-
Culture

West Coast Swing vs East Coast
Swing dance enthusiasts, are you ready to dive into the captivating world of East Coast Swing (ECS) and West Coast Swing (WCS)? These two iconic swing dance styles, though sharing some common roots, offer distinct experiences on the dance floor. East Coast Swing (ECS): ECS, also known as the "six-count" or "triple-step" swing, has a rich history dating back to the swing era of the 1930s and 1940s. Its hallmark is its energetic and lively nature, with a basic 6-count footwork pattern that involves a triple step and a rock step. This style is synonymous with the upbeat tempo of swing music, making it perfect for lively gatherings and social events. ECS typically maintains an open dance frame with a lighter connection between partners, creating an atmosphere of fun and playfulness. It's an excellent choice for beginners and those who enjoy the vibrant swing music of the past. West Coast Swing (WCS): WCS, on the other hand, emerged on the West Coast of the United States in the 1940s, evolving from Lindy Hop with a focus on refinement and adaptability. It dances to an 8-count rhythm with a smoother and slotted style. WCS's versatility shines as it accommodates a wide range of music genres, from blues and R&B to contemporary pop. Unlike ECS, WCS employs a closer, more connected frame with subtle arm tension, enabling intricate footwork and sophisticated moves. WCS has a strong presence in both social and competitive dance scenes, with dedicated communities and a thriving competitive circuit.
-
Analytical Chemistry

Molarity vs Concentration
In the intricate world of chemistry, two fundamental concepts often steal the spotlight: Concentration and Molarity. They might appear synonymous at first glance, both pertaining to the measure of solute in a solution, but beneath the surface, they diverge into distinct entities. Let's embark on a journey to dissect and comprehend the intriguing Differences Between Concentration vs Molarity. Concentration, a versatile term, encapsulates various expressions to quantify the solute's presence within a solution. Whether it's mass percentage, volume percentage, or mole fraction, concentration provides insights into the solution's "strength" or "intensity." This concept plays a pivotal role in diverse applications, from concocting culinary delights in the kitchen to monitoring environmental pollutants in the great outdoors. Molarity (M), on the other hand, hones in on precision. It's all about the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. When you need exactitude in chemical reactions, especially in stoichiometry, molarity becomes the go-to unit. It facilitates precise control of reactant quantities, ensuring that chemical equations unfold as planned.
-
Culture

West vs East
In the captivating exploration of East vs West, we embark on a journey through the rich tapestry of cultural contrasts that define these two significant regions. From values and communication styles to perceptions of time and societal norms, the distinctions between the East and the West shape the unique identities of each. In the East, collectivism reigns supreme, emphasizing community bonds and family ties. Here, indirect communication and hierarchical societies prevail, often rooted in centuries-old traditions. Time is perceived as cyclical, and a harmonious relationship with nature is deeply ingrained in the culture. Education may prioritize conformity and achievement, and strong work ethics reflect dedication and long hours. Conversely, the West champions individualism, valuing personal freedom and autonomy. Communication is direct, and egalitarianism is the norm. Linear time perspectives and a utilitarian approach to the environment are characteristic. Education fosters creativity and critical thinking, and a work-life balance is highly esteemed.
-
Pathology

SEIR Model vs SIR
In the realm of epidemiological modeling, two stalwarts, the SIR (Susceptible-Infectious-Recovered) and SEIR (Susceptible-Exposed-Infectious-Recovered) models, stand ready to decode the intricate dynamics of infectious diseases. These models, like versatile tools in a scientist's arsenal, offer unique insights into the spread of diseases, guiding crucial decisions in public health. But what sets them apart? Let's delve into the fascinating Differences Between SIR vs SEIR Model. The SIR model, a classic in epidemiology, partitions the population into three compartments: Susceptible (S), Infectious (I), and Recovered (R). It operates on the assumption of immediate infectiousness upon infection and is ideal for diseases with short incubation periods. Conversely, the SEIR model introduces an additional Exposed (E) compartment, accounting for incubation periods before individuals become infectious. This enhanced complexity suits diseases like COVID-19, where understanding latent periods is pivotal. So, which model should you choose? The answer hinges on your research objectives and the characteristics of the disease you're studying. Whether you opt for the simplicity of the SIR model or the nuanced capabilities of the SEIR model, both hold the key to unraveling the mysteries of infectious disease dynamics.
-
Psychology

Perceptual vs Conceptual
In the intricate tapestry of human cognition, two distinct thinking styles weave their threads: conceptual and perceptual thinking. These cognitive modes, while fundamentally different, coexist harmoniously, shaping our understanding of the world and guiding our actions. Conceptual thinking, like an architect designing the blueprints of a skyscraper, deals with abstract ideas, principles, and intellectual concepts. It involves dissecting complex notions, forming generalizations, and drawing connections between ideas that transcend sensory details. Conceptual thinking thrives in the realm of philosophy, theoretical science, and abstract problem-solving. It shapes the language we use to discuss profound topics, the thought processes behind intricate analyses, and the foundations of our knowledge structures. On the other hand, perceptual thinking is the swift and intuitive responder to the tangible world around us. It processes real-time sensory information, guides our actions in the physical environment, and responds rapidly to sensory cues. Perceptual thinking excels in everyday scenarios where quick decision-making is crucial, such as driving a car, catching a ball, or responding to an emergency. It's the mode of thinking that allows us to interact with the world in a sensory-rich way, appreciating the immediate experiences that unfold before us. While these thinking styles have their unique strengths and applications, they often collaborate, enhancing our ability to navigate the intricacies of existence. Join us on a journey to explore the nuanced Differences Between Conceptual vs Perceptual thinking, and how they shape our world, our language, and our understanding of ourselves.
-
Environmental Science

