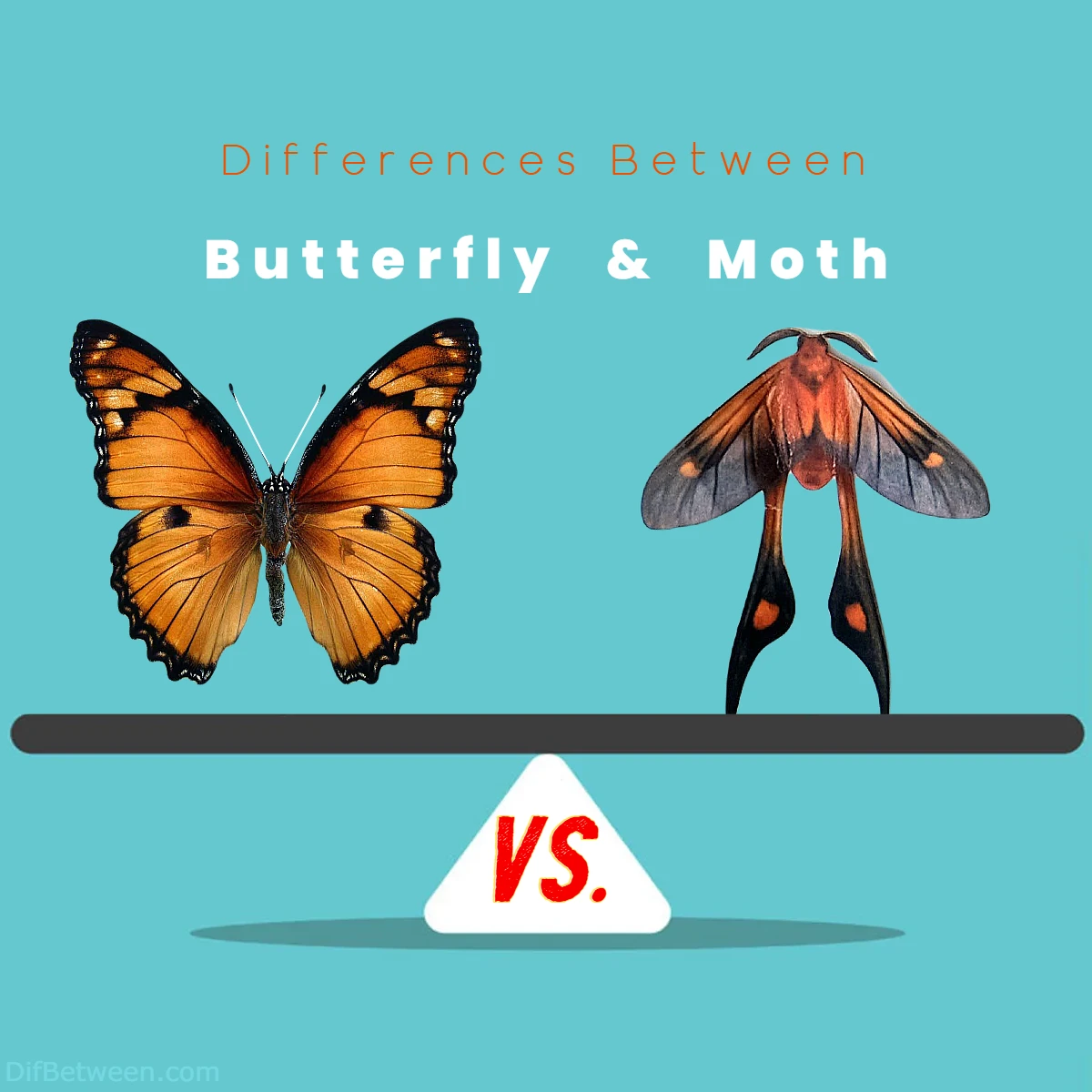
| Characteristic | Butterflies | Moths |
|---|---|---|
| Colors | Bright and vibrant | Subdued, earthy tones |
| Wing Patterns | Elaborate patterns | Often intricate patterns |
| Camouflage | Less common due to bright colors | Common due to muted tones |
| Activity Time | Daytime | Nighttime |
| Feeding Habits | Nectar from flowers | Varied, including nectar, sap, and rotting fruit |
| Attracted to Light | Not as much | Highly attracted |
| Resting Posture | Wings open vertically | Wings folded horizontally |
| Body Appearance | Slimmer and smoother | Stockier, fuzzier appearance |
| Wing Resting Style | Wide open display | Camouflaged appearance |
| Antennae Shape | Thin and clubbed tips | Diverse shapes: filamentous, feathery, comb-like |
| Sensory Function | Odor and chemical sensing | Critical for navigation and mating |
| Pupation Structure | Chrysalis | Cocoon |
| Cocoon Appearance | Smooth and often decorated | Silky, textured, and diverse |
| Preferred Habitats | Open and sunny areas | Diverse range of habitats |
| Distribution | Widespread, migrations are common | Global, from Arctic to deserts |
| Feeding Habits | Mainly nectar, some other sources | Varied, including nectar, sap, fungi, and detritus |
| Sexual Dimorphism | Sometimes subtle | Varied, from subtle to striking |
| Mating Behaviors | Territorial behaviors | Often rely on pheromones for attraction |
| Pollination Role | Important pollinators | Crucial pollinators and food sources |
| Ecological Impact | Biodiversity support | Food chain stability and nutrient cycling |
| Symbolic Meanings | Transformation, rebirth | Intuition, hidden truths, pursuit of knowledge |
From colors that dazzle to behaviors that intrigue, each aspect of these creatures is a testament to nature’s endless creativity. Butterflies, those daytime dancers of the floral stage, captivate with their vivid hues and breathtaking wing patterns. On the flip side, moths, the night’s silent navigators, unveil their beauty through subtle earthy tones and intriguingly intricate antennae. But it’s not just their appearances that set them apart – it’s their entire way of life.
