
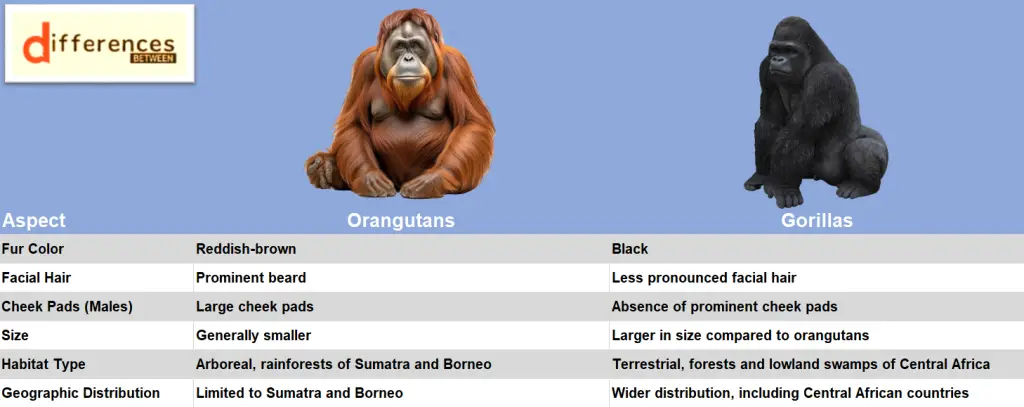
The main differences between Orangutans and Gorillas lie in their physical characteristics, habitats, and social behaviors. Orangutans, with their reddish-brown fur and distinctive cheek pads, are arboreal beings found in the rainforests of Sumatra and Borneo, leading predominantly solitary lives. On the contrary, Gorillas, with their powerful black coats, inhabit the forests of Central Africa and thrive in cohesive family groups led by a dominant silverback male. While Orangutans are primarily frugivores with a nomadic foraging style, Gorillas are herbivores with a more methodical approach to plant-based sustenance. Understanding these distinctions sheds light on the diverse evolutionary paths and ecological niches these incredible primates occupy in our natural world.
| Characteristic | Orangutans | Gorillas |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Characteristics | ||
| Fur Color | Reddish-brown | Black |
| Facial Hair | Prominent beard | Less pronounced facial hair |
| Cheek Pads (Males) | Large cheek pads | Absence of prominent cheek pads |
| Size | Generally smaller | Larger in size compared to orangutans |
| Habitat and Distribution | ||
| Habitat Type | Arboreal, rainforests of Sumatra and Borneo | Terrestrial, forests and lowland swamps of Central Africa |
| Geographic Distribution | Limited to Sumatra and Borneo | Wider distribution, including Central African countries |
| Social Structure | ||
| Social Behavior | Predominantly solitary, especially males | Form cohesive family groups led by a silverback |
| Group Structure | Loose associations (females with offspring) | Family groups with dominant silverback male |
| Communication | Vocalizations for territory and dominance | Vocalizations, body language, and grooming |
| Diet and Feeding Habits | ||
| Primary Food Source | Fruits, leaves, bark, insects | Fruits, leaves, shoots, stems |
| Dietary Flexibility | Opportunistic feeders | Herbivores with a predominantly vegetarian diet |
| Foraging Habits | Nomadic foraging based on fruit availability | Methodical foraging for plant-based sustenance |
| Reproductive Traits | ||
| Reproductive Rate | Slow-paced with long interbirth interval | Regular with a shorter interbirth interval |
| Mother’s Care | Dedicated maternal care | Shared caregiving within family groups |
| Cultural Significance | ||
| Folklore Symbolism | Wisdom and patience | Strength and unity |
| Cultural Conservation Efforts | Active involvement in orangutan conservation | Collaboration with local communities for gorilla protection |
| Conservation Challenges | ||
| Primary Threats | Habitat loss, illegal pet trade | Poaching, habitat loss, and disease transmission |
| Conservation Initiatives | Rainforest preservation, sustainable practices | Protected areas, anti-poaching measures, and community engagement |
| Call to Action | ||
| Conservation Focus | Preserve rainforests, sustainable palm oil | Safeguard habitats, anti-poaching, and sustainable practices |
Picture the majestic orangutans, gracefully swinging through the verdant canopy, their reddish-brown fur a beacon in the emerald sea of leaves. On the other side of the jungle, imagine the awe-inspiring gorillas, navigating the dense underbrush with a dignified presence, their black coats reflecting the dappled sunlight filtering through the trees.
