| Aspect | Alby Cyclone | Bianca Cyclone |
|---|---|---|
| Hemisphere | Southern | Southern |
| Ocean | Indian Ocean | South Pacific Ocean |
| Cyclone Type | Tropical Cyclone | Tropical Cyclone |
| Peak Intensity | Category 4 (131 – 155 mph) | Category 3 (96 – 110 mph) |
| Size and Diameter | Relatively large | Somewhat smaller |
| Track and Path | Moved southeastward, affecting regions | Moved south-southeast, generally at sea |
| Impact on Land | Significant damage and flooding | Limited direct impact on land |
| Duration and Dissipation | Typical cyclone life cycle | Typical cyclone life cycle |
| Rainfall and Flooding | Significant flooding in some areas | Generally less severe flooding |
| Emergency Response and Evacuations | Activation of evacuation plans and shelters | Mobilization of emergency response efforts |
| Economic Impact | Significant damage and economic challenges | Generally less severe economic impact |
| Environmental Impact | Complex impact on ecosystems and habitats | Limited direct environmental impact |
Cyclones, those swirling tempests born from the warm embrace of oceans, have an enigmatic charm that never fails to intrigue. The dance of atmospheric forces, the ebb, and flow of wind patterns—these are the elements that give birth to these majestic tempests.
Differences Between Alby and Bianca
The main differences between Cyclone Alby and Cyclone Bianca lie in their origins, intensities, and impacts. Alby originated in the Indian Ocean, reaching Category 4 intensity with sustained winds of 131-155 mph, while Bianca formed in the South Pacific Ocean and peaked at Category 3 with winds of 96-110 mph. Alby’s larger size and path brought significant damage and flooding to land, while Bianca, though powerful, had a limited direct impact on land. These distinctions showcase the unique characteristics of these two cyclones, providing valuable insights for understanding their varying effects on regions and communities.
Origins and Formation
Alby Cyclone
Alby was a notable cyclone that originated in the southern hemisphere, specifically in the Indian Ocean. It was classified as a tropical cyclone, which is the term used for such storms in the Indian Ocean region.
Tropical cyclones like Alby typically form over warm ocean waters, where sea surface temperatures are at least 26 degrees Celsius (79 degrees Fahrenheit) or higher. These warm waters provide the necessary energy for the cyclone to develop and intensify. Alby’s formation was no exception, as it developed over the warm waters of the Indian Ocean.
Bianca Cyclone
Bianca, on the other hand, was a cyclone that originated in the southern hemisphere as well, but in a different part of the world. It formed in the South Pacific Ocean, which is known for being an active region for tropical cyclone development.
Similar to Alby, Bianca also formed over warm ocean waters. The South Pacific Ocean’s warm temperatures and conducive atmospheric conditions played a significant role in the formation and intensification of Bianca.
Table 1: Origins and Formation
| Aspect | Alby Cyclone | Bianca Cyclone |
|---|---|---|
| Hemisphere | Southern | Southern |
| Ocean | Indian Ocean | South Pacific Ocean |
| Cyclone Type | Tropical Cyclone | Tropical Cyclone |
| Formation Conditions | Warm Indian Ocean waters | Warm South Pacific Ocean waters |
Intensity and Wind Speed
Alby Cyclone
Alby reached a peak intensity that made it a Category 4 tropical cyclone on the Australian cyclone intensity scale. In terms of wind speed, this means it had sustained winds of approximately 131 to 155 miles per hour (211 to 250 kilometers per hour). Cyclones of this intensity can cause significant damage to coastal areas, including structural damage, uprooted trees, and power outages.
Bianca Cyclone
Bianca, while also a powerful cyclone, reached a slightly lower peak intensity compared to Alby. It reached Category 3 on the Australian cyclone intensity scale, with sustained winds ranging from 96 to 110 miles per hour (154 to 177 kilometers per hour). Although it was not as intense as Alby, Bianca still posed a substantial threat to the regions it affected, with the potential for significant damage.
