Science and Nature
In this engaging corner of knowledge, we embark on a fascinating journey to explore the intricacies and distinctions between various terms, concepts, and phenomena that shape our understanding of the world around us. Join us as we unlock the secrets behind scientific theories, ecological wonders, and so much more.
-

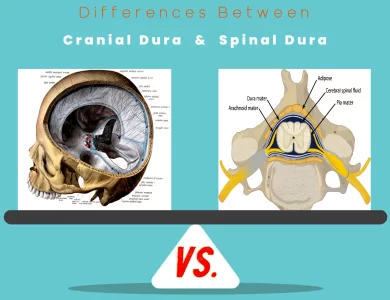
Spinal Dura vs Cranial Dura
In the realm of human anatomy, few structures are as essential yet enigmatic as the cranial dura and spinal dura. These protective membranes form the frontline guardians of our central nervous system, enveloping the brain and spinal cord, respectively. Understanding the disparities between these two critical components is not only intriguing but also pivotal in the world of medicine. Cranial dura, nestled within the cranial cavity, lines the inner surface of the skull, creating an impenetrable fortress around the brain. Its counterpart, the spinal dura, takes residence within the spinal cavity, cradling the spinal cord as it extends down the vertebral column. While both share similar dual-layered structures, their roles and interactions with their respective environments are vastly different. One striking contrast lies in their permeability. The cranial dura acts as a selective barrier, regulating the composition of cerebrospinal fluid and maintaining the brain's ionic balance. In contrast, the spinal dura is more permeable, facilitating the exchange of substances to support the spinal cord. The clinical implications of these disparities are also noteworthy. Understanding these differences is not only essential for medical professionals but also offers a fascinating glimpse into the intricate workings of our body's defense mechanisms. So, embark on this journey to unlock the secrets of cranial dura vs. spinal dura, and gain a newfound appreciation for the complexity of our central nervous system.
-

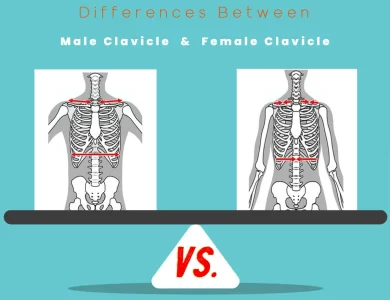
Female Clavicle vs Male
The clavicle, or collarbone, often considered one of the more inconspicuous bones in our bodies, holds a fascinating secret – it differs significantly between males and females. Beyond mere size and shape disparities, male and female clavicles reveal profound functional and structural distinctions. Male clavicles tend to be larger and more robust, equipped for tasks requiring strength and stability, such as heavy lifting. In contrast, female clavicles are daintier, embracing agility and flexibility, making them perfect for activities like dance or yoga. These distinctions extend to how the clavicle articulates with other bones, affecting the range of motion and the types of activities each gender excels in. Understanding these differences goes beyond mere curiosity; they have practical implications in sports, orthopedics, and physical therapy. While anatomy may seem like an esoteric realm, the disparities in male and female clavicles exemplify how even the subtlest variations can influence the human experience. Dive into our exploration of "Male vs Female Clavicle Differences" to appreciate the uniqueness of our skeletal framework and how it shapes our physical capabilities.
-

Prostate vs Colon
When it comes to our health, understanding the nuances of the human body is paramount. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the vital distinctions between two essential organs—our colon and prostate. The colon, a lengthy tube in our digestive system, serves a crucial role in water absorption and waste elimination. Meanwhile, the prostate, a small gland exclusive to men, takes center stage in the male reproductive system, producing seminal fluid for sperm nourishment and transport. What sets these two remarkable structures apart? The answers lie in their anatomy, function, and associated health issues. While the colon is present in both men and women and remains relatively consistent throughout adulthood, the prostate undergoes significant changes with age, potentially leading to issues like benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer. In this exploration, we'll uncover the key factors that differentiate the colon from the prostate. We'll examine their functions, gender specificity, age-related variations, health concerns, diagnostic methods, risk factors, treatment options, and prevention strategies. By the end of this journey, you'll be well-equipped with the knowledge needed to prioritize and safeguard the well-being of these vital organs. So, let's embark on this enlightening quest into the "Differences Between Colon vs Prostate."
-

