Nature
Here, we explore the fascinating world of nature, diving into the various terms, concepts, and other items that make it truly unique. Whether you’re a seasoned nature enthusiast or just starting to explore the wonders of the natural world, this category is the perfect place to expand your knowledge and gain a deeper understanding of the diversity that surrounds us.
In this comprehensive collection of articles, we aim to shed light on the differences that exist in nature, from the tiniest organisms to the grandest ecosystems. We’ll unravel the mysteries of taxonomy, delve into the contrasting characteristics of species, and uncover the distinctions between various natural phenomena. Our goal is to provide you with an engaging and informative resource that will enrich your appreciation of the natural world.
-

Saturn vs Earth
In our quest to understand the cosmic wonders of our universe, we find ourselves irresistibly drawn to Earth, our home, and Saturn, the majestic ringed giant. These two celestial entities are as distinct as they come, each offering a unique tapestry of features and mysteries that set them apart in our solar system. Earth, the third planet from the Sun, welcomes us with its life-sustaining embrace. Its atmosphere, composed mainly of nitrogen and oxygen, forms a protective shield that allows for a diversity of life unparalleled in the cosmos. From the deep blues of our oceans to the towering heights of our mountains, Earth's varied topography is a testament to the planet's dynamic geological history. Saturn, in stark contrast, is a gas giant of the outer realms. Its rings, a sight to behold, extend outward in a dazzling display of icy brilliance. Saturn's extreme weather, lack of solid ground, and turbulent winds make it a challenging environment for human habitation. Yet, its magnetic allure, complex moons, and unique auroras continue to captivate the imaginations of scientists and stargazers alike. As we traverse the cosmos, the differences between Earth and Saturn serve as a reminder of the vast diversity our universe holds. Each of these celestial entities has its own story to tell and lessons to teach, showcasing the awe-inspiring beauty and complexity of our solar system. Join us in this celestial journey as we unveil the captivating disparities between Earth and Saturn, shedding light on the cosmic wonders that surround us.
-

Jupiter vs Saturn
Saturn and Jupiter, the grand celestial giants of our solar system, share the stage but couldn't be more distinct in various aspects. Size sets them apart significantly, with Jupiter reigning as the largest planet, boasting a diameter of 86,881 miles, and Saturn trailing with a diameter of 74,900 miles. The majestic rings of Saturn are a standout feature, known for their intricate beauty, while Jupiter's ring system, though present, is faint and less visually striking. In terms of composition, both are primarily hydrogen and helium, but Jupiter's slightly higher metallicity gives its atmosphere its colorful bands and zones, which differ from Saturn's subtler cloud patterns. Jupiter's powerful magnetic field, approximately 20,000 times stronger than Earth's, surpasses Saturn's magnetic influence. The moon systems of both planets are vast, with over 80 confirmed moons each, offering diverse celestial bodies for exploration. These gas giants are not only celestial marvels but also hold crucial clues about the formation and evolution of our solar system. As we delve deeper into the distinct characteristics of Saturn and Jupiter, it becomes evident that each has a unique role in the cosmic symphony of our celestial neighborhood.
-

Mars vs Earth
In the vast expanse of our solar system, Earth and Mars stand out as two distinctive worlds, each holding its own unique charm and intrigue. From their respective positions in orbit to their atmospheres, surface features, and potential for human colonization, these celestial neighbors offer a captivating study in contrasts. Earth, the third rock from the Sun, is our cherished home, boasting a rich tapestry of life, lush landscapes, and a breathable atmosphere. Its size, approximately 12,742 kilometers (7,918 miles) in diameter, sets it apart as the largest terrestrial planet in our solar system. Earth's atmosphere is a life-supporting blend of nitrogen and oxygen, providing a hospitable environment for a staggering diversity of life forms. Its climate ranges from polar ice caps to scorching deserts, creating a rich tapestry of ecosystems that thrive across the planet. Mars, often referred to as the "Red Planet," is the fourth world from the Sun, with a diameter of about 6,779 kilometers (4,212 miles). Its atmosphere, primarily composed of carbon dioxide, is much thinner than Earth's, making it inhospitable for humans without advanced life support systems. Mars presents a stark, cold, and dusty landscape, marked by deep canyons and towering volcanoes. However, it tantalizes with the potential for future human colonization, as the quest for terraforming to create a more Earth-like environment gains momentum. In this exploration, we'll delve into the significant distinctions between Earth and Mars, unveiling their unique characteristics and the endless opportunities they offer for scientific discovery and human curiosity. Join us on this cosmic journey to understand these two captivating celestial neighbors better.
-