Differences Between Butterfly and Moth
The main differences between butterflies and moths lie in their appearances, behaviors, and habitats. Butterflies are known for their vibrant, eye-catching colors and elaborate wing patterns, often seen fluttering in daylight and sipping nectar from flowers. In contrast, moths usually exhibit more subdued tones and intricate antennae, and are predominantly nocturnal creatures that rely on their keen sense of smell to locate mates and food sources. While butterflies prefer open, sunny spaces, moths thrive in diverse habitats, adapting to various environments. Overall, these distinctions in color, behavior, activity patterns, and habitats set butterflies and moths apart, making them unique and captivating members of the insect world.
Appearance and Colors
Butterflies: A Kaleidoscope of Colors
Picture a sunny day in a blooming garden, and what comes to mind? Likely a kaleidoscope of colorful butterflies fluttering from flower to flower. Butterflies are known for their bright, eye-catching hues. Their wings, often featuring intricate patterns and striking combinations of colors, make them the poster children of nature’s artistry. Think of the iconic Monarch butterfly with its vibrant orange and black wings, or the electric blue of the Blue Morpho.
Moths: A Subdued Elegance
Moths, on the other hand, are often characterized by a more subtle palette. While there are exceptions, many moth species lean towards earthy tones like browns, grays, and muted greens. This subdued elegance helps them blend seamlessly into their natural surroundings, acting as a form of camouflage against predators. Unlike butterflies, moths might not be as showy, but their understated beauty and intricate patterns are a testament to their own unique charm.
| Characteristic | Butterflies | Moths |
|---|---|---|
| Colors | Bright and vibrant | Subdued, earthy tones |
| Wing Patterns | Elaborate patterns | Often intricate patterns |
| Camouflage | Less common due to bright colors | Common due to muted tones |
Activity and Behavior
Butterflies: Daytime Delight
Imagine waking up to a warm, sunny morning and heading out to your garden. Chances are, you’ll be greeted by the delightful dance of butterflies. These creatures are primarily diurnal, which means they are most active during the day. Their vision is adapted to daylight, and their feeding habits involve nectar-sipping from flowers. Butterflies are social insects, often spotted in groups fluttering around blossoms and puddling on damp surfaces.
Moths: Nighttime Enchanters
As the sun sets and the world transforms into a canvas of moonlight, moths take center stage. Unlike their diurnal counterparts, moths are nocturnal creatures, meaning they are most active during the night. They rely on their keen sense of smell, rather than sight, to locate mates and find food. Moths are drawn to artificial light sources, which can sometimes lead them astray from their natural behaviors.
| Characteristic | Butterflies | Moths |
|---|---|---|
| Activity Time | Daytime | Nighttime |
| Feeding Habits | Nectar from flowers | Varied, including nectar, sap, and rotting fruit |
| Attracted to Light | Not as much | Highly attracted |
Resting Posture and Anatomy
Butterflies: Wings Wide Open
The way these winged beauties rest provides an easy clue to their identification. Butterflies tend to keep their wings held vertically when at rest, with their wings wide open. This exposes their captivating colors and patterns, even while resting. Their bodies are often slender and smoother, with a more streamlined appearance.
