Biology Science Nature
Welcome to our comprehensive category page dedicated to the intriguing subject of differences in biology, science, and nature! Here, we delve into the captivating realm of variations and distinctions that exist within these fields, shedding light on diverse terms, concepts, and other fascinating elements. Whether you’re a biology enthusiast, a science lover, or simply curious about the wonders of nature, this collection of content will leave you amazed and enlightened.
-

Complete Metamorphosis vs Incomplete
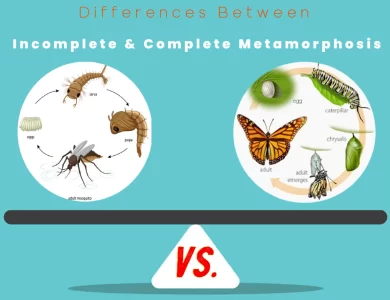
Embark on a journey through the captivating world of insect transformation as we delve into the contrasts between incomplete and complete metamorphosis. In incomplete metamorphosis, insects progress through three stages—egg, nymph, and adult—undergoing gradual changes with each molt. Nymphs, resembling miniature adults, molt as they grow. On the other hand, complete metamorphosis unfolds in four stages—egg, larva, pupa, and adult—featuring striking differences between larval forms (e.g., caterpillars) and adults. The pupal stage is a pinnacle of transformation, marked by reorganization and the emergence of fully developed adults. These metamorphic processes offer insights into evolution, ecological roles, and the delicate dance between humans and the natural world. For a comprehensive exploration, read our detailed guide on the "Differences Between Incomplete vs Complete Metamorphosis," and uncover the secrets of nature's astonishing adaptations and transformations.
-

Anamniotes vs Amniotes
Dive into the captivating world of amniotes and anamniotes, two pivotal branches in the vertebrate family tree. Amniotes, including reptiles, birds, and mammals, boast an extraordinary adaptation – the amniotic egg. This ingenious innovation shields developing embryos with protective membranes, liberating these creatures from the confines of aquatic reproduction. As amniotes conquer diverse terrestrial landscapes, they embody evolutionary diversity at its finest. On the other hand, anamniotes, represented by jawless and cartilaginous fish, lack the amniotic egg's protective embrace. Their aquatic habitats remain their reproductive strongholds, as they lay eggs vulnerable to desiccation and predators. This restriction has shaped their evolutionary trajectory, highlighting the significance of adaptation in nature's delicate balance. From genetic intricacies to cultural echoes, the differences between these groups extend far beyond reproduction. Explore how amniotes' genetic adaptations have led to feathers in birds and unique immune systems in cartilaginous fish. Delve into the conservation concerns arising from habitat preservation for amniotes and sustainable fishing practices for anamniotes.
-

Amphibians vs Tetrapods
Embark on an enlightening journey to uncover the captivating contrasts that define tetrapods and amphibians. These two intriguing groups of creatures, each with their unique traits, showcase the breathtaking diversity of life on Earth. Tetrapods, a diverse assembly of vertebrates including mammals, reptiles, birds, and amphibians, are united by their possession of four limbs or adaptations thereof. These limbs, intricately designed for a variety of movements, distinguish tetrapods as masters of terrestrial, aerial, and aquatic domains. On the other hand, amphibians, with their enchanting ability to transition between watery and land-based realms, beckon us to delve into their world of permeable skin and dual life stages. This attribute allows amphibians to respire through their skin, while their metamorphosis from aquatic larvae to adults showcases their exceptional adaptability.
-

Synapsid vs Diapsid
Delving into the world of evolutionary biology, we uncover the intriguing disparities that set diapsid and synapsid vertebrates apart. At the heart of their dissimilarity lies the skull structure – diapsids flaunt two pairs of temporal fenestrae that anchor powerful jaw muscles, while synapsids feature a single pair linked to the jaw joint, hinting at their mammalian ancestry. These distinctions paved distinct evolutionary paths. Diapsids, known for their reign in the Mesozoic era, encompass dinosaurs, reptiles, and the awe-inspiring world of birds. In contrast, synapsids, thriving during the Permian and Triassic periods, laid the groundwork for the rise of mammals. The story of diapsids unfolds in the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous periods, with dinosaurs dominating land and pterosaurs taking to the skies. Synapsids, tracing back to the Late Carboniferous, evolved into diverse forms like therapsids, marking the journey towards endothermy and mammalian characteristics. This narrative of divergence and adaptation continues to shape Earth's diverse ecosystems, providing us with an invaluable window into the tapestry of life's evolution.
-

Toads vs Frogs
Delving into the world of amphibians, one encounters the charming duo of frogs and toads. While they share habitats and appearances, a closer look unveils intriguing disparities that set them apart. Frogs, with their smooth, moist skin and long hind legs built for leaping, tend to inhabit aquatic environments like ponds and rivers. On the other hand, toads, characterized by their rough, warty skin and shorter hind legs, can be found in diverse settings from forests to grasslands. This diversity in habitat preference is just the beginning; their coloration showcases a vivid contrast too. Frogs dazzle with vibrant shades, signaling their presence, while toads rely on earthy tones for camouflage. Reproduction strategies vary as well—frogs lay eggs in clusters, whereas toads prefer strings. Their communication methods further emphasize distinctions; frogs possess diverse calls that resonate through their habitats, while toads' calls are often trills and whistles. The differences extend to feeding habits, movement styles, and defense mechanisms. In essence, these fascinating disparities celebrate nature's ability to craft unique solutions for varied ecosystems. As we delve into the rich intricacies of frogs and toads, we uncover a world where adaptation and diversity intertwine, enhancing our appreciation for the remarkable wonders that inhabit our planet.
-

