-
Polymer Chemistry

Polymer vs Resin
In the realm of materials science, the choice between resin and polymer can significantly impact the success of a project. While these terms are sometimes used interchangeably, they refer to distinct classes of materials with unique characteristics and applications. Resin encompasses a diverse range of materials, including both natural and synthetic compounds. What sets resins apart is their adhesive nature and versatility in coatings and encapsulation. They can be found in everything from woodworking adhesives to the protective coatings on your smartphone screen. Resins are often praised for their chemical resistance and thermal stability, making them valuable in various industrial settings. Polymers, on the other hand, are a more extensive category of materials characterized by the repetition of monomer units. This repeating structure grants polymers their remarkable diversity, from everyday plastics like polyethylene to high-strength composites used in aerospace. Polymers excel in applications where flexibility, lightweight properties, and elasticity are crucial. Intriguingly, some polymers can also function as resins when adhesive or coating properties are required, blurring the lines between these two material classes. Therefore, understanding their differences is paramount in selecting the right material for specific tasks, whether it's crafting artful creations or engineering cutting-edge technologies.
-
Cookery

Boil vs Simmer
When it comes to the art of cooking, mastering the nuances of simmering and boiling can make all the difference in your culinary creations. These two seemingly similar techniques, with just a slight difference in temperature and intensity, can lead to entirely distinct outcomes on your plate. Simmering is a gentle cooking method that operates at a temperature range of 180°F to 205°F (82°C to 96°C). It's characterized by small, delicate bubbles dancing on the surface of the liquid. This low and slow approach is ideal for dishes that require tenderness and the development of intricate flavors. Think of simmering as your go-to technique for crafting hearty stews, tender braised meats, and delicately poached eggs. Boiling, on the other hand, is a more vigorous process, reaching the boiling point at 212°F (100°C). Here, you'll encounter the unmistakable sight of large, rolling bubbles. Boiling is your go-to method for rapid cooking, making it perfect for quickly blanching vegetables to preserve their vibrant colors or preparing pasta to that coveted "al dente" perfection. It's also the technique of choice when you need to sterilize equipment or reduce liquids swiftly to create concentrated sauces and syrups. Understanding when to use simmering vs. boiling can transform your culinary endeavors. Simmering lends itself to dishes that require patience and flavor development, while boiling shines in scenarios where speed and efficiency are key. So, whether you're simmering a soul-warming stew or boiling pasta for a quick weeknight dinner, mastering these techniques will undoubtedly elevate your culinary prowess.
-
Foods & Drinks

High Fructose Corn Syrup vs Corn Syrup
In the world of sweeteners, the distinctions between corn syrup and high fructose corn syrup (HFCS) can be as puzzling as they are sweet. These two sugary substances, both derived from corn, are staples in the food industry and are often found in our favorite recipes. However, understanding the nuances between them is crucial, whether you're a culinary enthusiast or someone striving for healthier dietary choices. Corn Syrup: Corn syrup is primarily composed of glucose molecules, making it a glucose syrup with minimal to no fructose content, typically less than 1%. This characteristic sets it apart from its sweeter counterpart, HFCS. Its mild sweetness and unique properties make it a beloved ingredient in various culinary applications. You'll often encounter corn syrup in the confectionery world, where it plays a crucial role in preventing sugar crystallization, enhancing texture, and contributing to the smoothness of many delightful treats. High Fructose Corn Syrup (HFCS): On the other side of the syrup spectrum is high fructose corn syrup (HFCS), which carries a more complex composition. HFCS contains a significant amount of fructose, along with glucose. Common variants include HFCS-42 (42% fructose) and HFCS-55 (55% fructose). This higher fructose content gives HFCS its notable sweetness, making it a popular choice for sweetening soft drinks, processed foods, and a plethora of convenience and snack items. While both corn syrup and HFCS have their roles in the culinary world, it's essential to consider your specific needs and health concerns when choosing between them. Whether you're baking a delectable dessert or carefully scrutinizing food labels, knowing the differences between these sweet syrups empowers you to make informed decisions for your palate and your well-being.
-
Raw Material foods