Difference Between Spring and Winter
Winter and spring, two of nature's most captivating acts, offer us a profound contrast in the grand spectacle of the changing seasons. As we journey through the transition from winter's icy grip to spring's vibrant blossoms, the differences that unfold are as diverse as the colors in a painter's palette. Winter, with its cold and often frosty mornings, blankets the world in a layer of snow and ice. It ushers in shorter days and longer nights, and a desire to cozy up indoors with warm cups of cocoa. Winter fashion brings out the heavy coats, scarves, and boots, all designed to ward off the chill. It's the season of snow sports, snowmen building, and cherished holidays like Christmas. In contrast, spring bursts onto the scene with milder temperatures and a gradual warm-up. It's a time when snow and frost give way to rain showers and the miraculous awakening of nature. With daylight hours stretching longer and blossoms adorning trees and gardens, outdoor activities shift from skiing to hiking, picnicking, and gardening. Spring cuisine embraces fresh greens, berries, and lighter fare, while fashion takes on a lighter, more colorful vibe.
-

Sea vs Ocean
The distinctions between oceans and seas are not just about the labels; they reflect a world of differences in size, salinity, ecosystems, and more. Oceans, the colossal giants of our planet, encompass vast expanses and account for over 70% of the Earth's surface. They are interconnected, forming a continuous, boundless body of saltwater, and include the renowned Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern (Antarctic), and Arctic Oceans. Oceans have relatively consistent salinity levels, which vary only slightly, thanks to their enormous size and the mixing action of ocean currents. Their depths are staggering, with the Mariana Trench in the Pacific Ocean boasting the deepest point on Earth, plunging to around 10,994 meters (36,070 feet). Conversely, seas, although impressive in their own right, are relatively smaller and often partially enclosed by land. They are typically connected to one of the major oceans, and their boundaries can be quite diverse. The salinity levels in seas can vary significantly, influenced by their proximity to freshwater sources, evaporation rates, and the exchange of water with the adjacent ocean. Some seas are well-known for their high salinity, while others have lower levels due to substantial freshwater inputs. This variation in salinity makes seas more susceptible to changes in local conditions, creating distinct marine ecosystems unique to each sea. Explore further to unravel these fascinating distinctions between oceans and seas, each offering a world of wonder and exploration.
-

Moon vs Earth
Step into the cosmic arena and embark on an awe-inspiring journey of celestial exploration as we unveil the striking and mesmerizing disparities between Earth and the Moon. These two celestial neighbors, while bound by their shared cosmic dance, couldn't be more different. From their origins and atmospheres to their gravitational forces and surface features, the contrasts are as vast as the cosmos itself. Earth, our cherished blue planet, stands as a beacon of life with its lush ecosystems, breathable atmosphere, and abundant liquid water. It's a cradle for humanity and a testament to the beauty of the natural world. In stark contrast, the Moon, Earth's cosmic companion, is a desolate, airless world, marked by extreme temperature variations and a surface adorned with countless craters. These fundamental distinctions extend to their gravitational forces, with Earth's powerful pull shaping our daily lives, while the Moon's weaker gravity creates a unique lunar environment. As we delve deeper into their differences, we'll explore their geological features, climates, and the influence they exert on Earth's tides. We'll also look to the future, with Earth's focus on environmental conservation and the Moon emerging as a frontier for lunar exploration and resource utilization. Join us in this cosmic odyssey and gain a newfound appreciation for the breathtaking diversity within our solar system.
-

Moon vs Sun
The Sun and the Moon, two celestial entities that have graced our skies since time immemorial, share the same stage in the heavens, yet they couldn't be more different in their characteristics and roles. The Sun, a searing ball of incandescent gases, reigns as the radiant heart of our solar system. It's the source of life-giving light and energy, primarily composed of hydrogen and helium. Its immense size dwarfs every other object in the sky, with a diameter of about 1.39 million kilometers. The Sun generates its own light and heat through nuclear fusion, powering Earth's climate, weather patterns, and photosynthesis. It's a cosmic beacon that has been revered and studied throughout human history. In stark contrast, the Moon is Earth's loyal companion, a modest rocky body about 3,475 kilometers in diameter. Unlike the Sun, it doesn't produce its own light but rather reflects the Sun's brilliance, casting its silvery glow upon our nighttime world. Its gravitational pull plays a pivotal role in creating the tides that ebb and flow along our coastlines. The Moon has captured the human imagination, inspiring myths, folklore, and scientific exploration, including historic Apollo missions. Exploring the differences between the Sun and the Moon is a journey that unveils the remarkable diversity of celestial bodies within our cosmic neighborhood. From their origins to their cultural symbolism and scientific significance, these two luminous companions continue to enrich our understanding of the universe.
-