Marsupial vs Mammal
Embark on a captivating journey into the realms of the animal kingdom as we unravel the fascinating distinctions that set mammals and marsupials apart. These two remarkable groups, though sharing a warm-blooded nature, exhibit striking differences in their approaches to reproduction, parental care, and adaptability to various ecosystems. Mammals, the charismatic inhabitants of diverse habitats across the globe, bring forth offspring in a more advanced state, thanks to their well-developed placentas that facilitate direct nutrient exchange between mother and embryo. In contrast, marsupials, the enchanting oddities primarily found in Australia and parts of the Americas, give birth to less developed young. These young then find solace within the protective confines of their mother's pouch, where they continue to mature while nursing. This distinctive strategy reflects the diversity of life's evolution, and it is within these differences that the captivating stories of survival and adaptation unfold. Join us in delving deeper into the intricacies of Mammal vs Marsupial, an exploration that sheds light on the remarkable world of nature's variety and the awe-inspiring ways in which creatures thrive in their unique niches.
-

Snakes vs Limbless Amphibians
Embark on a captivating journey through the intricate world of limbless creatures as we unveil the distinctive contrasts between limbless amphibians, represented by caecilians, and the elegant slithering wonders known as snakes. These remarkable beings have evolved in divergent paths, each embracing a life without limbs in their unique ways. Limbless amphibians, such as caecilians, share a hidden ancestry with frogs and salamanders, gradually transitioning to their snake-like appearance to navigate subterranean realms. Their cylindrical bodies, often mistaken for worms, are equipped with specialized tentacles that allow them to sense their environment through touch and chemical cues. In contrast, snakes, born from legged ancestors, have fully embraced limblessness. With elongated bodies optimized for graceful movement, they boast unique adaptations like infrared-sensitive pits for detecting prey's heat signatures and kinetic skulls for consuming larger meals. Both groups employ intriguing hunting techniques; limbless amphibians utilize prey-swallowing and ambush, while snakes excel in ambush and constriction. As you delve into the sensory adaptations, reproductive strategies, and conservation challenges of these creatures, you'll gain a profound appreciation for the diverse paths evolution has carved. Join us on this enthralling expedition as we uncover the captivating Differences Between Limbless Amphibians vs Snakes.
-

Amphibian vs Reptile
Embark on a fascinating journey through the captivating realms of reptiles and amphibians as we unravel the intriguing differences that set these two remarkable groups apart. From their distinct skin characteristics to their unique reproductive strategies, the divergence between reptiles and amphibians is a captivating tale of adaptation and evolution. Reptiles, characterized by scaled skin made of keratin, wield these scales as armor, providing protection while aiding in the art of camouflage. On the other hand, amphibians flaunt moist and permeable skin, serving multiple purposes—respiration, defense, and even communication—within their ever-changing environments. Diving deeper, we encounter their contrasting approaches to reproduction. Reptiles lay eggs enveloped in protective shells, with incubation methods ranging from nesting to ovoviviparity. In contrast, amphibians lay exposed eggs that rely heavily on moisture for proper development, and many undergo remarkable metamorphoses as they transition from aquatic larvae to terrestrial adults. The tale continues with their habitat preferences—reptiles' dominance on land and their reliance on external heat sources for thermoregulation, and amphibians' duality in thriving both in water and on land, thanks to their permeable skin.
-

Reptile vs Mammal
Delving into the captivating realm of the natural world, we uncover the intriguing contrasts that set mammals and reptiles apart. Mammals, characterized by their warm-blooded nature and fur-covered bodies, stand in stark contrast to the resilient reptiles with their scaly skin and cold-blooded physiology. Reproduction unfolds differently in these two groups, with mammals giving birth to live young and providing nurturing care, while reptiles often lay eggs or give birth to independent offspring. From communication strategies to habitats and evolutionary histories, each facet of these creatures unveils a tale of survival and adaptation. Mammals communicate through complex vocalizations and flourish in various environments due to their internal temperature regulation. Reptiles, on the other hand, utilize visual cues and thrive in diverse ecosystems thanks to their ability to adapt to fluctuating temperatures. As we delve into these differences, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate diversity that enriches our natural world. Join us on this captivating journey as we explore the marvels of Mammal vs Reptile distinctions, uncovering the threads that weave the fabric of life on Earth.
-

Blood vs Plasma
Blood and plasma are vital components of our circulatory system, each with its own unique characteristics and functions. While blood consists of cellular components such as red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, plasma is the liquid portion of blood that remains after these cells have been removed. Blood carries oxygen, nutrients, and waste products, while plasma acts as a carrier for blood cells, hormones, and nutrients. Blood plays a crucial role in oxygen transport, immune responses, and blood clotting. It is used in transfusions, treating blood disorders, and providing support during surgeries and emergency situations. Plasma, on the other hand, is used to produce plasma-derived therapies, treat autoimmune diseases, and support burn and trauma care. Understanding the distinctions between blood and plasma is essential for appreciating their significance in maintaining overall health and saving lives. By donating blood or plasma, individuals can contribute to the well-being of others and make a tangible difference. Regular blood and plasma donations are vital for ensuring a sufficient supply to meet medical needs. Explore the fascinating world of blood and plasma, and consider becoming a donor to support those in need. Your act of kindness can make a remarkable impact on the lives of others.