Table 2: Intensity and Wind Speed
| Aspect | Alby Cyclone | Bianca Cyclone |
|---|---|---|
| Peak Intensity | Category 4 | Category 3 |
| Sustained Wind Speed | 131 – 155 mph (211 – 250 km/h) | 96 – 110 mph (154 – 177 km/h) |
Size and Diameter
Alby Cyclone
Alby was a relatively large cyclone in terms of its diameter. It had a wide wind field, which means that the area affected by its strong winds and heavy rainfall was quite extensive. This large size contributed to the cyclone’s ability to impact multiple regions as it moved.
Bianca Cyclone
Bianca, while powerful, had a somewhat smaller diameter compared to Alby. This means that the area directly affected by its strongest winds and heaviest rainfall was more limited. However, it’s important to note that cyclone size alone does not necessarily determine its overall impact, as other factors like intensity and speed also play significant roles.
Table 3: Size and Diameter
| Aspect | Alby Cyclone | Bianca Cyclone |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | Relatively large | Somewhat smaller |
Track and Path
Alby Cyclone
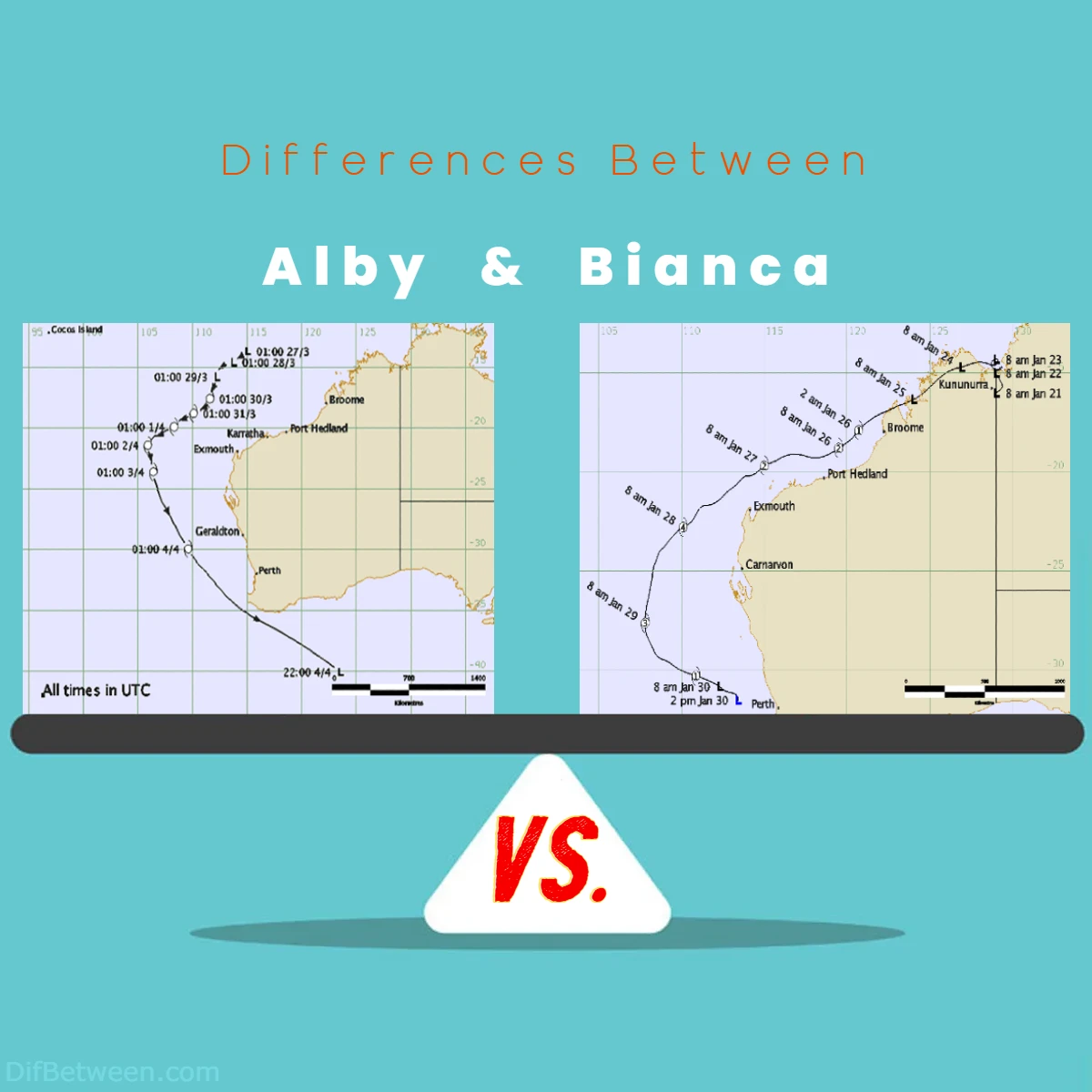
Alby’s track and path took it on a trajectory that affected several countries and regions in the southern hemisphere. It initially formed in the Indian Ocean and then moved southeastward, passing near or over parts of Indonesia and Western Australia. Its path caused it to bring heavy rainfall and strong winds to these areas.