Yellow Cornmeal vs White
When it comes to cooking and baking, the choice between white and yellow cornmeal can make a significant difference in your culinary creations. These two cornmeal varieties may seem similar at first glance, but they have distinct characteristics that can impact the flavor, texture, and appearance of your dishes. In this exploration of white vs yellow cornmeal, we'll uncover the essential differences between these pantry staples, helping you make informed decisions in the kitchen. Color: The most obvious contrast between white and yellow cornmeal is their color. White cornmeal has a pale, almost ivory hue, while yellow cornmeal boasts a vibrant, golden-yellow shade. This color difference is not merely aesthetic; it can influence the visual appeal of your food and, in some cases, the overall flavor of your dishes. Flavor and Texture: White cornmeal offers a milder, more subtle corn flavor. Its fine texture makes it ideal for recipes like delicate cakes, pancakes, and certain types of cornbread. In contrast, yellow cornmeal has a bolder and more pronounced corn flavor, adding a robust corniness to dishes. Its coarser texture provides a satisfying crunch, making it perfect for recipes like cornbread and corn fritters. Culinary Adaptability: White cornmeal is versatile, working well in both sweet and savory dishes without dominating the flavor profile. Yellow cornmeal, on the other hand, is the go-to choice for recipes where a strong corn flavor is desired, such as Latin American and Mexican dishes like tamales, arepas, and corn tortillas. Understanding these distinctions allows you to choose the right cornmeal for your recipes, ensuring that your culinary creations turn out just the way you envision them. So, whether you're aiming for a neutral corn presence or a bold and hearty corn flavor, the choice between white and yellow cornmeal opens up a world of culinary possibilities…
-
Sports

MotoGP vs AMA
When it comes to the electrifying world of motorcycle racing, two premier championships, AMA and MotoGP, stand in the spotlight. While both offer heart-pounding action on two wheels, they are distinguished by a series of captivating differences. Let's take a closer look at what sets these two iconic competitions apart. Origins and Focus: AMA, or the American Motorcyclist Association, boasts deep American roots and serves as a governing body for motorcycle racing primarily within the United States. It encompasses a diverse array of racing disciplines, including motocross, supercross, flat track racing, and road racing. In contrast, MotoGP stands as the pinnacle of international motorcycle road racing. Originating in 1949 as the FIM Road Racing World Championship Grand Prix and later rebranded as MotoGP in 2002, this championship transcends borders, featuring riders and teams from around the world and placing an exclusive emphasis on road racing. Racing Format and Regulations: AMA's charm lies in its varied racing disciplines, which allow riders to showcase their skills across different terrains and formats. It features more lenient regulations, permitting manufacturers to experiment with modifications and innovations. On the other hand, MotoGP is synonymous with precision engineering, with a strict focus on road racing and highly sophisticated prototype motorcycles. The championship's technical regulations are stringent, emphasizing rider skill and strategy over machine modifications. International Appeal: While AMA primarily caters to a domestic audience with some international participation, MotoGP's global reach knows no bounds. With races held at iconic circuits worldwide, it has established itself as the ultimate stage for the best riders on the planet.
-
Polymer Chemistry

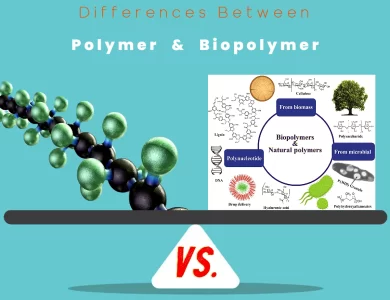
Biopolymer vs Polymer
In the ever-evolving realm of materials science, the distinction between polymers and biopolymers is a pivotal one. These substances, although related by name, possess vastly different characteristics, sources, and environmental impacts. Understanding these differences is not only essential for scientists and engineers but also for anyone interested in the sustainable future of our planet. Polymers, often synonymous with synthetic plastics, are derived from petrochemicals through intricate chemical processes. These versatile materials have become ubiquitous in our daily lives, finding applications in countless industries. From the plastic bottles that hold our beverages to the insulation in our homes, polymers are the workhorses of modern manufacturing. However, their dominance comes at a price - their environmental footprint. Many synthetic polymers are non-biodegradable, contributing to long-lasting pollution and resource depletion. Biopolymers, on the other hand, are the natural counterparts. These materials, as the name suggests, originate from living organisms. They include substances like cellulose, found in plant cell walls, and DNA, the genetic code of all life forms. What sets biopolymers apart is their sustainable nature. They are often derived from renewable biological sources and possess the remarkable ability to biodegrade, returning to the Earth without leaving a lasting mark. This eco-friendliness has fueled their adoption in various eco-conscious industries, such as biodegradable packaging and regenerative medicine. As we venture deeper into the realm of polymers and biopolymers, we'll uncover their composition, sources, properties, and applications. We'll also explore the environmental impact, recycling challenges, cost considerations, and regulatory aspects that shape these materials' roles in our world. Join us on this enlightening journey to grasp the "Differences Between Polymer vs Biopolymer" and their significance in the grand tapestry of materials science.
-
Agriculture