Vulva vs Labia
In the realm of female anatomy, the terms "labia" and "vulva" are often used interchangeably, leading to confusion about their actual differences. It's essential to grasp these distinctions, not only for accurate understanding but also to promote body positivity and informed discussions about the female reproductive system. Labia, a subset of the vulva, refer to the two sets of skin folds, encompassing the labia majora (outer lips) and labia minora (inner lips). The labia majora serve as a protective barrier, while the labia minora contain a wealth of nerve endings, contributing to heightened sensitivity and pleasure. It's important to note that the appearance of the labia varies greatly among individuals in terms of size, shape, and color. On the other hand, the vulva is an all-encompassing term, referring to the complete external female genitalia. This includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vaginal opening, and urethral opening. The vulva plays a multifaceted role in sexual pleasure, reproduction, and protection. Understanding these differences is crucial, as it dispels common myths and misconceptions about female anatomy. By embracing the natural diversity of the labia and vulva, we can promote body positivity, foster informed conversations, and enhance overall well-being. So, let's dive into this enlightening journey and unravel the intricate tapestry of labia vs vulva.
-

Macula vs Crista
In the intricate landscape of the human body, the Crista and Macula are two inconspicuous yet pivotal players responsible for maintaining our balance and spatial orientation. Nestled within the inner ear, these structures are designed for distinct purposes, and understanding their differences can shed light on the marvels of human anatomy. The Crista, situated within the semicircular canals, excels at detecting rotational movements, helping us maintain equilibrium during activities like dancing, spinning, and engaging in sports. Its sensory hair cells, nestled within a gel-like cupula, are finely tuned to respond to changes in angular acceleration. In contrast, the Macula, found in the utricle and saccule, is the expert in linear acceleration and head orientation concerning gravity. It ensures that we stay steady on our feet when we stand, walk, or make subtle adjustments to our posture. The Macula's sensory hair cells are ingeniously embedded in an otolithic membrane filled with tiny crystals known as otoliths, making it exceptionally adept at detecting linear movements. By delving into the differences between these two inner ear structures, we embark on a fascinating journey of understanding how our bodies maintain balance and navigate the world around us. So, let's dive into the intricacies of Crista and Macula and appreciate their indispensable roles in our day-to-day lives.
-

Viruses vs Bacteria
In the vast microcosm of microorganisms, bacteria and viruses stand as two distinct and captivating entities. The contrast between these tiny but influential agents of life and disease is nothing short of remarkable. Bacteria, classified as living, prokaryotic single-celled organisms, wield their unique structures, shapes, and metabolic abilities, making them adaptable residents of diverse ecosystems. Their independent replication through binary fission, response to antibiotics, and pivotal role in nutrient cycling underscore their place in the natural world. On the other hand, viruses, seemingly lifeless entities, challenge the definition of life itself. Composed of genetic material encased in a protein coat, viruses depend entirely on host cells to propagate, engaging in a parasitic dance that has led to some of the most significant pandemics in history. Understanding the multifaceted differences between these microorganisms is crucial in the realms of microbiology, medicine, and public health. It guides our approach to treating and preventing infectious diseases, whether bacterial infections that yield to antibiotics or viral infections necessitating vaccines and antiviral strategies. The journey into the world of "Differences Between Bacteria vs Viruses" unveils the intricate dynamics of these minute yet impactful entities, shedding light on their roles in life and health.
-

