Science
Prepare to embark on an enlightening journey as we uncover the nuances and distinctions that make the scientific field so diverse and awe-inspiring. Whether you’re a science enthusiast or a curious mind seeking knowledge, this collection of content will satiate your thirst for understanding the intricacies of scientific terminology and concepts.
-

Liver vs Spleen
Embark on an illuminating journey into the intricate world of human anatomy as we unravel the differences between two often-overlooked yet indispensable organs: the spleen and the liver. While these organs reside within our abdominal cavities, they couldn't be more distinct in terms of their roles, locations, and impacts on our well-being. The spleen, though small and tucked beneath the left ribcage, emerges as a vital player in immune defense, blood filtration, and blood storage. It even contributes to fetal blood cell production during prenatal development. However, it's marked by limited regenerative capacity, and living without it is possible but not without certain risks. On the flip side, the liver, situated in the upper right quadrant under the ribcage, commands attention as a metabolic powerhouse. It's the maestro of glucose regulation, fat processing, and detoxification. The liver's exceptional regenerative capabilities have earned it a reputation as the body's ultimate repair center. These distinctions are just the tip of the iceberg. In our in-depth exploration, we delve into their functions, blood supply, tissue composition, and so much more. So, join us in understanding the mesmerizing intricacies that set the spleen and liver apart and learn how they collaborate to orchestrate the symphony of life within your body.
-

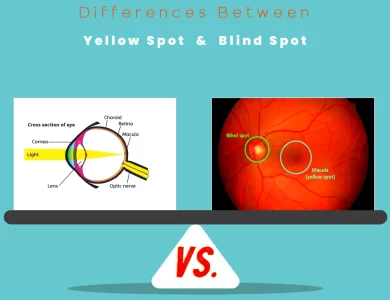
Blind Spot vs Yellow Spot
The human eye, a marvel of biological engineering, houses several intricate components that collectively enable us to perceive the world around us. Two of these components, the Yellow Spot and the Blind Spot, stand out as fascinating features with distinct roles in our visual experience. Let's embark on a journey to uncover the differences between these two essential aspects of our eyes. The Yellow Spot, scientifically known as the macula lutea, is a small but mighty region nestled at the very center of the retina, the eye's innermost layer. Its name is derived from the slight yellowish appearance it possesses, thanks to the presence of macular pigment. The Yellow Spot's function is nothing short of extraordinary; it specializes in providing central vision. This means that when you read a book, gaze at a painting, or recognize a face, you can thank your Yellow Spot. It's responsible for the remarkable clarity of fine details and the ability to perceive a rich spectrum of colors. In essence, the Yellow Spot acts as a spotlight, ensuring that what you focus on is presented with exceptional sharpness and vibrancy. In contrast, the Blind Spot, often referred to as the optic disc, is an intriguing and slightly mysterious area located toward the nasal side of the retina, just a bit away from the Yellow Spot. The Blind Spot is unique in that it lacks photoreceptor cells, the rods and cones that are vital for converting light into electrical signals for the brain to interpret. While it doesn't directly contribute to your visual perception, it serves as an exit point for the optic nerve, which is responsible for transmitting visual information to the brain. You might wonder, "If it's devoid of photoreceptor cells, how do we not notice a gap in our vision?" Well, the answer…
-

Female Bones vs Male
In the realm of human anatomy, the distinctions between male and female bones are not just about size; they tell a captivating story of nature's exquisite design. Male bones tend to be larger, thicker, and more densely packed, primarily due to the influence of testosterone during puberty. This results in a robust skeletal structure that contributes to the broader shoulders and larger frame commonly associated with men. In contrast, female bones are generally smaller and less dense, influenced by estrogen, leading to a more delicate appearance. One of the most remarkable differences lies in the pelvic structure. The male pelvis is narrower and characterized by a deeper sacrum, while the female pelvis is wider and shallower. These variations are a testament to the tailored design of the human body for its unique reproductive functions. These structural disparities not only impact physical appearance but also play a significant role in athletic performance and susceptibility to certain health conditions. As we explore the captivating world of male vs female bones, we unveil a mosaic of differences that have shaped human evolution and adaptation. These distinctions celebrate the intricacies of our biology and remind us of the incredible diversity that makes each of us wonderfully unique. So, let's embark on a journey through the remarkable narrative of human anatomy, where every bone has a story to tell.
-