Difference Between Autumn and Winter
As the seasons transition and the Earth dons its ever-changing attire, the question of "Winter vs. Autumn" arises, inviting us to explore the remarkable distinctions between these two captivating chapters in the annual cycle. Winter, spanning from December to February in the Northern Hemisphere, introduces a world shrouded in subfreezing temperatures, pristine snowfall, and the stark beauty of bare branches against a backdrop of white. It's a time for bundling up in cozy layers, sipping steaming hot cocoa by the fireplace, and engaging in winter sports like skiing and ice skating. In contrast, Autumn, which stretches from September to November, welcomes us with a gentle, crisp embrace. The landscape transforms into a living canvas as deciduous trees trade their green attire for a spectacular palette of red, orange, and gold. This magical transformation, known as fall foliage, sets the stage for a season of outdoor delights. Hiking through rustling leaves, picking apples in orchards, and exploring pumpkin patches become cherished pastimes. These two seasons paint nature's canvas with distinct strokes, each catering to different tastes and experiences. So, whether you're captivated by the hushed serenity of winter's icy landscapes or the warm, vibrant embrace of autumn's falling leaves, this exploration of "Differences Between Winter vs Autumn" promises to be a delightful journey through the ever-evolving tapestry of our world.
-

Ice vs Snow
In the midst of winter's icy embrace, two enchanting natural phenomena often take center stage: snow and ice. While they both share the cold spotlight, their differences are as pronounced as their similarities. Let's embark on a captivating journey to uncover the distinctive qualities that set snow and ice apart, making each of them a remarkable entity in their own right. Snow, with its ethereal beauty, forms in the Earth's atmosphere as ice crystals when water vapor freezes. Its delicate, six-sided snowflakes create landscapes akin to a fairy tale, providing the perfect canvas for winter sports and turning mundane scenes into winter wonderlands. Ice, on the other hand, is the solid form of water, born when liquid water freezes. This unyielding structure offers transparency and versatility, from preserving food in freezers to becoming a medium for intricate ice sculptures. As we delve into their composition, physical properties, and environmental impacts, you'll come to appreciate their distinct roles in nature. While snow blankets the world in serene white, offering insulation and seasonal delight, ice stands year-round, a steadfast companion with practical uses that extend far beyond winter. The differences between these frozen wonders enrich our understanding of the natural world and the diverse ways we interact with it, leaving us in awe of their icy charm.
-

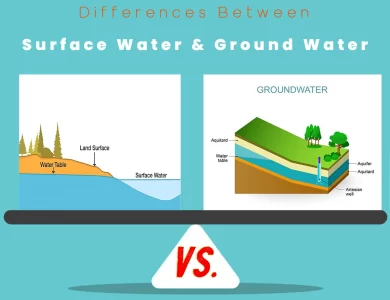
Ground Water vs Surface Water
Surface water and ground water are two fundamental sources of freshwater that play pivotal roles in our daily lives and the environment. Understanding their key differences is essential for effective water resource management and conservation efforts. Surface Water: Surface water refers to any body of water that rests on the Earth's surface, including rivers, lakes, streams, and oceans. It primarily derives from precipitation, runoff, and melting snow or glaciers. One of its distinct characteristics is visibility, as it flows above ground, making it more prone to immediate environmental changes such as pollution and temperature fluctuations. Surface water is readily accessible and widely used for various purposes, from drinking and irrigation to industrial processes and recreation. However, its quality often necessitates extensive treatment due to the risk of contamination. Ground Water: In contrast, ground water resides beneath the Earth's surface, stored in underground aquifers. It originates from rainwater and surface water that infiltrates the ground, gradually replenishing these hidden reservoirs. Groundwater moves at a significantly slower pace compared to surface water and is less susceptible to short-term environmental fluctuations. It is a vital source of drinking water for many communities, often requiring less treatment due to its natural filtration through soil and rock layers. However, improper management can lead to challenges such as overpumping and contamination.