Differences Between Orangutan and Gorilla
Physical Characteristics
Orangutan’s Distinctive Features
Let’s start our journey by examining the distinctive physical features that set orangutans apart from their gorilla counterparts. Orangutans are renowned for their distinctive reddish-brown fur, which serves as a remarkable identifier. Their faces are adorned with a charismatic beard of sorts, and males often develop large cheek pads, emphasizing their mature status.

Table: Orangutan Physical Characteristics
| Feature | Orangutan | Gorilla |
|---|---|---|
| Fur Color | Reddish-brown | Black |
| Facial Hair | Prominent beard | Less pronounced facial hair |
| Cheek Pads (Males) | Large cheek pads | Absence of prominent cheek pads |
| Size | Generally smaller | Larger in size compared to orangutans |
Gorilla’s Majestic Presence
On the other side of the jungle, we encounter the majestic gorilla. Easily recognizable by their robust build and striking black fur, gorillas exude a powerful and commanding presence. Unlike orangutans, gorillas lack the distinctive cheek pads, and their facial hair is less prominent.

Gorillas are notably larger than orangutans, with mature males exhibiting impressive physical strength. Their muscular build and black fur contribute to a commanding presence in the dense forests they inhabit.
Habitat and Geographic Distribution
Orangutan’s Treetop Haven
Orangutans, often referred to as the “people of the forest,” are primarily arboreal creatures. They are found swinging gracefully through the treetops of the lush rainforests of Sumatra and Borneo in Southeast Asia. Their unique adaptations for tree-dwelling include long arms and hook-like hands, allowing them to effortlessly navigate the dense canopy.
The geographic distribution of orangutans is limited to specific regions, making the preservation of their habitats crucial for their survival. Deforestation poses a severe threat to these gentle primates, emphasizing the importance of conservation efforts.
Gorilla’s Grounded Dominion
Contrasting the arboreal lifestyle of orangutans, gorillas are terrestrial beings that inhabit the dense forests and lowland swamps of Central Africa. They navigate the forest floor with a distinctive knuckle-walking gait, showcasing their adaptation to a life closer to the ground.
Gorillas exhibit a wider distribution compared to orangutans, with populations residing in countries such as Cameroon, Gabon, and the Democratic Republic of Congo. The gorilla’s habitat faces similar challenges, including habitat destruction and poaching, necessitating concerted conservation endeavors.
Social Structure and Behavior
Orangutan’s Solitary Elegance
Orangutans are known for their predominantly solitary lifestyle, especially among adult males. Adult females, however, may form loose associations with their offspring. This solitary behavior is partly due to the scarcity of their primary food source, ripe fruit, which requires extensive foraging ranges.
Male orangutans, in particular, are highly territorial and often engage in long calls to establish and maintain their dominance. These vocalizations echo through the dense rainforest, creating an ethereal atmosphere.
Gorilla’s Familial Bonds
Gorillas, in contrast, are renowned for their intricate social structures. They form cohesive family groups led by a dominant silverback male, who serves as the protector and leader. These groups consist of females, juveniles, and occasionally, subordinate males.
The familial bonds within gorilla groups are heartwarming, with individuals displaying affection through grooming and playing. The silverback male plays a crucial role in maintaining order and ensuring the safety of the group, showcasing a sophisticated level of social organization.