Gas vs Fuel
In the energy world, the debate often revolves around fuel vs. gas, two terms frequently used interchangeably but with significant differences. Fuel is a broad term encompassing various energy sources, including solid, liquid, and gaseous forms, while gas primarily refers to substances in a gaseous state at standard conditions. These distinctions are just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to the disparities between these energy sources. The origins of fuel and gas vary widely. Fuel sources can range from organic matter like wood and coal to petroleum-based products such as gasoline and diesel. On the other hand, gas primarily includes natural gas, propane, and hydrogen, often sourced from underground reservoirs or industrial processing. The diverse sources of these energy forms have a profound impact on their environmental and economic characteristics. One of the critical differences between fuel and gas is their usage. Fuel finds its place in a wide array of applications, from powering vehicles to heating homes and fueling industrial processes. In contrast, gas is commonly employed for heating, cooking, and as an alternative transportation fuel. Furthermore, when it comes to energy density, gas generally has a lower energy content than liquid fuels like gasoline, making it suitable for specific applications but not all. Understanding these discrepancies is paramount, as it helps individuals and industries make informed choices based on their needs and sustainability goals. The journey of understanding the differences between fuel and gas goes beyond the surface, encompassing various facets from storage and transportation to cost considerations and environmental impact. So, whether you're pondering your home heating choices, contemplating sustainable transportation, or exploring clean cooking options, delving into the nuances of fuel vs. gas is your ticket to making energy choices that align with your priorities.
-

Oxygen vs Helium
Helium and oxygen, though both elemental gases, are worlds apart in terms of their properties, applications, and significance. Helium, symbolized as He, is a lightweight, inert gas known for its low density and has become synonymous with buoyant party balloons. In contrast, oxygen, denoted as O, is the breath of life, a reactive gas that constitutes about 21% of the Earth's atmosphere and plays a pivotal role in respiration and combustion. The primary distinction between these gases arises from their chemical properties and behavior. Helium remains a gas at room temperature with a low density of about 0.1786 kg/m³, making it lighter than air and ideal for making balloons float. Oxygen, also a gas at room temperature, possesses a significantly higher density of approximately 1.429 kg/m³ and is vital for combustion, making it a cornerstone of industrial processes and rocket propulsion. These differences are not limited to their physical characteristics. Helium is primarily used in cryogenic applications and as a buoyant gas for celebratory balloons, whereas oxygen is essential for life and is administered in medical settings to assist patients with respiratory issues. Furthermore, while helium is environmentally inert, oxygen can support combustion and has implications for industrial production. Intriguingly, these two gases, despite their vast dissimilarities, each hold a crucial place in various aspects of our lives, from medicine and industry to aerospace and deep-sea diving. Understanding these distinctions is key to appreciating the unique roles they play in our world.
-

Oxygen vs Hydrogen
Hydrogen and oxygen, two elemental powerhouses, stand as distinct entities in the realm of chemistry, each with its unique characteristics and roles. Hydrogen, with its atomic number of 1, is the lightest and most abundant element in the universe. In contrast, oxygen, bearing atomic number 8, is a fundamental component of the air we breathe. These elements play diverse and essential roles in our world. Hydrogen, often found as a diatomic molecule (H2), is celebrated for its versatility, serving as a clean energy source and a potent reducing agent in various chemical reactions. It is a key player in industries such as fuel cells, metallurgy, and rocket propulsion, offering a glimpse of a sustainable energy future. On the other hand, oxygen, primarily as O2, is the life-sustaining element that fuels our respiration and supports combustion, playing a pivotal role in everything from medical applications to space exploration. Understanding the differences between hydrogen and oxygen not only deepens our knowledge of the elements themselves but also sheds light on their significant impact on science, industry, and our daily lives. These two elements, one a potential green energy carrier and the other the breath of life, continue to shape our world in remarkable ways.
-

