountains for our vacation.
- Doubt and Uncertainty: To express uncertainty or doubt.She’s uncertain whether the meeting will be rescheduled.
- Indirect Questions: In place of “if” when forming indirect questions.I wonder whether she has completed the project.
Now that we’ve explored the usage differences between “weather” and “whether,” let’s summarize them in a table for quick reference:
| Aspect | Weather | Whether |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Atmospheric conditions | Introduces choices |
| Usage | Describe weather-related | Conditional statements |
| conditions | Doubt and uncertainty | |
| Small talk and weather | Choice and alternatives | |
| reports | Indirect questions |
Pronunciation and Spelling
While “weather” and “whether” may look similar in writing, their pronunciation and spelling are distinct. Understanding these differences can help you avoid common spelling and pronunciation errors.
Pronunciation of “Weather”
“Weather” is pronounced as /ˈwɛðər/ with two syllables. The initial “w” is pronounced as a voiced labiodental fricative, similar to the sound in “wet.” The “ea” in “weather” is pronounced as a long “e” sound, as in “beet.” The final “er” is pronounced as a schwa sound, which is a neutral, unstressed vowel sound.
Pronunciation of “Whether”
“Whether” is pronounced as /ˈwɛðər/ with two syllables, just like “weather.” The pronunciation of “whether” is identical to that of “weather,” which adds to the confusion between the two words. However, their meanings and usage set them apart.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even though “weather” and “whether” have distinct meanings and uses, they are often confused in writing due to their similar pronunciation. Here are some common mistakes to watch out for:
- Spelling Errors: Confusing the spelling of “weather” with “whether” or vice versa. Careful proofreading can help prevent this mistake.Incorrect: I can’t decide on the weathers we should go to the beach. Correct: I can’t decide on whether we should go to the beach.
- Misplaced Words: Using “whether” when “weather” is appropriate and vice versa. Double-check the context to ensure you’re using the right word.Incorrect: The whether today is sunny. Correct: The weather today is sunny.
- Pronunciation: Mispronouncing “weather” or “whether” can lead to misunderstandings. Be mindful of their correct pronunciation.Incorrect: I heard the wether forecast. Correct: I heard the weather forecast.
How to Remember the Difference
To avoid mixing up “weather” and “whether,” you can use some mnemonics or memory aids. Here are a few tips to help you remember the distinction between these words:
- Weather Is About the Atmosphere: Remember that “weather” is related to the atmospheric conditions and has an “atmosphere” in it. This can help you associate it with meteorological topics.
- Whether Offers a Choice: Think of “whether” as introducing options or choices, as it often comes with an “or” clause. The word “whether” itself contains the word “whether,” which can serve as a reminder of choice.
- Visualize the Spellings: Visual learners can benefit from picturing the words in their mind. Imagine a sunny day with clear “weather” and visualize a fork in the road when thinking about “whether” as a choice.
Advanced Usage: Idioms and Phrases
Beyond their basic meanings and usage, “weather” and “whether” also appear in various idiomatic expressions and phrases. Let’s explore some of these expressions to broaden your understanding of these words.
Idioms with “Weather”
- Under the Weather: This idiom means to feel unwell or slightly sick. It is often used when someone is not in their best physical condition.I’m feeling a bit under the weather today, so I’ll stay home.
- Weather the Storm: To endure difficulties or challenges without giving up. This phrase is often used in a metaphorical sense.Despite facing setbacks, they managed to weather the storm and succeed in their business.
Idioms with “Whether”
- Whether or Not: This is a common phrase used to emphasize that a decision or action is not dependent on specific conditions. It implies that the choice is entirely up to the individual.I will attend the party whether or not it rains.
- Whether You Like It or Not: This phrase is used to convey that a situation or decision is inevitable, whether someone approves of it or not.The changes in the company are happening whether you like it or not.
Regional Variations
The English language is incredibly diverse, with regional variations in pronunciation, vocabulary, and even grammar. Interestingly, the differences between “weather” and “whether” are not immune to these regional quirks. While the basic meanings and usages remain consistent, the way these words are pronounced can vary from one English-speaking region to another.
British English
In British English, both “weather” and “whether” are typically pronounced with a clearer distinction between the two words. “Weather” is often pronounced as /ˈwɛðə/, and “whether” is pronounced as /ˈwɛðə/. The British accent tends to emphasize the “th” sound more distinctly.