Moths: Wings Wrapped Around
Moths, in contrast, have a distinct resting posture that sets them apart. When at rest, most moths fold their wings horizontally, wrapping them snugly around their bodies. This posture provides effective camouflage and helps them blend into their surroundings. Moths often have stockier bodies with hair-like scales that give them a fuzzier appearance compared to butterflies.
| Characteristic | Butterflies | Moths |
|---|---|---|
| Resting Posture | Wings open vertically | Wings folded horizontally |
| Body Appearance | Slimmer and smoother | Stockier, fuzzier appearance |
| Wing Resting Style | Wide open display | Camouflaged appearance |
Antennae Shape and Structure
Butterflies: The Clubbed Tips
The antennae of butterflies are a captivating feature in themselves. They typically have thin, slender antennae that end in club-like tips. These clubbed tips can vary in shape and are often more pronounced in males. Butterflies use their antennae to sense odors and chemicals in the environment, aiding in the search for suitable mates and food sources.
Moths: A Variety of Forms
When it comes to antennae, moths offer a diverse array of shapes and structures. Some moths have filamentous antennae, which are long, thread-like structures. Others sport feathery or comb-like antennae that are designed to capture scent particles from the air more effectively. Moths’ antennae play a crucial role in their nighttime activities, helping them navigate and find mates in the dark.
| Characteristic | Butterflies | Moths |
|---|---|---|
| Antennae Shape | Thin and clubbed tips | Diverse shapes: filamentous, feathery, comb-like |
| Sensory Function | Odor and chemical sensing | Critical for navigation and mating |
Pupation and Cocoon Formation
Butterflies: The Art of Chrysalis
The transformation from caterpillar to adult is a marvel in itself. Butterflies form a protective casing known as a chrysalis, where their metamorphosis takes place. The chrysalis is typically smooth, hard, and often adorned with golden accents. Inside this shell, the caterpillar undergoes a miraculous change, emerging as a fully formed butterfly ready to take flight.
Moths: The Magic of Cocoons
Moths, too, undergo a transformative journey within the safety of a cocoon. However, the cocoon varies greatly from the chrysalis. Moth cocoons are often silkier, with a more textured and rugged appearance. Some moth species spin their cocoons among leaves or branches, while others create them underground or in hidden crevices. The diversity in cocoon design is as fascinating as the range of moth species itself.
| Characteristic | Butterflies | Moths |
|---|---|---|
| Pupation Structure | Chrysalis | Cocoon |
| Cocoon Appearance | Smooth and often decorated | Silky, textured, and diverse |
Habitat and Distribution
Butterflies: Explorers of Open Spaces
Butterflies are often associated with open and sunny spaces. They thrive in a variety of habitats, including meadows, gardens, and fields. These areas provide ample nectar sources for their feeding habits. Butterflies are highly mobile insects, capable of traveling long distances in search of suitable habitats, especially during their migrations. This adaptability to diverse environments contributes to their widespread distribution across the globe.
Moths: Masters of Diversity
Moths are true masters of adaptability, occupying an incredibly diverse range of habitats. You can find moths in forests, grasslands, deserts, and even urban areas. They’re less selective about their habitats compared to butterflies, which might explain their astounding species diversity. Moths have colonized nearly every corner of the Earth, from the frozen Arctic tundra to the scorching hot deserts.
| Characteristic | Butterflies | Moths |
|---|---|---|
| Preferred Habitats | Open and sunny areas | Diverse range of habitats |
| Distribution | Widespread, migrations are common | Global, from Arctic to deserts |
Feeding Preferences
Butterflies: Nectar Enthusiasts
Butterflies are famous for their penchant for sipping nectar from flowers. Their long, straw-like proboscis allows them to reach deep into the floral tubes to extract this sweet sustenance. In doing so, they inadvertently assist in pollination, playing a vital role in ecosystem health. Beyond nectar, some species are known to feed on rotting fruit or animal droppings.
Moths: Varied Appetites
The dining preferences of moths are more diverse. While some moths do feed on nectar, many species have evolved to consume a wider range of foods. Some are pollinators like butterflies, while others feed on sap, tree fluids, or even fungi. Certain moth species are carnivorous in their caterpillar stages, hunting other insects or feeding on detritus. The vast array of feeding habits among moths underscores their adaptability to different ecological niches.
| Characteristic | Butterflies | Moths |
|---|---|---|
| Feeding Habits | Mainly nectar, some other sources | Varied, including nectar, sap, fungi, and detritus |
Sexual Dimorphism and Behavior
Butterflies: Subtle Differences
In many butterfly species, there’s a level of sexual dimorphism, meaning males and females have distinct characteristics. These differences can be subtle and might include variations in wing patterns or color intensity. Male butterflies are often observed engaging in territorial behaviors, defending prime nectar sources or perch sites to attract potential mates.