Prion vs Virus
In the world of microbiology, two enigmatic entities, viruses and prions, stand as remarkable examples of microscopic adversaries with profoundly different natures and behaviors. This exploration takes us on a journey to uncover the distinct differences that set them apart. Viruses, these genetic infiltrators, come clad in DNA or RNA, ensconced within a protein coat. They are genetic freeloaders, entirely dependent on host cells for replication. Infectious agents extraordinaire, they're responsible for a myriad of diseases, from the seasonal flu to global pandemics. Prions, on the contrary, are the renegades of the microbial world. They are purely composed of misfolded proteins, devoid of genetic material. Their nefarious modus operandi involves corrupting innocent proteins within the host, setting in motion a slow and progressive chain reaction. While viruses are detectable through various molecular techniques, prion diseases often escape early diagnosis, revealing their damage only when it's advanced. The impact of these adversaries on human health is profound but remarkably different. Viruses can be managed through antiviral treatments and preventive measures like vaccination, while prion diseases, currently devoid of effective treatments, are often a one-way ticket to neurodegenerative devastation. As we journey deeper into this microscopic showdown, we'll explore the living entity debate surrounding prions, the evolutionary mysteries they present, and the future of research in unraveling their enigmatic world. So, let's dive into the captivating realm of "Differences Between Virus vs Prion."
-

Oil vs Fuel
In the dynamic world of energy resources, two significant players take center stage: fuel and oil. While both are vital components in driving our modern world, they possess unique characteristics, applications, and implications for our environment. Understanding the disparities between these two energy sources is crucial for making informed decisions regarding our energy needs. Fuel, a broad category, encompasses a variety of substances in solid, liquid, or gaseous forms. Derived from sources as diverse as coal, natural gas, and wood, fuels serve numerous purposes, from powering vehicles to generating electricity and heating homes. Their energy density, influenced by chemical composition and physical state, can significantly impact their efficiency in various applications. Oil, often referred to as petroleum or crude oil, stands as a naturally occurring hydrocarbon-based liquid. Originating from the remains of ancient marine microorganisms buried deep within the Earth's crust, it is predominantly composed of carbon and hydrogen, with smaller traces of sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen. Oil is renowned for its high energy density, making it a favored choice for powering transportation and energy production, despite the environmental challenges it poses. As society pivots towards environmentally responsible and sustainable energy sources, comprehending the differences between fuel and oil is instrumental in shaping our energy landscape and the choices we make. From composition to environmental regulations, these distinctions guide us toward a more informed and eco-conscious energy future.
-

Hydrogen vs Deuterium
Delving into the world of elemental disparities, the comparison between Deuterium and Hydrogen reveals subtle yet profound distinctions. Deuterium, often referred to as "heavy hydrogen," bears a unique atomic composition, featuring one proton, one neutron, and one electron, giving it an atomic mass of approximately 2.01410 atomic mass units (amu). In contrast, Hydrogen, the lightest and most abundant element in the universe, consists of just one proton and one electron, with an atomic mass of about 1.00784 amu. The differences extend to physical properties, as Deuterium is denser than Hydrogen, boasting a higher boiling point and a lower freezing point. While Hydrogen is highly flammable, Deuterium, though less flammable, can still ignite under certain conditions. These elemental distinctions hold significant implications for various applications. Hydrogen finds use in fuel cells, ammonia production, and as a rocket fuel, offering potential as a clean energy source. Deuterium, on the other hand, plays a crucial role in nuclear fusion research, isotopic labeling for biological studies, and cosmology, aiding in our understanding of the early universe. As we navigate the realms of chemistry, physics, and astrophysics, the contrast between Deuterium and Hydrogen continues to unravel, shaping our quest for clean energy and our comprehension of the cosmos.
-

Gas vs Oil
In the ever-evolving landscape of energy resources, the distinctions between oil and gas play a pivotal role in shaping our world. While both are hydrocarbon-based fossil fuels, their unique characteristics set them apart in terms of physical state, energy density, environmental impact, and primary applications. Oil, a liquid hydrocarbon, boasts a high energy density, making it an efficient source of power for various sectors, from transportation to heating. However, it carries a more significant environmental footprint due to emissions and oil spills. On the other hand, gas, primarily composed of methane, exists in a gaseous state. It burns cleaner, producing fewer carbon emissions and air pollutants, making it an appealing choice for environmentally-conscious consumers. The decision between oil and gas isn't just about convenience; it's about aligning with sustainability goals and understanding the environmental consequences. This article delves into these differences to help you make informed choices for your energy needs. So, join us on this journey as we explore the semantic and entity-based distinctions between oil and gas, providing insights into the cleaner, more efficient, and eco-friendly option.