Organic Evolution vs Chemical
The narrative of life on Earth is an awe-inspiring tale of transformation and diversity, composed of two distinct yet interconnected chapters: Chemical Evolution and Organic Evolution. Chemical Evolution kicks off the saga by unravelling the enigmatic origins of life itself. It delves into the prehistoric Earth, when simple non-living molecules danced with the elements to give rise to complex organic compounds. The process, driven by abiotic reactions, bestowed us with fundamental building blocks like amino acids and nucleotides. This narrative transports us to a time when Earth was a cradle of chemical reactions, birthing the very essence of life. In stark contrast, Organic Evolution takes center stage as the ongoing epic that unfolds from the emergence of life. It's a story of adaptation, survival, and the ever-shifting mosaic of life's diversity. Within this narrative, the driving forces are natural selection, genetic variation, and the intricate interactions of living organisms. It traces the evolutionary journey from common ancestors to the vast biodiversity that graces our planet today. So, as we embark on this enlightening journey, let's uncover the nuances that set Chemical and Organic Evolution apart while understanding how they weave together in the grand tapestry of life's history.
-

Australopithecus vs Paranthropus
In the fascinating realm of human evolution, the contrast between Paranthropus and Australopithecus unveils a captivating narrative of our ancient ancestors. These two hominin genera, both part of the same family tree, represent distinctive branches in the complex mosaic of human evolution. Cranial and Facial Morphology: Paranthropus, known for its robust cranial structure and large cheekbones, exhibits a pronounced sagittal crest, giving its face a distinctive dish-like appearance. In contrast, Australopithecus possesses less robust cranial features, presenting a more human-like facial structure. Dentition: A critical disparity emerges in dentition. Paranthropus showcases megadontia, with notably large molars and premolars adapted for a fibrous plant-based diet. Australopithecus, with moderate-sized teeth and thick enamel, displays adaptability to a varied omnivorous diet. Dietary Adaptations: Paranthropus specialized in consuming fibrous vegetation, while Australopithecus embraced a more versatile diet, including plant materials and occasional meat. This exploration delves into their limb proportions, environmental contexts, evolutionary relationships, and the significance of these hominins in the broader story of our evolution. As we decipher the distinctions between Paranthropus and Australopithecus, we gain deeper insights into the incredible journey that led to modern humans.
-

Darwinism vs Lamarckism
Lamarckism and Darwinism, two fundamental theories of evolution, have etched their names in the annals of biology, each offering unique insights into how species adapt and change over time. Lamarckism, proposed by Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, posits that acquired characteristics during an organism's lifetime are inherited, guiding evolution towards a predetermined goal. In contrast, Darwinism, the brainchild of Charles Darwin, underscores natural selection as the driving force, emphasizing the non-teleological nature of evolution. The core divergence lies in their views on inheritance, with Lamarckism leaning on the inheritance of acquired traits and Darwinism resting on the inheritance of genetic variations. While Lamarckism held sway in its time, modern biology heavily favors Darwinism due to its robust empirical support and alignment with contemporary genetic knowledge. This ongoing juxtaposition highlights the ever-evolving nature of scientific understanding and the enduring quest to decipher the intricate mechanisms of life's evolution. In this exploration of Lamarckism vs. Darwinism, we uncover not only their historical roots but also their relevance in shaping the course of biology and our comprehension of the magnificent tapestry of life on Earth.
-

Modern Man vs Early Man
The disparities between early man and modern man form a captivating narrative of human evolution. In our exploration of these differences, one cannot ignore the profound changes that have taken place over millions of years. From cognitive abilities to physical appearance, early man's robust features and limited problem-solving skills stand in stark contrast to modern man's larger, more advanced brain, capable of abstract thinking and complex language. Dietary habits have also evolved, as early man relied on raw and unprocessed foods, while modern man savors a diverse culinary palette, thanks to the wonders of cooking and food processing. Technology plays a pivotal role in this transition, with early man's rudimentary tools and weapons contrasting with the advanced technology that modern man wields, from smartphones to spacecraft. As we journey through time, the shift from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to settled agriculture and the development of complex language and societal structures become evident. The impact on the environment has evolved from local to global, and globalization has interconnected societies and economies like never before. Challenges and opportunities await modern man, as we address issues like environmental degradation while harnessing the potential of science and technology to shape a promising future. The story of early man versus modern man is one of transformation, adaptation, and boundless potential.