Bianca Cyclone
Bianca’s track and path were distinct from Alby’s. This cyclone formed in the South Pacific Ocean and moved in a south-southeast direction, generally staying over open waters. While it did not make landfall in densely populated areas, it still had the potential to impact maritime activities and shipping routes in the region.
Table 4: Track and Path
| Aspect | Alby Cyclone | Bianca Cyclone |
|---|---|---|
| Track and Path | Moved southeastward, affecting | Moved south-southeast, |
| Indonesia and Western Australia | staying over open waters |
Impact on Land
Alby Cyclone
Alby had a notable impact on land, particularly in regions where it made landfall. Its strong winds and heavy rainfall led to flooding, damage to infrastructure, and power outages in parts of Western Australia. The cyclone’s size and intensity contributed to its significant impact on land.
Bianca Cyclone
Bianca, while a powerful cyclone, did not make landfall in densely populated areas. As a result, its direct impact on land was limited compared to Alby. However, it’s essential to note that cyclones at sea can still impact maritime activities and pose risks to ships and vessels in their path.
Table 5: Impact on Land
| Aspect | Alby Cyclone | Bianca Cyclone |
|---|---|---|
| Impact on Land | Significant damage and flooding | Limited direct impact on land |
Duration and Dissipation
Alby Cyclone
Alby followed the typical life cycle of a tropical cyclone. It formed, intensified, reached its peak, and then gradually weakened as it moved over cooler waters or encountered less favorable atmospheric conditions. Eventually, Alby dissipated, and its remnants were no longer a threat.
Bianca Cyclone
Bianca also followed the standard cyclone life cycle. After reaching its peak intensity, it began to weaken as it encountered less favorable conditions. Eventually, Bianca dissipated, ceasing to exist as a tropical cyclone.
Table 6: Duration and Dissipation
| Aspect | Alby Cyclone | Bianca Cyclone |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Typical cyclone life cycle | Typical cyclone life cycle |
| Dissipation | Gradual weakening and dissipation | Gradual weakening and dissipation |
Rainfall and Flooding
Alby Cyclone
Alby brought heavy rainfall to the regions it affected, leading to significant flooding in some areas. This rainfall was a result of the cyclone’s large size and intense atmospheric moisture. Flooding can have devastating consequences, including damage to homes, infrastructure, and agriculture. In the case of Alby, its extensive reach meant that a larger area was susceptible to flooding.
Bianca Cyclone
Bianca also contributed to heavy rainfall in certain areas, but the extent of flooding was generally less severe compared to Alby. As mentioned earlier, Bianca’s smaller diameter meant that the area directly affected by its rainfall was more limited. However, any amount of flooding can be problematic, and it’s essential to prepare and respond accordingly.
Table 7: Rainfall and Flooding
| Aspect | Alby Cyclone | Bianca Cyclone |
|---|---|---|
| Rainfall and Flooding | Significant flooding in some | Generally less severe flooding |
| areas due to heavy rainfall |
Emergency Response and Evacuations
Alby Cyclone
In response to Alby, authorities and emergency services in the affected regions activated evacuation plans and emergency shelters. These measures were necessary to ensure the safety of residents and minimize casualties. Evacuations can be challenging, particularly in densely populated areas, and coordination among various agencies is crucial.