Table: Social Structure Comparison
| Social Structure | Orangutan | Gorilla |
|---|---|---|
| Solitary Behavior | Predominantly solitary, especially males | Form cohesive family groups led by a silverback |
| Group Structure | Loose associations (females with offspring) | Family groups with dominant silverback male |
| Communication | Vocalizations for territory and dominance | Vocalizations, body language, and grooming |
Diet and Feeding Habits
Orangutan’s Culinary Variety
Orangutans have a diverse and frugivorous diet, primarily consisting of fruits. However, they are opportunistic feeders and also consume leaves, bark, insects, and even bird eggs. Their foraging habits are influenced by the seasonal availability of fruits, leading them to be more nomadic in their search for sustenance.
The ability to adapt their diet based on food availability showcases the resourcefulness of orangutans in the dynamic rainforest environment. This dietary flexibility aids in their survival in the face of changing ecological conditions.
Gorilla’s Vegetarian Feast
Gorillas are herbivores with a predominantly vegetarian diet. Their meals include an assortment of fruits, leaves, shoots, and stems. The silverback male, being the leader of the group, enjoys the privilege of choosing the feeding location, ensuring the safety and well-being of the entire family.
Gorillas are known for their methodical feeding habits, spending a significant portion of their day foraging for plant-based sustenance. This herbivorous lifestyle contributes to the ecological balance of their habitats.
Table: Diet and Feeding Habits
| Diet | Orangutan | Gorilla |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Food Source | Fruits, leaves, bark, insects | Fruits, leaves, shoots, stems |
| Dietary Flexibility | Opportunistic feeders | Herbivores with a predominantly vegetarian diet |
| Foraging Habits | Nomadic foraging based on fruit availability | Methodical foraging for plant-based sustenance |
Reproductive Traits
Orangutan’s Patient Parenthood
Orangutans exhibit a slow-paced reproductive pattern. Females have a lengthy interbirth interval, often waiting six to eight years between pregnancies. This prolonged period ensures that the offspring receive sufficient maternal care and attention before the arrival of a new sibling.
Mother orangutans are dedicated caregivers, providing their young with a nurturing environment. The slow reproductive rate makes orangutan populations particularly vulnerable to external threats, underscoring the importance of conservation efforts.
Gorilla’s Family Expansion
Gorillas, in contrast, have a more regular reproductive pattern. Females typically give birth every four years, contributing to the gradual expansion of their family groups. The silverback male plays a crucial role in protecting the infants and ensuring the stability of the group.
The faster reproductive rate of gorillas, coupled with their complex social structure, contributes to the resilience of their populations. However, like orangutans, gorillas face threats to their existence, emphasizing the need for comprehensive conservation measures.
Cultural Significance
Orangutans: Symbols of Wisdom and Patience
Orangutans hold a special place in the hearts and cultures of the regions they inhabit. In Indonesian and Malaysian folklore, these gentle creatures are often revered as symbols of wisdom and patience. Local communities attribute human-like qualities to orangutans, fostering a deep cultural connection.
The plight of orangutans has inspired various conservation initiatives, with local communities actively participating in efforts to protect their habitats. Cultural awareness and appreciation play a crucial role in garnering support for the conservation of these remarkable primates.
Gorillas: Icons of Strength and Unity
Similarly, gorillas have become icons of strength and unity in the cultural narratives of Central African communities. In some indigenous belief systems, gorillas are revered as spiritual beings, embodying the essence of family bonds and communal living.
The presence of gorillas in local folklore has contributed to a sense of responsibility among communities to protect these majestic creatures. Conservation efforts often involve collaboration with local communities, recognizing the cultural significance of gorillas in the collective identity of the region.
Conservation Challenges
Orangutans: Battling Habitat Loss and Illegal Trade
Orangutans face significant challenges, primarily stemming from habitat loss due to palm oil plantations and deforestation. The encroachment of human activities into their territories has led to fragmented habitats, isolating populations and making them more vulnerable to threats.