Horticulture vs Agriculture
Agriculture and horticulture, while both involving the cultivation of plants, are distinct fields with unique characteristics and contributions. Agriculture, with its broad scope, focuses on large-scale production of various crops, including staple foods like wheat and rice. In contrast, horticulture specializes in the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, herbs, flowers, and ornamental plants, with an emphasis on quality and diversity. The differences extend to their methods; agriculture often relies on modern machinery and synthetic chemicals for efficiency, while horticulture embraces sustainable and organic practices. These distinctions also manifest in their environmental impact, with agriculture occasionally having a more substantial footprint due to its scale. Despite these disparities, both agriculture and horticulture play crucial roles in our lives. Agriculture feeds the world's population, while horticulture enriches our diets, landscapes, and urban environments. This exploration of their differences sheds light on the intricate tapestry of plant cultivation, showcasing how these fields contribute to the food we eat, the environments we inhabit, and the beauty we enjoy.
-
Polymer Chemistry

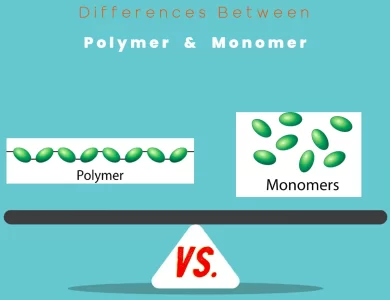
Monomer vs Polymer
Polymers and monomers may sound like scientific jargon, but they play pivotal roles in our daily lives. At their core, these terms encapsulate the fundamental building blocks of matter, with unique properties and applications. In our journey to comprehend the distinctions between polymers and monomers, we delve into their molecular structures, chemical properties, and real-world significance. Polymers, those long chains of repeating monomer units, are the unsung heroes of modernity. From the synthetic fibers in our clothes to the plastic containers that store our food, polymers are everywhere. They offer versatility that can be tailored to meet specific needs, making them the backbone of various industries. Monomers, on the other hand, are the precursors, the individual molecules that join together to form polymers. Think of them as the bricks in the construction of molecular architecture. While smaller in size, monomers wield precision and control in chemical synthesis, allowing scientists and engineers to craft materials with exacting specifications. In this guide, we explore the key differences between polymers and monomers, shedding light on their distinct roles in chemistry, industry, and our evolving understanding of materials. From their size and structure to their diverse applications and environmental impacts, we navigate the fascinating world of these chemical entities. Join us as we embark on an enlightening journey to unravel the mysteries of Polymer vs Monomer.
-
Martial Arts

Difference Between Kickboxing and Muay Thai
Muay Thai and Kickboxing are two of the most exhilarating and physically demanding striking combat sports globally, each offering a unique martial arts experience. In our exploration of the Differences Between Muay Thai vs Kickboxing, we unveil the intricate nuances that set these disciplines apart. Muay Thai, known as the "Art of Eight Limbs," is steeped in Thai culture and history. It stands out for its versatility, allowing fighters to employ punches, kicks, elbows, and knees. The sport's emphasis on clinching and close-quarters combat adds a dynamic dimension to the striking game. Muay Thai also boasts a rich tradition of cultural rituals, including the Wai Khru dance and Ram Muay, which reflect deep respect for Thai heritage. Kickboxing, on the other hand, is a modern hybrid sport that blends elements from various striking arts, such as Boxing, Karate, and even Muay Thai itself. It offers a versatile striking style, primarily focusing on punches and kicks. Kickboxing competitions come in various rulesets, catering to a broad range of preferences and styles.
-
Polymer Chemistry

Vinyl vs PVC
In the realm of construction and interior design, the choice of materials can make or break a project's success. Two commonly confused materials, PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) and Vinyl, each bring their unique qualities to the table. To clarify the distinctions and help you make informed decisions for your next endeavor, let's delve into the key differences between PVC vs Vinyl. Material Composition: The primary difference between PVC and Vinyl lies in their material composition. PVC is a synthetic polymer made from vinyl chloride monomers, available in both rigid and flexible forms. Rigid PVC, often referred to as uPVC, is sturdy and used in applications like plumbing and window frames. In contrast, flexible PVC contains plasticizers that make it pliable and ideal for vinyl flooring and medical tubing. On the other hand, Vinyl, specifically PVC-based vinyl, shares the same PVC resin base but is inherently flexible, making it a go-to choice for interior design elements like flooring, upholstery, and wall coverings. Applications: The applications of PVC and Vinyl differ significantly due to their flexibility and durability attributes. PVC is often employed in structural and industrial applications where rigidity and resistance to corrosion are paramount. This includes water pipes, electrical conduits, and window frames. In contrast, Vinyl, with its inherent flexibility, is a preferred choice for interior design projects. It excels in applications such as luxury vinyl flooring (LVP), vinyl upholstery, banners, decals, and more. Vinyl offers a broad spectrum of design options, mimicking the appearance of natural materials like wood and stone, making it a favorite among interior designers and homeowners alike.