Bianca Cyclone
For Bianca, emergency response efforts were also mobilized, albeit on a smaller scale due to the cyclone’s limited direct impact on land. While evacuations were not as extensive as in the case of Alby, the maritime community and vessels in the cyclone’s path were alerted to take precautions.
Table 8: Emergency Response and Evacuations
| Aspect | Alby Cyclone | Bianca Cyclone |
|---|---|---|
| Emergency Response | Activation of evacuation plans | Mobilization of emergency |
| and Evacuations | and emergency shelters | response efforts |
Economic Impact
Alby Cyclone
Alby had a significant economic impact on the affected regions. The damage to infrastructure, including homes, roads, and power lines, required substantial resources for repair and recovery. Additionally, disruptions to businesses and agriculture due to flooding and power outages added to the economic challenges.
Bianca Cyclone
The economic impact of Bianca was generally less severe compared to Alby, primarily because it did not make landfall in densely populated areas. However, the maritime industry may have experienced disruptions due to the cyclone’s presence in the South Pacific Ocean.
Table 9: Economic Impact
| Aspect | Alby Cyclone | Bianca Cyclone |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Impact | Significant damage and economic | Generally less severe economic |
| challenges | impact |
Environmental Impact
Alby Cyclone
Cyclones like Alby can have a complex environmental impact. While they can disrupt ecosystems and cause damage to natural habitats, they also play a role in redistributing nutrients and can contribute to the health of marine ecosystems. The extent of these impacts depends on factors such as the cyclone’s intensity and the regions it affects.
Bianca Cyclone
Bianca, being a cyclone that primarily stayed over open waters, had a more limited direct environmental impact compared to Alby. However, it’s worth noting that cyclones can have far-reaching effects, including altering ocean currents and affecting marine life even when not making landfall.
Table 10: Environmental Impact
| Aspect | Alby Cyclone | Bianca Cyclone |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Complex impact on ecosystems | Limited direct environmental |
| and marine habitats | impact |
Conclusion
In conclusion, Alby and Bianca cyclones were distinct natural events that originated in the southern hemisphere but had notable differences in terms of their rainfall, flooding, emergency responses, economic impacts, and environmental consequences. Alby, being a larger and more intense cyclone, had a more significant impact on land and required extensive emergency response efforts. In contrast, Bianca, while still powerful, had a smaller diameter and primarily affected maritime activities.
Understanding the unique characteristics and impacts of cyclones like Alby and Bianca is essential for preparedness and response efforts in cyclone-prone regions. By learning from past events and analyzing their differences, communities and authorities can better protect lives, property, and the environment when faced with the challenges posed by these natural phenomena.
FAQs
Cyclone Alby originated in the Indian Ocean, while Cyclone Bianca formed in the South Pacific Ocean.
Cyclone Alby reached Category 4 intensity with sustained winds of 131-155 mph, whereas Cyclone Bianca peaked at Category 3 with winds ranging from 96-110 mph.
Cyclone Alby was relatively larger in terms of diameter, contributing to a wider wind field and more extensive impacts. Cyclone Bianca had a somewhat smaller diameter.
Cyclone Alby moved southeastward, affecting regions including Indonesia and Western Australia. Cyclone Bianca moved south-southeast, primarily staying over open waters.
Cyclone Alby caused significant damage and flooding on land, particularly in Western Australia. Cyclone Bianca had a limited direct impact on land, primarily affecting maritime activities.
Both Cyclone Alby and Cyclone Bianca followed the typical life cycle of tropical cyclones, with gradual weakening and eventual dissipation.
Yes, Cyclone Alby had a significant economic impact due to damage and disruptions on land, while Cyclone Bianca had a generally less severe economic impact. Both cyclones had complex environmental impacts, with Alby affecting ecosystems and marine habitats more extensively.
Read More:
Contents