American English
In American English, the pronunciation of “weather” and “whether” can sometimes be more similar due to the flattening of certain vowel sounds. Both words may be pronounced as /ˈwɛðə/ in some American dialects. However, in formal American English, a clearer distinction is maintained, with “weather” pronounced as /ˈwɛðər/ and “whether” as /ˈwɛðər/.
Remember that these regional differences are not strict rules but rather variations influenced by accent and dialect. It’s essential to understand the meaning and usage of the words in context, regardless of regional pronunciation.
Complex Sentences and Clauses
To truly master the use of “weather” and “whether,” it’s essential to be comfortable with complex sentence structures and clauses. Both words can appear in a variety of sentence types, including conditional sentences, indirect questions, and embedded clauses.
Conditional Sentences
Conditional sentences are a common context for using “whether.” They express a condition and its possible consequences or alternatives. The structure often involves an “if” clause.
Examples:
- I’ll go to the park whether it’s sunny or rainy.
- She couldn’t decide whether to call him or send a text.
Indirect Questions
“Whether” is frequently used in indirect questions, where it takes the place of “if” when forming a question.
Examples:
- I wonder whether she has finished her homework.
- He’s uncertain whether they will arrive on time.
Embedded Clauses
In more complex sentences, you might encounter embedded clauses where “whether” introduces a subordinate clause within the main sentence.
Example:
- She was undecided, pondering whether her decision would impact her future.
These examples demonstrate the versatility of “whether” in constructing sentences that involve choices, conditions, and uncertainty.
Synonyms and Alternatives
In some cases, you may find synonyms or alternative words that can replace “weather” or “whether” in certain contexts. While these alternatives may not be direct replacements, they can help you express similar ideas in different ways.
Synonyms for “Weather”
- Climate: Refers to the typical weather conditions in a particular region. The climate in this area is quite tropical.
- Atmosphere: Can be used in a metaphorical sense to describe the overall feeling or mood of a place or situation. There was a tense atmosphere in the room.
Synonyms for “Whether”
- If: The word “if” is often used interchangeably with “whether” in many contexts. I’m unsure if I should attend the conference.
- Dilemma: This term is used to describe a difficult choice or decision. She faced a dilemma when choosing between the two job offers.
Commonly Confused Phrases
In addition to the words “weather” and “whether” themselves, there are some phrases that can lead to confusion due to their similar-sounding components. Let’s explore a few of these phrases:
“Weather Permitting”
The phrase “weather permitting” is used to indicate that an event or activity is subject to favorable weather conditions. It often appears in event announcements or plans.
Example:
- The outdoor concert will take place in the park, weather permitting.
“Whether or Not”
As mentioned earlier, “whether or not” is a phrase used to emphasize that a decision is not dependent on specific conditions. It’s worth noting that the inclusion of “or not” is optional, and “whether” alone suffices in most cases.
Examples:
- I will attend the meeting, whether or not I receive the agenda in advance.
- I will attend the meeting, whether I receive the agenda in advance.
Conclusion
Navigating the distinctions between “weather” and “whether” may seem like a linguistic puzzle at times, but with practice and a deeper understanding of their meanings and contexts, you can confidently incorporate these words into your writing and conversation. Remember that while these two words may share similar pronunciation, their roles in language are as distinct as sunny skies and tough decisions. So, whether you’re discussing the weather forecast or pondering whether to use “weather” or “whether” correctly, you’re now equipped with the knowledge to do so with ease and precision.
FAQs
The primary difference is in their meanings and usage. “Weather” refers to atmospheric conditions like rain or sunshine, while “whether” is a conjunction used to introduce choices, conditions, or alternatives.
Certainly! Here’s an example: “The weather forecast predicts thunderstorms for tomorrow.”
“Whether” is often used in conditional sentences to introduce a condition with two or more possible outcomes. For instance: “I’m undecided about whether to go to the party or stay home.”
Yes, there can be slight regional variations in pronunciation, particularly in British and American English, but the fundamental differences in meaning and usage remain consistent.
Yes, “whether” is frequently used to convey doubt or uncertainty. For example: “She’s unsure whether the flight will be delayed.”
Yes, phrases like “under the weather” (meaning feeling unwell) and “weather permitting” (indicating an event depends on weather conditions) involve the word “weather.” “Whether or not” is a common phrase with “whether,” emphasizing a decision not dependent on specific conditions.
To remember, associate “weather” with atmospheric conditions and “whether” with choices. Visual cues and practicing their usage in sentences can also be helpful.
The key takeaway is to understand their distinct meanings and contexts. “Weather” relates to the environment, while “whether” introduces choices and conditions. Using the right word ensures effective communication.
Read More:
Contents