Additionally, the illegal pet trade poses a severe danger to orangutans. The allure of keeping these intelligent primates as exotic pets contributes to their exploitation. Conservation organizations work tirelessly to combat these challenges, emphasizing the importance of sustainable practices and protecting the remaining pristine forests.
Gorillas: Defending Against Poaching and Disease
Gorillas, too, confront critical conservation challenges. Poaching, fueled by demand for bushmeat and the illegal wildlife trade, poses a constant threat to their populations. The loss of family members due to poaching disrupts the intricate social structures within gorilla groups.
Infectious diseases, especially those transmitted by humans, further jeopardize gorilla populations. Conservationists implement strict protocols to minimize the risk of disease transmission, including limiting human-gorilla contact. The collaborative efforts of conservation organizations, local communities, and governments are essential to address these multifaceted challenges.
The Call to Conservation Action
Orangutans: A Plea for Rainforest Preservation
Preserving the rainforests of Sumatra and Borneo is crucial for the survival of orangutans. Conservation organizations emphasize the importance of sustainable forestry practices and the establishment of protected areas to safeguard their habitats. Eco-friendly initiatives and responsible consumer choices, such as opting for sustainable palm oil, contribute to the broader mission of orangutan conservation.
Gorillas: Safeguarding Habitats and Promoting Sustainable Practices
For gorillas, habitat preservation and anti-poaching measures are paramount. Creating and maintaining protected areas ensures that gorillas can thrive in their natural environment. Conservationists also collaborate with local communities to develop sustainable livelihoods, reducing the reliance on activities that harm gorilla habitats.
By fostering awareness and garnering support from a global audience, conservationists aim to secure a future where both orangutans and gorillas coexist harmoniously with their ecosystems.
Conclusion
As we conclude our delightful journey into the worlds of orangutans and gorillas, we’ve uncovered a myriad of differences that make each of these primates truly unique. From their physical characteristics and habitats to their social structures and dietary habits, orangutans and gorillas captivate us with their individual charm.
In the face of environmental challenges and the need for conservation, understanding these distinctions becomes essential. Whether swinging gracefully through the treetops or commanding attention on the forest floor, both orangutans and gorillas play crucial roles in maintaining the delicate balance of their ecosystems.
FAQs
Orangutans are characterized by their reddish-brown fur, prominent beards, and large cheek pads in males. In contrast, Gorillas exhibit black fur with less pronounced facial hair and an absence of prominent cheek pads. Gorillas are generally larger in size compared to orangutans.
Orangutans are arboreal beings, residing in the rainforests of Sumatra and Borneo, while Gorillas are terrestrial, inhabiting the forests and lowland swamps of Central Africa. Orangutans’ habitats are primarily treetop canopies, while Gorillas navigate the forest floor with a distinctive knuckle-walking gait.
Orangutans tend to be predominantly solitary, especially males, with loose associations formed by adult females with their offspring. Gorillas, on the other hand, form cohesive family groups led by a dominant silverback male. Their social behavior includes intricate communication through vocalizations, body language, and grooming.
Orangutans are opportunistic feeders with a diverse diet, including fruits, leaves, bark, insects, and bird eggs. Gorillas, being herbivores, predominantly consume fruits, leaves, shoots, and stems. Orangutans display nomadic foraging habits based on fruit availability, while Gorillas have a more methodical approach to plant-based sustenance.
Orangutans face threats such as habitat loss due to palm oil plantations and illegal pet trade, while Gorillas confront challenges like poaching for bushmeat, habitat loss, and disease transmission. Conservation efforts for both species involve habitat preservation, anti-poaching measures, and community engagement.
Understanding the differences between Orangutans and Gorillas is crucial for fostering awareness about their unique ecological roles and the conservation efforts required to ensure their survival. Appreciating these distinctions encourages a collective commitment to protecting these incredible primates and their habitats.
Read More:
Contents