Natural Climate Change vs Anthropogenic
Climate change is a topic of global concern, but it's essential to differentiate between anthropogenic (human-caused) and natural climate change. Anthropogenic climate change is primarily driven by human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes. These actions release significant amounts of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, leading to a rapid rise in global temperatures. In contrast, natural climate change is a result of processes like volcanic eruptions, solar radiation variations, and long-term geological factors. One of the key distinctions lies in the time scale. Anthropogenic climate change unfolds over decades and centuries, whereas natural climate change operates over geological time scales, often spanning millennia. The impacts of anthropogenic climate change are profound, including more frequent and severe heatwaves, melting ice caps, and disruptions to ecosystems. Understanding these differences is crucial for informed decision-making and collective action to mitigate anthropogenic climate change and adapt to the changes already underway. Join the global effort to combat climate change and safeguard our planet for future generations.
-
Nature

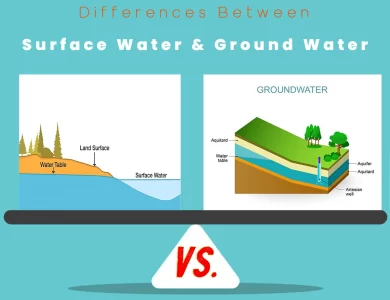
Ground Water vs Surface Water
Surface water and ground water are two fundamental sources of freshwater that play pivotal roles in our daily lives and the environment. Understanding their key differences is essential for effective water resource management and conservation efforts. Surface Water: Surface water refers to any body of water that rests on the Earth's surface, including rivers, lakes, streams, and oceans. It primarily derives from precipitation, runoff, and melting snow or glaciers. One of its distinct characteristics is visibility, as it flows above ground, making it more prone to immediate environmental changes such as pollution and temperature fluctuations. Surface water is readily accessible and widely used for various purposes, from drinking and irrigation to industrial processes and recreation. However, its quality often necessitates extensive treatment due to the risk of contamination. Ground Water: In contrast, ground water resides beneath the Earth's surface, stored in underground aquifers. It originates from rainwater and surface water that infiltrates the ground, gradually replenishing these hidden reservoirs. Groundwater moves at a significantly slower pace compared to surface water and is less susceptible to short-term environmental fluctuations. It is a vital source of drinking water for many communities, often requiring less treatment due to its natural filtration through soil and rock layers. However, improper management can lead to challenges such as overpumping and contamination.
-
Training

QTP 11 vs QTP 10
In the realm of software testing, choosing the right tool can make all the difference. QuickTest Professional, popularly known as QTP, has evolved over the years, with QTP 10 and QTP 11 standing as significant milestones in its journey. The question that often arises is, "What sets these two versions apart, and which one should you opt for?" QTP 10, with its classic user interface and support for VBScript, has been a trusted companion for testers. However, QTP 11 brought a modern twist with its ribbon interface, introducing JavaScript support alongside VBScript. The enhancements don't stop there; QTP 11 also boasts smart object identification, native mobile testing for Android and iOS, and built-in support for web service testing. Parallel test execution, improved integration with ALM, and an enhanced extensibility framework further distinguish QTP 11. Whether you're navigating the waters of mobile testing, web service testing, or seeking better collaboration tools, the choice between QTP 10 and QTP 11 depends on your unique testing needs. Dive into our comprehensive comparison to uncover the nuances that will help you make an informed decision and elevate your testing endeavors.
-
Training

Residency vs Fellowship
Are you a medical student or recent graduate standing at the crossroads of your career, contemplating the critical choice between a Fellowship and a Residency? This decision will significantly shape your journey in the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare. To make an informed choice, it's crucial to understand the main distinctions between these two pivotal phases of medical training. Fellowship: This specialized postgraduate program follows a Residency and offers in-depth training in a particular subspecialty, such as cardiology, neurosurgery, or pediatric endocrinology. The primary purpose of a Fellowship is to nurture experts in their chosen field. It typically lasts one to four years, providing ample time for gaining specialized knowledge and conducting advanced research. Fellows often contribute to groundbreaking advancements in their subspecialty and may eventually pursue academic careers. Residency: In contrast, a Residency program is the next step following medical school, offering a broader foundation in clinical medicine. It's designed to prepare physicians for either general practice or further specialization. The duration of a Residency varies from three to seven years, depending on the specialty. During this time, residents rotate through various departments, gaining diverse clinical experiences under the supervision of attending physicians. Understanding these core differences can help you align your personal aspirations and career goals with the right path, whether you aim to become a subspecialty expert or prefer a versatile foundation for your medical career. So, dive deeper into the contrasts between Fellowship and Residency to embark on the path that best suits your ambitions in the world of medicine.
-
Psychology

Social Anxiety vs Shyness
Shyness and social anxiety may seem similar at first glance, but they are fundamentally different experiences that impact how individuals navigate the social world. Shyness is a common personality trait characterized by occasional feelings of discomfort or unease in social situations. It's a natural part of the human spectrum of behavior and is often manageable and temporary. On the other hand, social anxiety, also known as social anxiety disorder (SAD), is a clinically recognized mental health condition. It involves intense and persistent fear of social interactions, often leading to severe symptoms such as panic attacks, avoidance of social situations, and irrational fears of humiliation or judgment. Understanding the nuances between these two emotional states is crucial. Shyness is typically milder, context-dependent, and often improves with time and experience. In contrast, social anxiety is chronic, pervasive across various social situations, and can significantly impact a person's daily life, relationships, and career. To shed light on the key differences and provide guidance for those affected, we've compiled an informative guide that explores the unique characteristics of shyness and social anxiety. Join us as we delve into the world of Shyness vs. Social Anxiety, offering insights to help individuals, friends, and family members better understand and manage these emotions effectively.