Moths: Varied Transformations
Sexual dimorphism among moths is quite varied. In some species, the differences are striking, with males and females displaying markedly different sizes, colors, or wing patterns. In others, the differences might be subtle, requiring closer observation to distinguish between the sexes. Moth mating behaviors also vary significantly, with some species relying on pheromone emissions to attract mates over long distances.
| Characteristic | Butterflies | Moths |
|---|---|---|
| Sexual Dimorphism | Sometimes subtle | Varied, from subtle to striking |
| Mating Behaviors | Territorial behaviors | Often rely on pheromones for attraction |
Economic and Ecological Importance
Butterflies: Pollination Partners
Butterflies play a crucial role as pollinators in many ecosystems. By transferring pollen from one flower to another, they facilitate the reproduction of numerous plant species. This process is essential for maintaining biodiversity and ensuring the production of fruits and seeds that support both wildlife and human populations. Additionally, butterflies have aesthetic and cultural value, attracting tourists and inspiring art and literature.
Moths: Silent Stewards of the Night
Moths might not receive as much attention as butterflies, but their ecological contributions are equally significant. Moths serve as important pollinators for various nocturnal flowering plants, contributing to the nighttime ecosystem’s stability. Their role in the food chain is vital as well; moth caterpillars are essential food sources for birds, bats, and other predators. Some moth species also assist in breaking down plant matter and recycling nutrients.
| Characteristic | Butterflies | Moths |
|---|---|---|
| Pollination Role | Important pollinators | Crucial pollinators and food sources |
| Ecological Impact | Biodiversity support | Food chain stability and nutrient cycling |
In Culture and Symbolism
Butterflies: Symbols of Transformation
Butterflies have captured human imagination for centuries, symbolizing transformation, rebirth, and freedom. Their metamorphosis from a humble caterpillar to a graceful butterfly is often associated with personal growth and change. In various cultures, butterflies are depicted as messengers of the soul or carriers of wishes. Their vibrant colors and delicate flight patterns have also inspired countless works of art and literature.
Moths: Hidden Meanings
Moths, with their nocturnal nature and mysterious allure, carry their own symbolism in cultures worldwide. In some traditions, moths are associated with intuition and hidden truths due to their ability to navigate through darkness. They’re also linked to a search for light and enlightenment. Moths’ inclination to be drawn to artificial light sources has been interpreted as a metaphor for the human pursuit of knowledge.
| Characteristic | Butterflies | Moths |
|---|---|---|
| Symbolic Meanings | Transformation, rebirth | Intuition, hidden truths, pursuit of knowledge |
FAQs
Butterflies are known for their bright and vibrant colors, often featuring intricate wing patterns. On the other hand, moths tend to have more subdued earthy tones and intricate antennae, with many species exhibiting camouflage to blend into their surroundings.
Butterflies are primarily active during the day (diurnal) and feed on nectar from flowers. They are often seen fluttering in groups and are less attracted to artificial lights. Moths, however, are mostly nocturnal, relying on their sense of smell to find mates and food sources. They are strongly attracted to artificial lights.
Butterflies rest with their wings held vertically and wide open. This exposes their colorful patterns even when resting. In contrast, moths rest with their wings folded horizontally around their bodies, providing effective camouflage.
Butterflies form a chrysalis, which is typically smooth and often decorated. Moths create cocoons, which are usually silkier and more textured. The appearance and location of these pupation structures vary widely among species.
Butterflies mainly feed on nectar from flowers. Moths have more varied diets, including nectar, sap, rotting fruit, fungi, and even detritus. Some moth caterpillars are carnivorous, feeding on other insects.
Butterflies symbolize transformation, rebirth, and freedom, while moths are often associated with intuition, hidden truths, and the pursuit of knowledge due to their nighttime nature and attraction to light.
Butterflies are important pollinators, aiding in the reproduction of various plant species. Moths play a crucial role in nighttime ecosystems as pollinators and as vital food sources for predators, contributing to the overall balance of the food chain.
Butterflies are more active during the day and prefer open, sunny areas like meadows and gardens. Moths are adapted to various habitats, occupying a diverse range of ecosystems, from forests to urban areas, and are primarily active at night.
Butterflies have thin antennae with club-like tips, while moths exhibit diverse antenna shapes, including filamentous, feathery, and comb-like structures, which are crucial for their sensory functions.
The distinctions between butterflies and moths extend beyond their appearances – they encompass behaviors, ecological roles, and even cultural symbolism. Understanding these differences offers a deeper appreciation for the incredible diversity that nature has to offer.
Read More:
Contents






